手把手教你使用LabVIEW OpenCV dnn實現物體識別(Object Detection)含原始碼
前言
今天和大家一起分享如何使用LabVIEW呼叫pb模型實現物體識別,本部落格中使用的智慧工具包可到主頁置頂部落格
一、物體識別演演算法原理概述
1、物體識別的概念
物體識別也稱目標檢測,目標檢測所要解決的問題是目標在哪裡以及其狀態的問題。但是,這個問題並不是很容易解決。形態不合理,物件出現的區域不確定,更不用說物件也可以是多個類別。 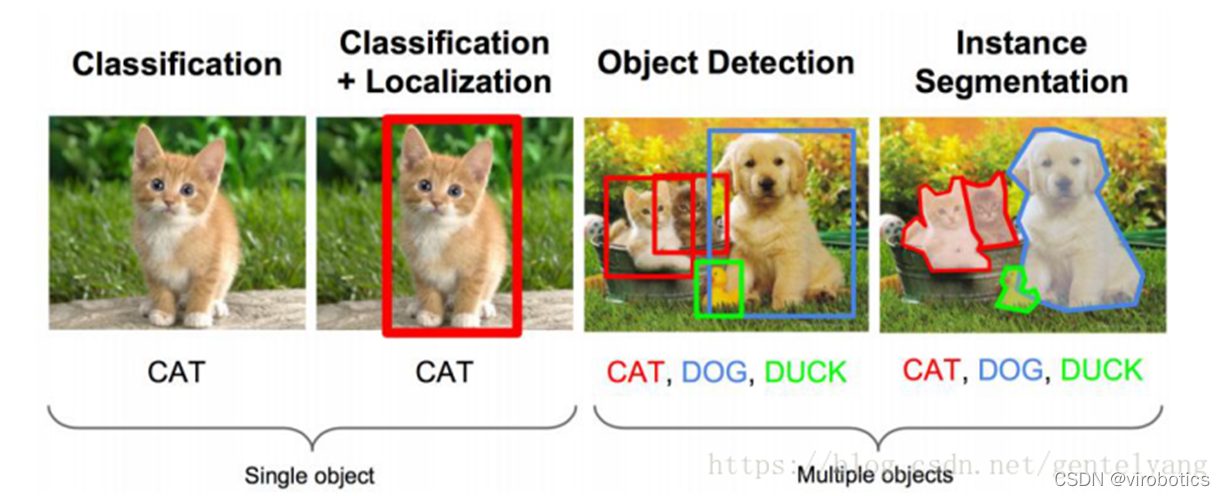
目標檢測用的比較多的主要是RCNN,spp- net,fast- rcnn,faster- rcnn;YOLO系列,如YOLOV3和YOLOV4;除此之外還有SSD,ResNet等。
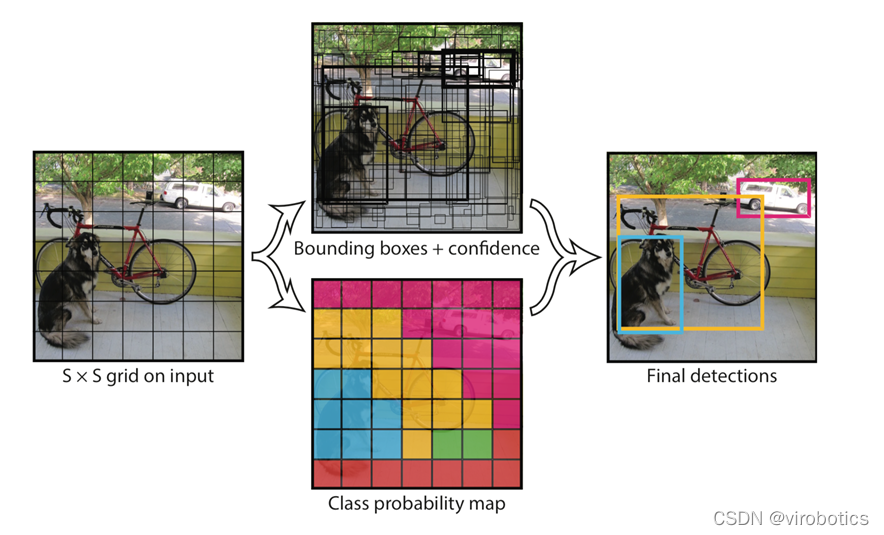
2、Yolo演演算法原理概述
Yolo的識別原理簡單清晰。對於輸入的圖片,將整張圖片分為7×7(7為引數,可調)個方格。當某個物體的中心點落在了某個方格中,該方格則負責預測該物體。每個方格會為被預測物體產生2(引數,可調)個候選框並生成每個框的置信度。最後選取置信度較高的方框作為預測結果。
二、opencv呼叫darknet物體識別模型(yolov3/yolov4)
相關原始碼及模型在darknt資料夾下
使用darknet訓練yolo的模型,生成weights檔案。使用opencv呼叫生成的模型
1、darknet模型的獲取
檔案含義:
-
cfg檔案:模型描述檔案
-
weights檔案:模型權重檔案
Yolov3獲取連結:
https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/blob/master/cfg/yolov3.cfg
https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
Yolov4獲取連結:
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v3_optimal/yolov4.cfg
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v3_optimal/yolov4.weights
2、python呼叫darknet模型實現物體識別
(1)dnn模組呼叫darknet模型
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet("yolov3/yolov3.cfg", "yolov3/yolov3.weights")(2)獲取三個輸出端的LayerName
使用getUnconnectedOutLayer獲取三個只有輸入,沒有輸出的層的名字,Yolov3的三個輸出端層名為:['yolo_82', 'yolo_94', 'yolo_106']
def getOutputsNames(net):
# Get the names of all the layers in the network
layersNames = net.getLayerNames()
# Get the names of the output layers, i.e. the layers with unconnected outputs
return [layersNames[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()](3)影象預處理
使用blobFromImage將影象轉為image Size=(416,416)或(608,608) Scale=1/255 Means=[0,0,0]
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1/255, (416, 416), [0,0,0], 1, crop=False)(4)推理
使用net.forward(multiNames)獲取多個層的結果,其中getOutputsNames(net)=['yolo_82', 'yolo_94', 'yolo_106']
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(getOutputsNames(net))(5)後處理(postrocess)
獲取的結果(outs)裡面有三個矩陣(out),每個矩陣的大小為85*n,n表示檢測到了n個物體,85的排列順序是這樣的:
-
第0列代表物體中心x在圖中的位置(0~1)
-
第1列表示物體中心y在圖中的位置(0~1)
-
第2列表示物體的寬度
-
第3列表示物體的高度
-
第4列是置信概率,值域為[0-1],用來與閾值作比較決定是否標記目標
-
第5~84列為基於COCO資料集的80分類的標記權重,最大的為輸出分類。使用這些引數保留置信度高的識別結果(confidence>confThreshold)
def postprocess(frame, outs):
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
classIds = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
