SpringBoot(二)
1、application.properties 和 application.yml 組態檔格式區別
1.1 檔案格式
application.properties
# 埠號
server.port=8096
application.yml
# 伺服器埠
server:
port: 8096
1.2 區別
- properties的優先順序高於yml,同等設定,高優先順序會覆蓋低優先順序,不同的設定時互補設定(增補,不管哪個組態檔中有,都可以生效);
- properties的核心語法是:通過 . 作為層級分隔符,設定值是用 = ,比如 server.port=9096
yml的核心語法是:通過層級+縮排的方式,同一給等級,縮排是相同的,設定使用key: value方式- server:
port: 8096 #注意值前面必須有空格
- server:
- 小結:yml格式設定,可以簡化設定內容,層次清晰,更適合作為核心組態檔;
2、自定義設定
2.1 設定資訊 yml 語法
注意:值前面必須有空格;
2.1.1 基本型別資料
user:
userId: kh96
user-Name: gala # 支援鬆散繫結
user_age: 17
adult: true # 是否成年
salary: 9696.0
userTel: 13501020304
birthday: 2002/10/11 10:10:10
email: [email protected]
2.1.2 陣列,List,Set
user:
hobbies: # 愛好 list集合
- springboot
- linux
- mysql
- ssm
- jvaweb
- springvloud
#行內寫法
#hobbies:[springboot,linux,mysql,ssm,jvaweb,springvloud]
2.1.3 Map
user:
carMap: # 愛車 map 集合
bnm: 寶馬325
audi: 奧迪A41
benz: 賓士C200
#行內寫法
#carMap:{bnm: 寶馬325;audi: 奧迪A41;benz: 賓士C200}
2.1.4 實體引數
user:
userRole:
role-id: R96 ${random.uuid} #${}可以去一些內建的自定義引數
role_name: root
2.1.5 值的寫法
2.1.5.1 單引號:
會跳脫特殊字元。
user:
msg: '你好!\n小可愛!'
輸出:
你好!\n小可愛!
2.1.5.2 雙引號:
不會跳脫字元裡的特殊字元,特殊字元仍然是本身的意思
user:
msg: "你好!\n小可愛!"
輸出:
你好!
小可愛!
2.2 獲取 設定資訊
2.2.1 批次自動讀取
使用註解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "xxx") ,必須配合@Component 註解獲取在核心啟動類上使用 @EnableConfigurationProperties(設定屬性讀取類.class)使用;
特點:支援鬆散繫結(可以自動識別駝峰,-,_),支援複雜型別繫結(實體,集合-list,set,array,map等),支援資料格式校驗;
@Component + @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
或
@Component
+
@EnableConfigurationProperties(UserProperties.class) //寫在主啟動類上
2.2.1.1 UserProperties
@Data
@Component //第一個寫法,使用普通元件
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user") //不能單獨使用,必須配合@EnableConfigurationProperties 或指定為spring容器中的普通元件
public class UserProperties {
//使用者編號
private String userId;
//使用者名稱
private String userName;
//使用者年齡
private Integer userAge;
//是否成年
private boolean adult;
//工資
private double salary;
//聯絡方式
private String userTel;
//生日
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8") //springMVC將將資料轉成json格式,時間格式規則
