集合框架——LinkedList集合原始碼分析
2022-10-01 15:00:45
目錄
總結:
- LinkedList繼承自List,具備有序性
- LinkedList繼承自Deque,具備連結串列關聯性
- LinkedList集合進行增刪改查操作底層實際是操作Node節點的前後連結關係
- LinkedList進行增刪操作時,僅需要操作節點的前後連結關係,因此效率較ArrayList高
- LinkedList進行查詢操作時,必須從頭或者從尾進行查詢,因此較底層依靠陣列進行儲存的ArrayList查詢效率低
範例程式碼
public class LinkedList01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(); //執行第1步
linkedList.add(1); //執行第2步
linkedList.add(2); //執行第3步
linkedList.add(3); //執行第4步
linkedList.add(1 , new Intger(8)); //執行第8步
linkedList.add(5);
linkedList.remove(); //執行第5步
linkedList.remove(2); //執行第6步
linkedList.remove(new Integer(3)); //執行第7步
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}
底層程式碼
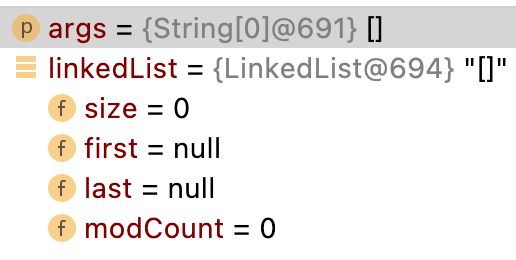
第1步(初始化集合)
//LinkedList類預設構造器
public LinkedList() {}
transient int size = 0; //集合存放物件個數
transient Node<E> first; //集合中第一個節點
transient Node<E> last; //集合中最後一個節點
...
//AbstractSequentialList類預設構造器
protected AbstractSequentialList() {}
...
//AbstractList類預設構造器
protected AbstractList() {}
protected transient int modCount = 0;
...
//AbstractCollection類預設構造器
protected AbstractCollection() {}
...
//Object類預設構造器
public Object() {}
結果:還沒有存放物件,屬於空集合
第2步(往集合中新增一個元素)
public boolean add(E e) { //e = 1
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
...
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;//l = null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);//建立新的節點,當前節點的prev和next屬性均為null,將存入集合的物件賦值給item
last = newNode;//LinkedList集合的last屬性指向新節點
if (l == null)//此時i=null,條件成立
first = newNode;//LinkedList集合的first屬性指向新節點
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;//LinkedList集合的容量自加1
modCount++;//LinkedList集合修改次數自加1
}
......
//Node是LinkedList類的內部類
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //LinkedLIst實際存放的物件
Node<E> next; //當前節點的下一個節點
Node<E> prev; //當前節點的前一個節點
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
結果:集合中存放1個元素,LinkedList類中first與last屬性相同,Node類中prev與next屬性為null
第3步(往集合中新增第二個元素)
public boolean add(E e) { //e = 2
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
...
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;//l = 1,表示上一個節點
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);//建立新的節點,節點的prev屬性指向上一個節點,item屬性存放當前物件
last = newNode;//LinkedList集合的last屬性指向新節點
if (l == null)//此時i!=null,條件不成立
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;//上一個節點的next屬性指向當前節點,即新建立的節點
size++;//LinkedList集合的容量自加1
modCount++;//LinkedList集合修改次數自加1
}
結果:
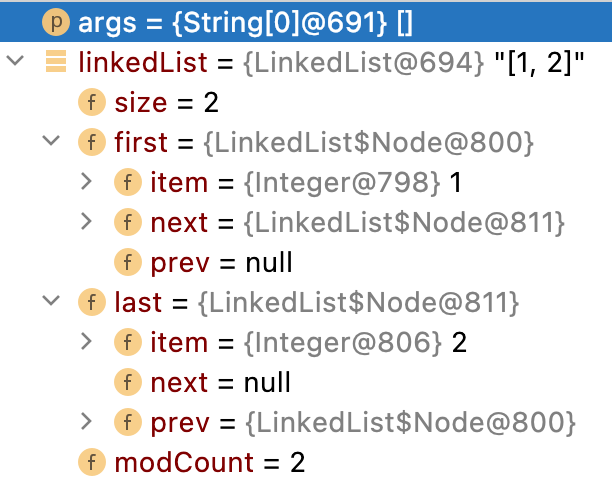
第4步(往集合中新增第三個元素)
public boolean add(E e) { //e = 3
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
...