classIds = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
classId = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classId]
if confidence > confThreshold:
center_x = int(detection[0] * frameWidth)
center_y = int(detection[1] * frameHeight)
width = int(detection[2] * frameWidth)
height = int(detection[3] * frameHeight)
left = int(center_x - width / 2)
top = int(center_y - height / 2)
classIds.append(classId)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
print(boxes)
print(confidences)(6)後處理(postrocess)
使用NMSBoxes函數過濾掉重複識別的區域。
indices = cv.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold)
for i in indices:
box = boxes[i]
left = box[0]
top = box[1]
width = box[2]
height = box[3]
drawPred(classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)(7)畫出檢測到的物件
def drawPred(classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):
# Draw a bounding box.
cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255))
label = '%.2f' % conf
# Get the label for the class name and its confidence
if classes:
assert(classId < len(classes))
label = '%s:%s' % (classes[classId], label)
#Display the label at the top of the bounding box
labelSize, baseLine = cv.getTextSize(label, cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
top = max(top, labelSize[1])
cv.putText(frame, label, (left, top), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))(8)完整原始碼及檢測結果(cv_call_yolo.py)
import cv2
cv=cv2
import numpy as np
import time
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet("yolov3/yolov3.cfg", "yolov3/yolov3.weights")
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
confThreshold = 0.5 #Confidence threshold
nmsThreshold = 0.4 #Non-maximum suppression threshold
frame=cv2.imread("dog.jpg")
classesFile = "coco.names";
classes = None
with open(classesFile, 'rt') as f:
classes = f.read().rstrip('\n').split('\n')
def getOutputsNames(net):
# Get the names of all the layers in the network
layersNames = net.getLayerNames()
# Get the names of the output layers, i.e. the layers with unconnected outputs
return [layersNames[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
print(getOutputsNames(net))
# Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence using non-maxima suppression
def postprocess(frame, outs):