private Date birthday;
//使用者角色
private UserRole userRole; //實體引數
//愛好
private List<String> hobbies;
//愛車
private Map<String,String> carMap;
//郵箱
@Email //郵箱格式校驗
private String email;
}
2.2.1.1.2 執行結果:
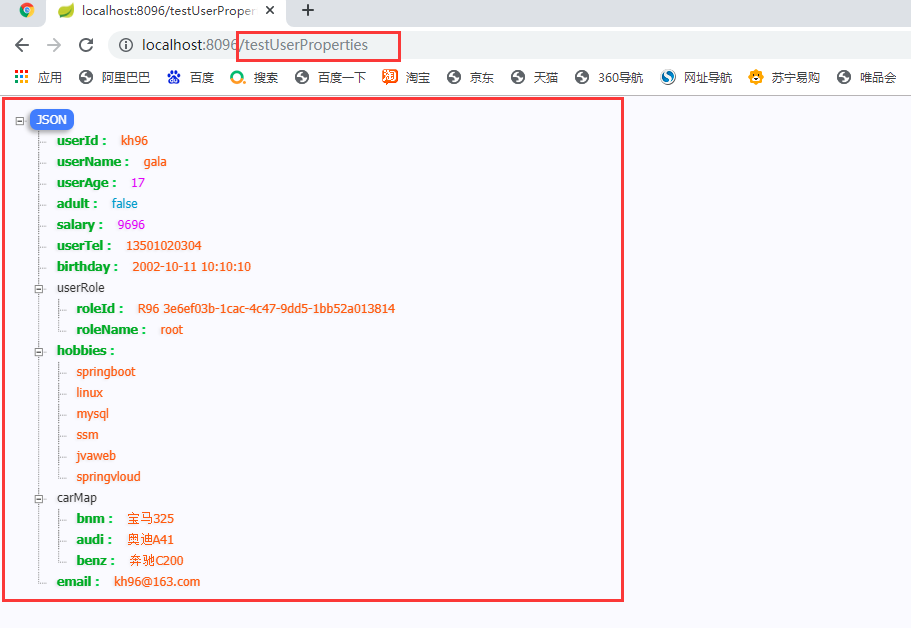
2.2.2 單個手動讀取
用法:使用註解@Value("${xxx.xxx}");
特點:寫法靈活,可以指定預設值等,但是不支援鬆散繫結,單個讀取的設定要求指定的讀取屬性key必須和自定義設定一直,否者報錯;
@Component + @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
2.2.2.1 UserProperties
@Data
@Component
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:user.properties")
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(UserProperties.class) //第二種方式,核心啟動類上,增加指定開啟自動設定讀取,但是一般不怎麼使用,且容易忘記
public class UserProperties {
//使用者編號
@Value("${user.userId}")
private String userId;
//使用者名稱
@Value("${user.user-Name}")
private String userName;
//暱稱
@Value("#{userValues.userName}") //獲取的是容器中已有的實體的值
//@Value("#{'xiaoming'}") //可以賦預設值
private String niceName;
//使用者年齡
@Value("${user.user_age}")
// @Value("16") //直接賦值
private Integer userAge;
//是否成年
@Value("#{(${user.user_age}>17)?true:false}") //spel 表示式
private boolean adult;
//工資
@Value("#{${user.salary}*10}") //#{} 和 ${}套用
private double salary;
//聯絡方式
@Value("${user.userTel}")
private String userTel;
//生日
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8") //springMVC將將資料轉成json格式,時間格式規則
@Value("${user.birthday}")
private Date birthday;
//使用者角色
//@Value("${user.userRole}") //不可以單個手動獲取石引數
private UserRole userRole; //實體引數
//愛好
//@Value("${user.hobbies}") //不可以單個手動獲取複雜引數
private List<String> hobbies;
//愛車
//@Value("${user.carMap}")
private Map<String,String> carMap;
//郵箱
@Email //郵箱格式校驗
@Value("${user.email:[email protected]}") //新增預設值,設定資訊沒有就使用預設值
private String email;
}
2.2.2.2執行結果:
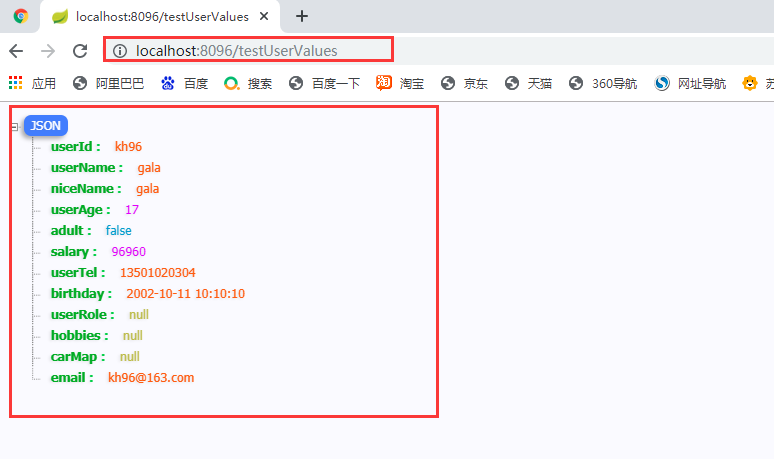
2.2.3 ${} 和 #{} 的區別
- ${}:用於讀取核心組態檔中的自定義設定,也可以給屬性指定預設值 (${xxx.xx:default值});
- #{}:不可以讀取核心組態檔中的自定義設定,可以給屬性發指定預設值#{default值} (可以使用表示式),還可以讀取容器中已用實體的屬性值;
- 兩種讀取自定義設定的方式,是可以混用的,但是實際開發中,儘量使用其中一種,,一般都是少量設定,單個讀取,多個讀取,使用批次讀取;
3、自定義組態檔並獲取設定資訊
3.1xxx.properties
3.1.1 student.properties