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;//l = 2,表示上一個節點
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);//建立新的節點,節點的prev屬性指向上一個節點,
item屬性存放當前物件
last = newNode;//LinkedList集合的last屬性指向新節點
if (l == null)//此時i!=null,條件不成立
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;//上一個節點的next屬性指向當前節點,即新建立的節點
size++;//LinkedList集合的容量自加1
modCount++;//LinkedList集合修改次數自加1
}
結果:
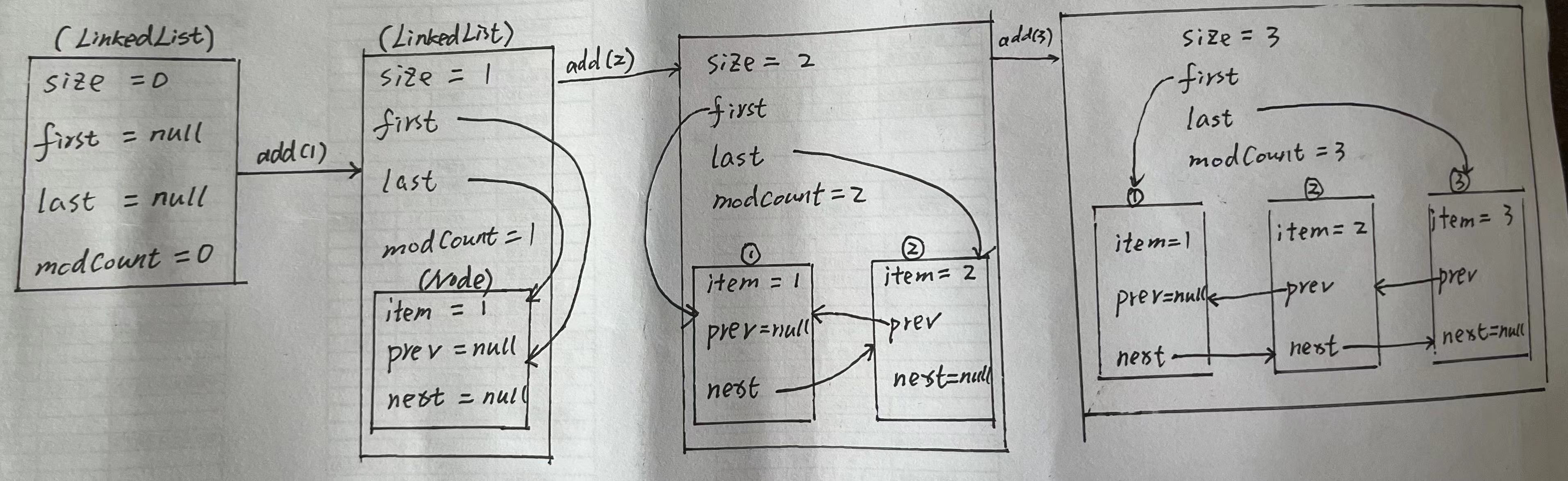
LinkedList新增元素流程示意圖
第5步(刪除集合中第一個元素)
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
...
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
...
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item; //將集合中第一個節點的item 屬性賦值給element
final Node<E> next = f.next; //將集合中第一個節點的next屬性賦值給next
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next; //將原集合中的第二個節點賦給集合的first屬性
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;//將原集合中的第二個節點的prev屬性賦值為null
size--; //集合元素個數自減1
modCount++; //集合修改次數自加1
return element; //返回被刪除的節點item值
}
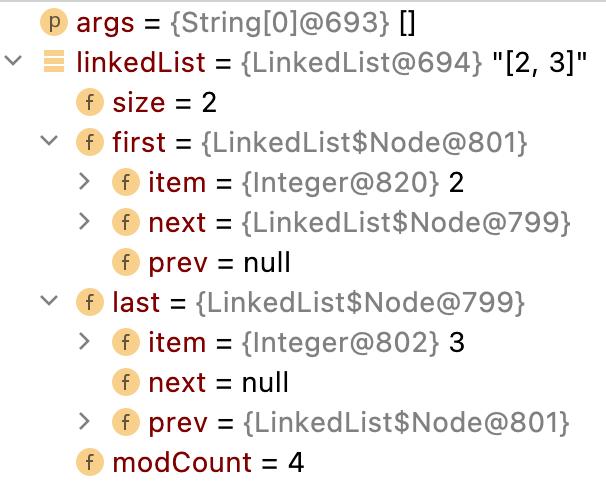
第6步(根據索引來刪除集合中的元素)
public E remove(int index) { //index = 2
checkElementIndex(index); //1.巢狀執行下邊兩個方法①和②,確定索引正確後繼續往下執行
return unlink(node(index)); //2.執行方法③與④
}
...
//方法①
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
...
//方法②
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
...
//方法③
Node<E> node(int index) { //index = 2, size = 4
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) { //index < size/2時
Node<E> x = first; //x記錄首個節點
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next; //找到索引位置對應的節點
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
...
//方法④
E unlink(Node<E> x) { //需要刪除的節點
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) { //對於首個節點的情況
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) { //對於尾端節點的情況
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null; //此時該節點中的屬性item、prev、next均為null
size--; //集合元素個數自減1
modCount++; //集合修改次數自加1
return element; //返回被刪除節點中的內容
}
第7步(根據物件內容來刪除集合中的元素)
//本方法可以用來刪除集合中物件和null
public boolean remove(Object o) { o = new Integer(3)
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x); //呼叫方法與第6步中流程一致
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
第8步(根據索引位置往集合中新增元素)
public void add(int index, E element) { //index=1, element = new Integer(8)
checkPositionIndex(index); //檢查索引沒有問題
if (index == size) //如果索引與集合大小相等
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index)); //node(index)方法找到該索引位置的節點,然後採用linkBefore方法在其節點前連結入新的節點
}
...
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null) //表示原集合中還沒有存放元素
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
...
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { //e = new Integer(8)待連結入的節點,succ為原index位置的節點
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}