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
classIds = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
# Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the
# ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class with the highest score.
classIds = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
classId = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classId]
if confidence > confThreshold:
center_x = int(detection[0] * frameWidth)
center_y = int(detection[1] * frameHeight)
width = int(detection[2] * frameWidth)
height = int(detection[3] * frameHeight)
left = int(center_x - width / 2)
top = int(center_y - height / 2)
classIds.append(classId)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
# Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
# lower confidences.
print(boxes)
print(confidences)
indices = cv.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold)
for i in indices:
#print(i)
#i = i[0]
box = boxes[i]
left = box[0]
top = box[1]
width = box[2]
height = box[3]
drawPred(classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)
# Draw the predicted bounding box
def drawPred(classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):
# Draw a bounding box.
cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255))
label = '%.2f' % conf
# Get the label for the class name and its confidence
if classes:
assert(classId < len(classes))
label = '%s:%s' % (classes[classId], label)
#Display the label at the top of the bounding box
labelSize, baseLine = cv.getTextSize(label, cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
top = max(top, labelSize[1])
cv.putText(frame, label, (left, top), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1/255, (416, 416), [0,0,0], 1, crop=False)
t1=time.time()
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(getOutputsNames(net))
print(time.time()-t1)
postprocess(frame, outs)
t, _ = net.getPerfProfile()
label = 'Inference time: %.2f ms' % (t * 1000.0 / cv.getTickFrequency())