student.studentId=19130010
student.studentName=huayu
student.studentClass=電腦科學與技術(2)
student.graduationSchool=金陵科技學院
student.graduationTime=2023/7/1 12:12:12
student.nativePlace=南京
student.hasGirFriends=true
3.1.2 StudentProperties.java
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
public class StudentProperties {
// 學號
private String studentId;
// 姓名
private String studentName;
// 班級
private String studentClass;
// 畢業院校
private String graduationSchool;
// 畢業時間
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date graduationTime;
// 籍貫
private String nativePlace;
// 有沒有女朋友
private boolean hasGirFriends;
}
3.1.3 StudentValues.java
@Data
@Component //第一個寫法,使用普通元件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:student.properties")//單個從student.properties 中獲取引數
public class StudentValues {
// 學號
@Value("${student.studentId}")
private String studentId;
// 姓名
@Value("${student.studentName}")
private String studentName;
// 班級
@Value("${student.studentClass}")
private String studentClass;
// 畢業院校
@Value("${student.graduationSchool}")
private String graduationSchool;
// 畢業時間
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
@Value("${student.graduationTime}")
private Date graduationTime;
// 籍貫
@Value("${student.nativePlace}")
private String nativePlace;
// 有沒有女朋友
@Value("${student.hasGirFriends}")
private boolean hasGirFriends;
}
3.2 xxx.yml
3.2.1 student.yml
student:
studentId: 19130010
studentName: huayu
studentClass: 電腦科學與技術(2)
graduationSchool: 金陵科技學院
graduationTime: 2023/7/1 12:12:12
nativePlace: 南京
hasGirFriends: true
3.2.2 StudentProperties.java
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:student.yml",encoding = "utf-8",factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class) //從自定義的 student.yml 中獲取
public class StudentProperties {
......
}
3.2.3 StudentValues.java
@Data
@Component
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:my.yml", factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class) //從自定義的 student.yml 中獲取
public class StudentValues {
......