cv.putText(frame, label, (0, 15), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255))
cv2.imshow("result",frame)
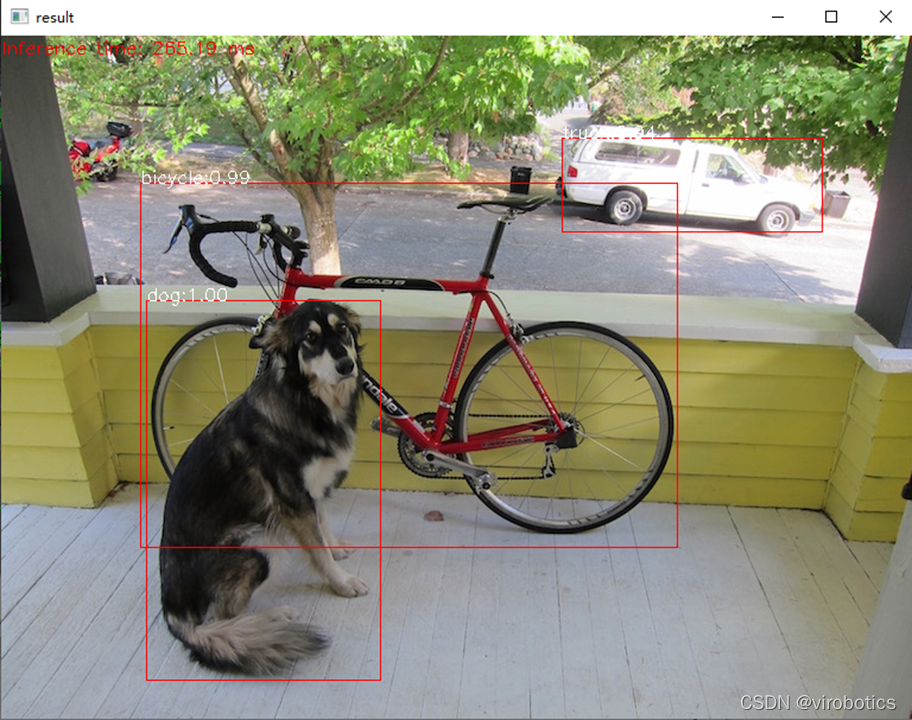
3、LabVIEW呼叫darknet模型實現物體識別yolo_example.vi
(1)LabVIEW呼叫yolov3的方式及步驟和python類似,原始碼如下所示: 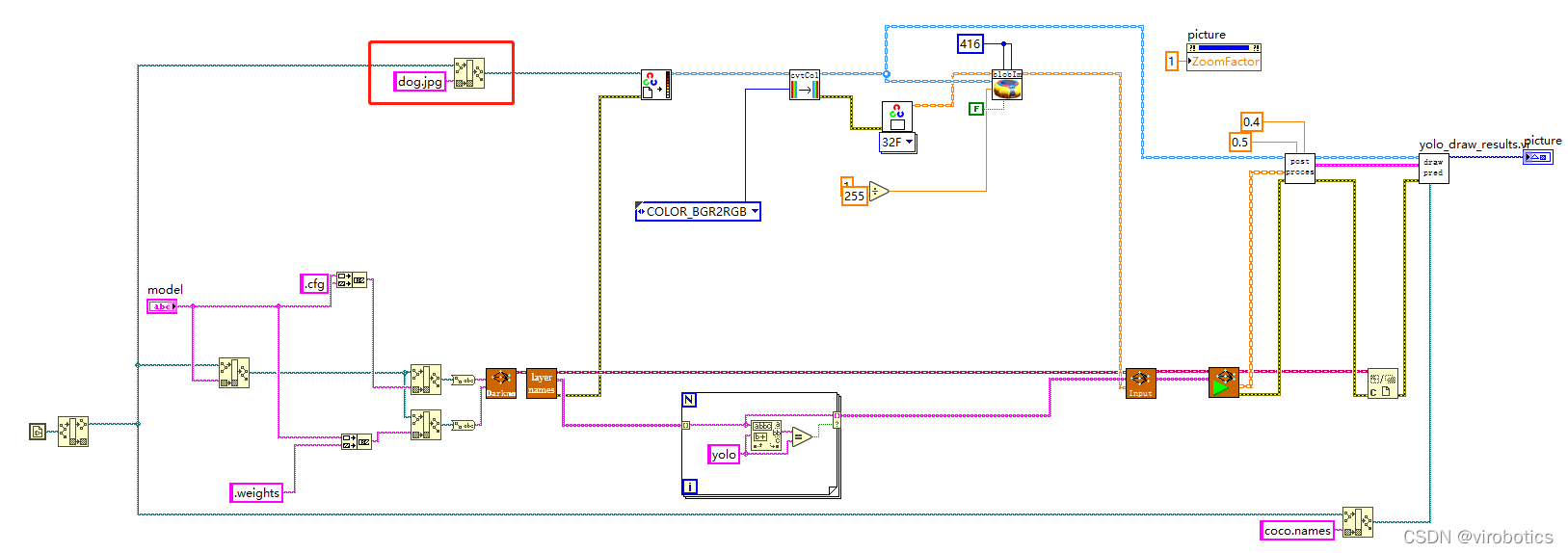 將帶識別圖片與yolo_example.vi置於同一路徑下,即可進行物體識別
將帶識別圖片與yolo_example.vi置於同一路徑下,即可進行物體識別
(2)識別結果如下:
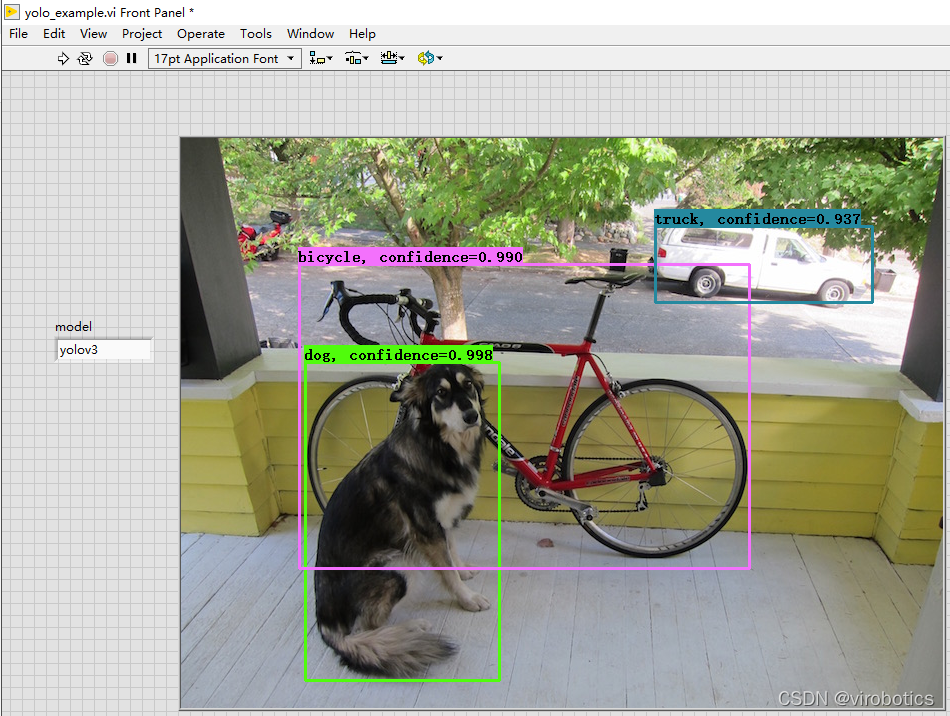
4、LabVIEW實現實時攝像頭物體識別(yolo_example_camera.vi)
(1)使用GPU加速
使用順序結構檢測神經網路推理的時間
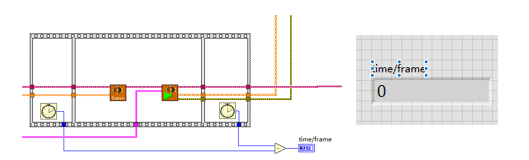
比較使用GPU和不使用GPU兩種情況下的推理速度
普通模式:net.serPerferenceBackend(0),net.serPerferenceTarget(0)
Nvidia GPU模式:net.serPreferenceBackend(5), net.serPerferenceTarget(6)
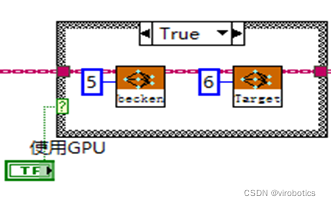