}
3.2.4 YamlPropertySourceFactory.java yml設定對映類
@PropertySource讀取不能直接自定義yaml組態檔,需要自定義一個繼承 PropertySourceFactory 的 YamlPropertySourceFactory 編寫設定對映類
public class YamlPropertySourceFactory implements PropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(String name, EncodedResource encodedResource) {
Resource resource = encodedResource.getResource();
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factory = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
factory.setResources(resource);
Properties props = factory.getObject();
return new PropertiesPropertySource(resource.getFilename(), props);
}
}
3.3 測試
3.3.1 testStudentProperties
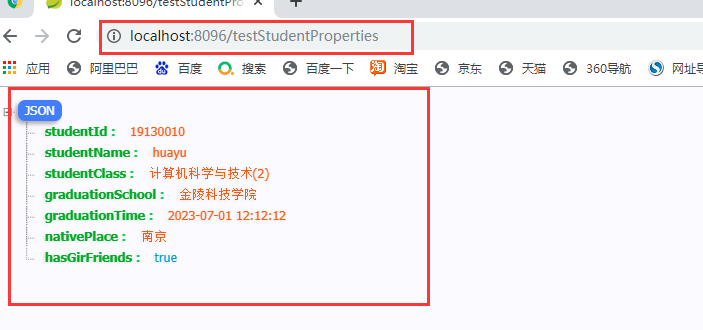
3.3.2 testStudentValues
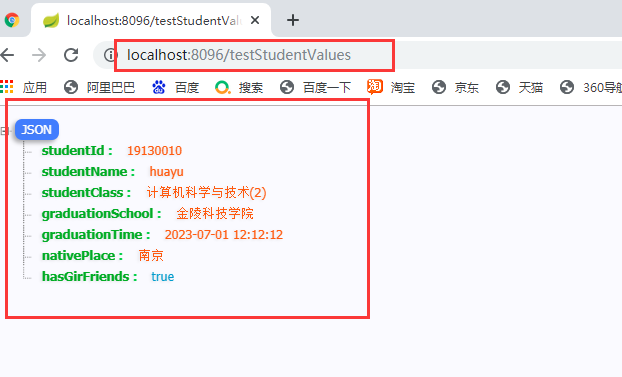
4、*@Configuration設定類的用法,可以實現自定義元件加入容器
4.1 實體
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserRole {
//角色
private String roleId;
//角色名稱
private String roleName;
}
4.2 UserRoleConfig 設定類
@Configuration //凡是被此註解修飾的類,就是一個設定類,在專案啟動是,自動載入,功能跟spring的核心組態檔xml檔案是同等的
public class UserRoleConfig {
//手動新增自定義物件,放入容器中以前spring框架,通過xml組態檔,新增<bean id="xx" class="xx">...</bran>
@Bean //標註的方法,會自動將當前方法返回的範例物件放入容器中,預設的bean的id值就是方法名
public UserRole userRole1(){
return UserRole.builder()
.roleId("R001")
.roleName("admin")
.build();
}
@Bean
public UserRole userRole2(){
return UserRole.builder()
.roleId("R002")
.roleName("admin")
.build();
}
}
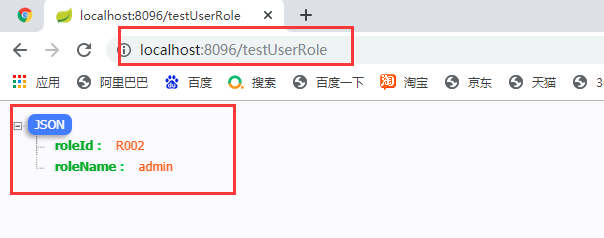
4.3 測試類
@RestController
public class SpringBootConfigController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userRole2")
UserRole userRole;
//可以實現自定義實體加入容器
@GetMapping("/testUserRole")
public UserRole testUserRole(){
return userRole;
}
}
執行結果:
5、啟用環境
5.1 多套環境組態檔
啟用環境 (實際開發中,主要有三個環境:開發環境,測試環境,生產環境(線上環境),還有一個環境,灰度環境,也是線上環境,叫預上限環境);
好處:可以隔離不同環境的不同設定,需要使用哪個環境,就直接切換核心組態檔;
application-devp.properties
application-prod.properties
application-test.properties
5.2 啟用環境
active: test # 指定當前的profiles值,環境是什麼是通過核心組態檔名中,application-${profiles},profiles寫的是什麼就是什麼環境;
spring:
profiles:
active: test #啟用測試環境
6、核心組態檔載入位置
優先順序從高到底依次為:
專案根路徑下的config目錄
專案根路徑下
類路徑(resource)下的
類路徑(resource)下
注意:模組專案的 專案根路徑 是 父專案的根路徑;
7、郵件傳送 和 簡訊測試傳送
7.1 郵件傳送
7.1.1 依賴
<!-- spring-boot-starter-mail start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-boot-starter-mail end -->
7.1.2 郵件設定資訊
7.1.3 類裡面寫設定資訊
設定資訊直接寫在 物件裡面;
@GetMapping("/sendEmail")
public String sendEmail(@RequestParam(value = "setToEmail",required = false) String setToEmail){
System.out.println("--------------[mail/mailSend] start------------------");
try {
MimeMessage message=javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper=new MimeMessageHelper(message,true);
helper.setFrom("[email protected]","2663092414");
helper.setTo(setToEmail);
helper.setSubject("KH-96-王鬆—核心組態檔讀取");
helper.setText("正在使用SpringBoot讀取自定義核心設定,傳送郵件成功!<br/>"+studentProperties.toString(),true);
javaMailSender.send(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("郵件傳送失敗"+ e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("--------------[mail/mailSend] end------------------");
return studentProperties.toString();
}
//範例化javaMailSender 並寫入設定資訊
private static JavaMailSenderImpl javaMailSender;
static {
javaMailSender = new JavaMailSenderImpl();
javaMailSender.setHost("smtp.qq.com");//連結伺服器
//javaMailSender.setPort(25);//預設使用25埠傳送
javaMailSender.setUsername("[email protected]");//賬號
javaMailSender.setPassword("dwxlbkrmdyagebhe");//授權碼