注:普通的c++、python、LabVIEW版本的opencv,即便選了GPU模式也沒用,程式仍然執行在CPU上,需要安裝CUDA和CUDNN後重新從原始碼編譯opencv
(2)程式原始碼如下:
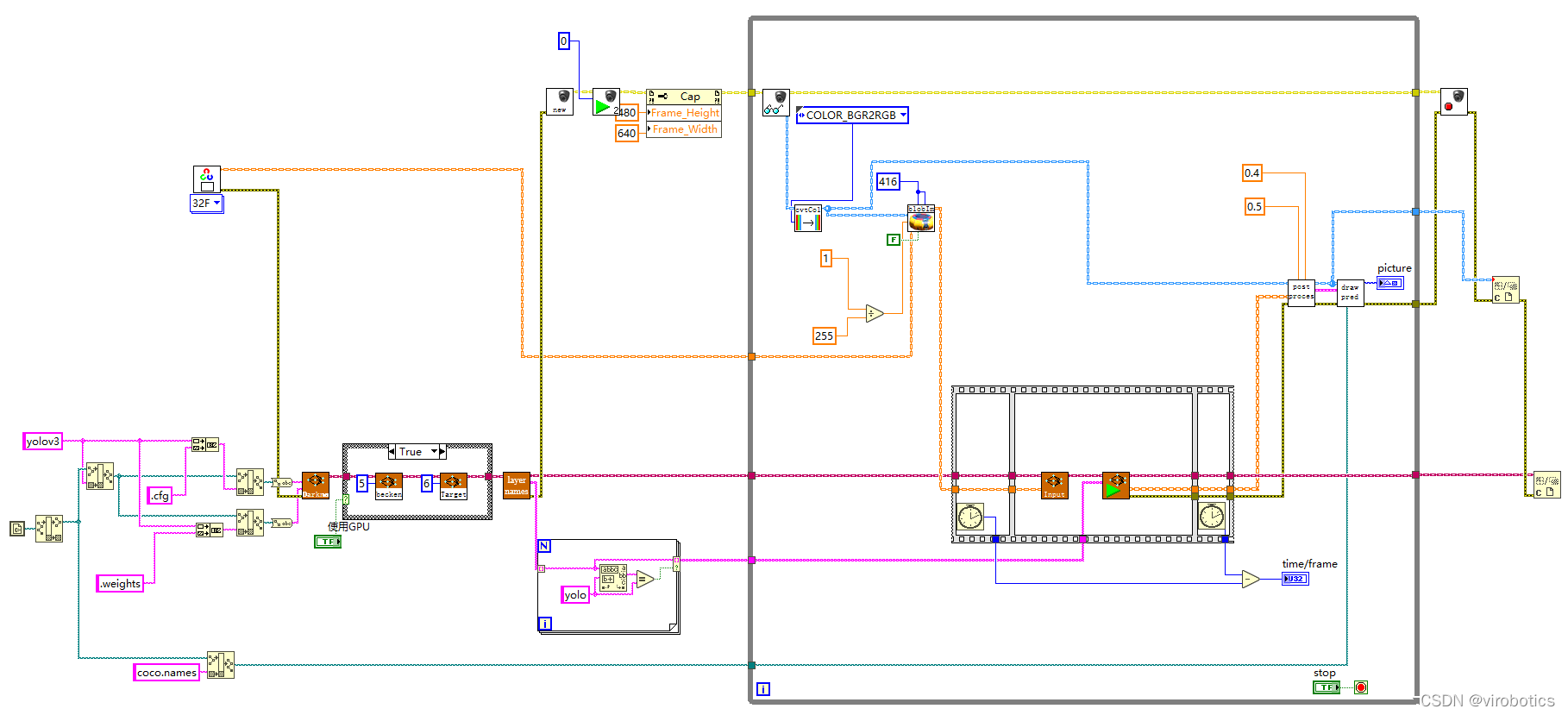 (3)物體識別結果如下:
(3)物體識別結果如下:
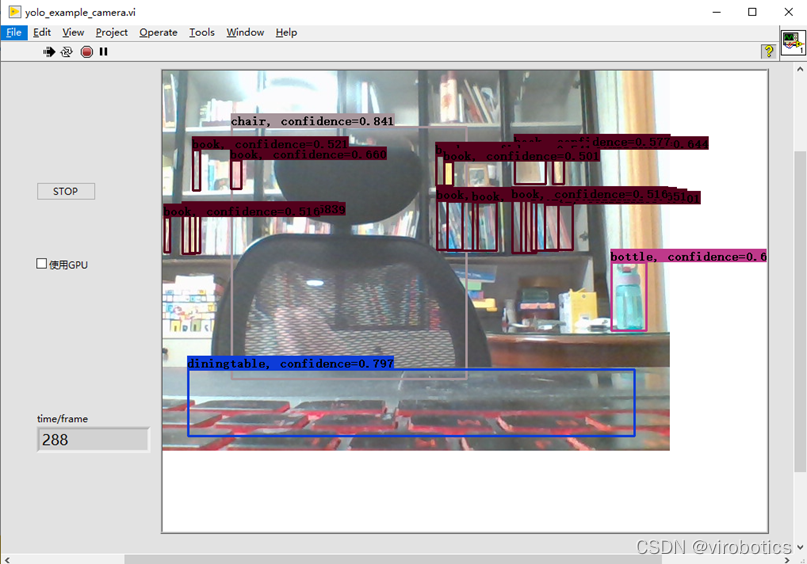
注意,使用如上程式,可以點選STOP按鈕,停止本次物體識別,也可勾選使用GPU進行加速
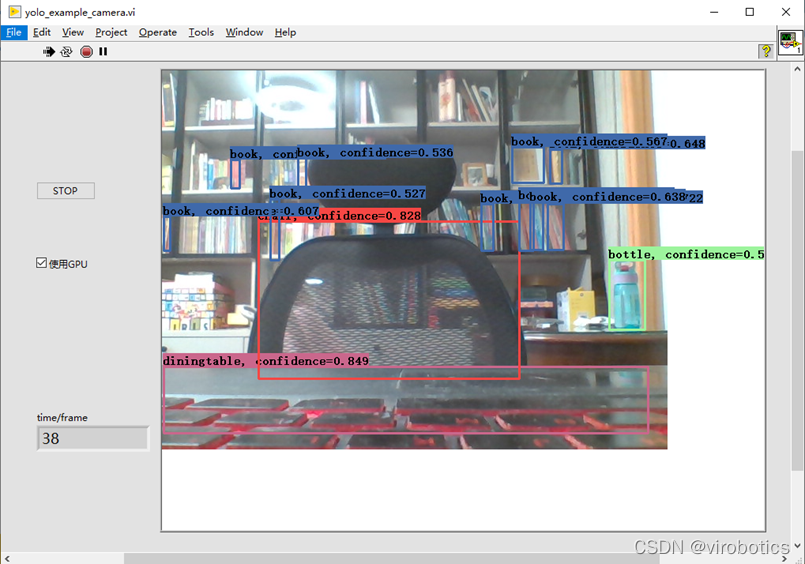
(4)使用GPU加速結果:
三、tensorflow的物體識別模型呼叫
相關原始碼及模型在tf1資料夾下
1、下載預訓練模型並生成pbtxt檔案
(1)下載ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco,下載地址如下: http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_03_29.tar.gz
(2)解壓後的檔案內容
(3)根據pb模型生成pbtxt檔案 執行 tf_text_graph_ssd.py以生成pptxt檔案 在cmd中執行: python tf_text_graph_ssd.py --input ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17/frozen_inference_graph.pb --config ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config --output ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17.pbtxt
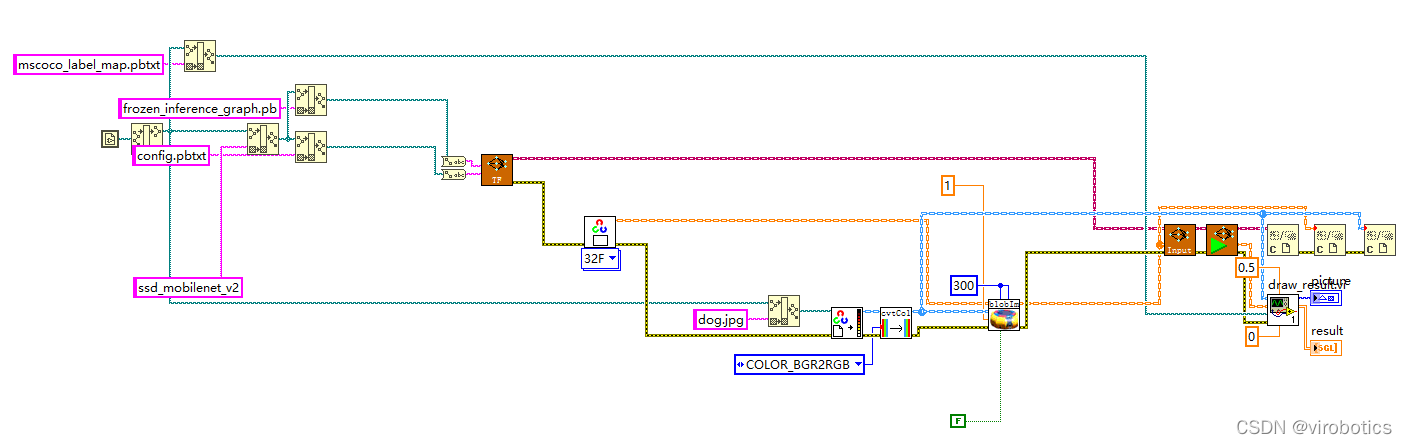
2、LabVIEW呼叫tensorflow模型推理並實現物體識別(callpb.vi)
(1)程式原始碼如下:
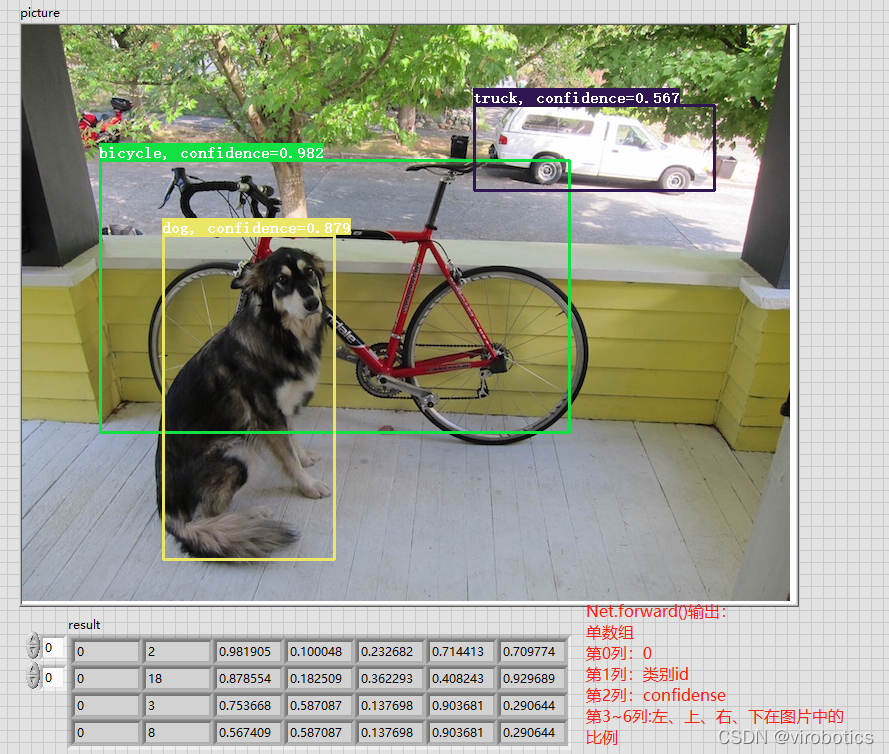
(2)執行結果如下:
四、專案原始碼及模型下載
連結:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1zwbLQe0VehGhsqNIHyaFRw?pwd=8888 提取碼:8888
總結拓展
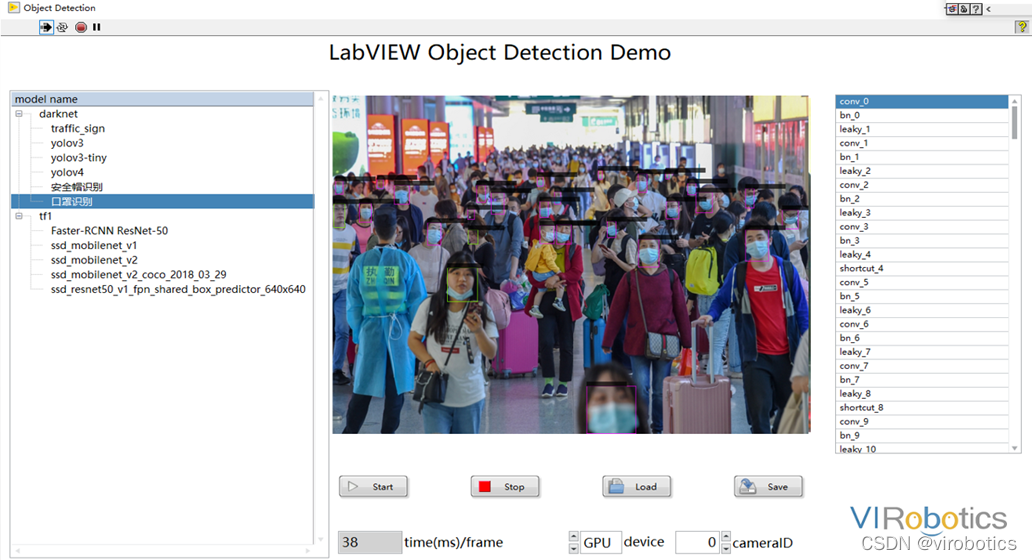
可以使用Yolov3訓練自己的資料集,具體訓練方法可參考部落格:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38915710/article/details/97112788 可實現案例:口罩佩戴識別、肺炎分類、CT等,如口罩佩戴檢測
更多關於LabVIEW與人工智慧技術,可新增技術交流群進一步探討。qq群號:705637299,請備註暗號:LabVIEW 機器學習