javaMailSender.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
Properties properties = new Properties();
//properties.setProperty("mail.debug", "true");//啟用偵錯
//properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.timeout", "1000");//設定連結超時
//設定通過ssl協定使用465埠傳送、使用預設埠(25)時下面三行不需要
properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.auth", "true");//開啟認證
properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.socketFactory.port", "465");//設定ssl埠
properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.socketFactory.class", "javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory");
javaMailSender.setJavaMailProperties(properties);
}
7.1.4 application.yaml中寫設定資訊
7.1.4.1 application.yaml
spring:
mail:
default-encoding: UTF-8
host: smtp.qq.com
port: 587
username: [email protected]
password: 授權碼
7.1.4.2 請求方法
@GetMapping("/sendEmail2")
public String sendEmail2(@RequestParam(value = "setToEmail",required = false) String setToEmail){
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
mailMessage.setFrom("[email protected]"); //傳送郵箱
mailMessage.setTo("[email protected]"); //目標郵箱
mailMessage.setText("你好 hello world");
mailMessage.setSubject("測試 Springboot 郵箱服務");
mailSender.send(mailMessage);
return "====完成傳送!====";
}
7.2 簡訊測試傳送
7.2.1 依賴
<!-- SMS star -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>dysmsapi20170525</artifactId>
<version>2.0.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>tea</artifactId>
<version>1.1.14</version>
</dependency>
<!-- SMS end -->
7.2.2 程式碼
其中:accessKeyId ,accessKeySecret 填寫自己的使用者 AccessKey,最好用子使用者 AccessKey;
public class Sample {
/**
* 使用AK&SK初始化賬號Client
*
* @param accessKeyId
* @param accessKeySecret
* @return Client
* @throws Exception
*/
public static com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client createClient(String accessKeyId, String accessKeySecret) throws Exception {
com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config()
// 您的 AccessKey ID
.setAccessKeyId(accessKeyId)
// 您的 AccessKey Secret
.setAccessKeySecret(accessKeySecret);
// 存取的域名
config.endpoint = "dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com";
return new com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client(config);
}
public static void main(String[] args_) throws Exception {
java.util.List<String> args = java.util.Arrays.asList(args_);
com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client client = Sample.createClient("accessKeyId", "accessKeySecret"); //accessKeyId ,accessKeySecret 填寫自己的使用者資訊
com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.models.SendSmsRequest sendSmsRequest = new com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.models.SendSmsRequest()
.setSignName("阿里雲簡訊測試")
.setTemplateCode("SMS_154950909")
.setPhoneNumbers("傳送簡訊的手機號")
.setTemplateParam("{\"code\":\"131313\"}");
com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions runtime = new com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions();
try {
// 複製程式碼執行請自行列印 API 的返回值
SendSmsResponse sendSmsResponse = client.sendSmsWithOptions(sendSmsRequest, runtime);
} catch (TeaException error) {
// 如有需要,請列印 error
String errerMsg = Common.assertAsString(error.message);
} catch (Exception _error) {
TeaException error = new TeaException(_error.getMessage(), _error);
// 如有需要,請列印 error
String errorMsg = Common.assertAsString(error.message);
}
}
}