瞭解Pytorch|Get Started with PyTorch
一個開源的機器學習框架,加速了從研究原型到生產部署的路徑。
!pip install torch -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
import torch
import numpy as np
Basics
就像Tensorflow一樣,我們也將繼續在PyTorch中玩轉Tensors。
從資料(列表)中建立張量
data = [[1, 2],[3, 4]]
tensors = torch.tensor(data)
tensors
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
從NumPy建立
np_array = np.arange(10)
tensor_np = torch.from_numpy(np_array)
tensor_np
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], dtype=torch.int32)
形狀、ndim和dtype
這與我們在《Numpy教學--第1天》中看到的相同。
tensor_np.shape
torch.Size([10])
tensor_np.ndim
1
tensor_np.dtype
torch.int32
張量操作(Tensor_Operations)
ten1 = torch.tensor([1,2,3])
ten2 = torch.tensor([4,5,6])
ten1+ten2
tensor([5, 7, 9])
你可以使用+或torch.add來執行張量新增。
torch.sub(ten2,ten1)
tensor([3, 3, 3])
torch.add(ten1,ten2)
tensor([5, 7, 9])
torch.subtract(ten2,ten1)
tensor([3, 3, 3])
你可以使用- 或torch.sub來執行張量新增。
ten1*10
tensor([10, 20, 30])
深度學習中非常重要的操作--矩陣乘法
Rules of Matrix Multiplication:
- (3,2) * (3,2) = Error
- (4,3) * (3,2) = (4,2)
- (2,2) * (2,5) = (2,5)
torch.matmul(ten1,ten2)
tensor(32)
matrix4_3 = torch.tensor([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9],
[10,11,12]])
matrix4_3.shape
torch.Size([4, 3])
matrix3_2 = torch.tensor([[1,2],
[3,4],
[5,6]])
matrix3_2.shape
torch.Size([3, 2])
result = torch.matmul(matrix4_3,matrix3_2) #=> will result in (4,2)
result
tensor([[ 22, 28],
[ 49, 64],
[ 76, 100],
[103, 136]])
result.shape
torch.Size([4, 2])
你也可以使用torch.mm(),這是torch.matmul()的簡稱。
torch.mm(matrix4_3,matrix3_2)
tensor([[ 22, 28],
[ 49, 64],
[ 76, 100],
[103, 136]])
#張量的轉置
matrix4_3
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]])
matrix4_3.T
tensor([[ 1, 4, 7, 10],
[ 2, 5, 8, 11],
[ 3, 6, 9, 12]])
torch.t(matrix4_3)
tensor([[ 1, 4, 7, 10],
[ 2, 5, 8, 11],
[ 3, 6, 9, 12]])
更多張量操作
- Zeros
- Ones
- Random
- Full
tensorZeroes = torch.zeros((3,3))
tensorZeroes
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
tensorOnes = torch.ones((3,3))
tensorOnes
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
tensorRandomN = torch.randn((3,3)) #includes negative tensors
tensorRandomN
tensor([[ 1.3255, -0.4937, 1.0488],
[ 1.1797, -0.5422, -0.9703],
[-0.1761, 1.0742, 0.5459]])
tensorRandom = torch.rand((3,3)) #includes only positive tensors
tensorRandom
tensor([[0.2013, 0.9272, 0.7866],
[0.5887, 0.9900, 0.3554],
[0.6128, 0.3316, 0.6635]])
customFill = torch.full((3,3),5)
customFill
tensor([[5, 5, 5],
[5, 5, 5],
[5, 5, 5]])
initialFill = torch.full((3,3),0.01)
initialFill
tensor([[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100],
[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100],
[0.0100, 0.0100, 0.0100]])
快速入門Torchvision
安裝Torchvision,Torchvision軟體包,包括流行的資料集、模型架構和計算機視覺的常見影象轉換。
!pip install torchvision --no-deps -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
from torch import nn
# Download training data from open datasets.
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor(),
)
# Download test data from open datasets.
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor(),
)
type(training_data)
torchvision.datasets.mnist.FashionMNIST
Dataloader在我們的資料集上包裹了一個迭代器,並支援自動批次處理、取樣、洗牌和多程序資料載入。這裡我們定義了一個64的批次處理量,即dataloader可迭代的每個元素將返回64個特徵和標籤的批次。
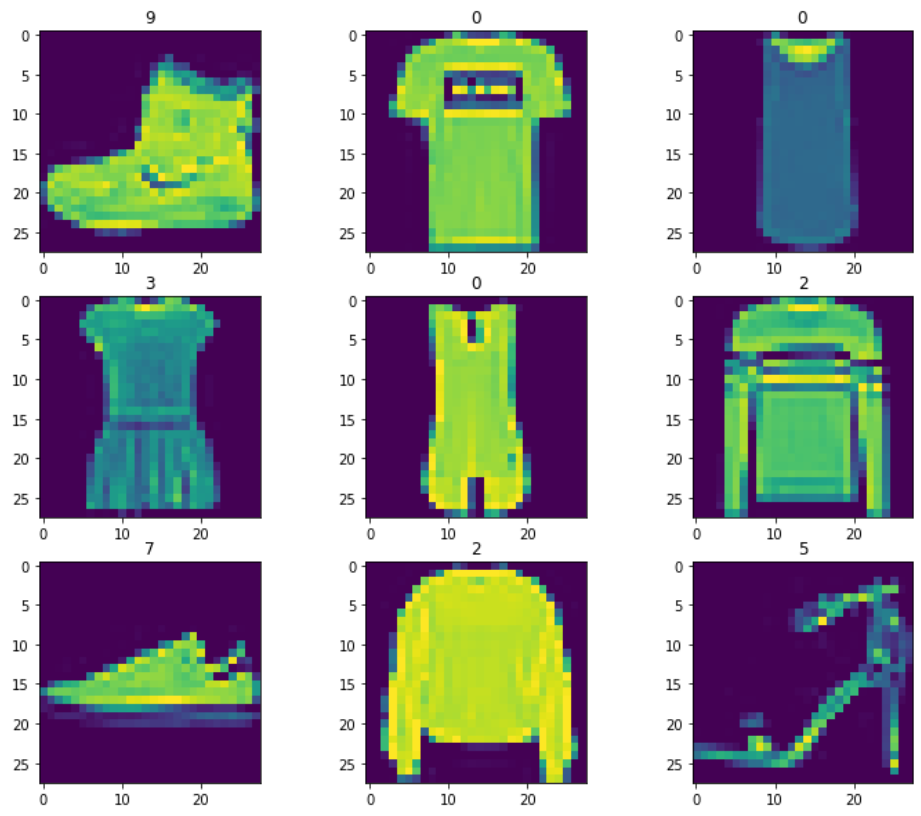
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
for i in range(9):
plt.subplot(3,3,i+1)
sample_image,sample_label = training_data[i]
plt.imshow(sample_image[0])
plt.title(sample_label)
batch_size = 64
training = DataLoader(training_data,batch_size=batch_size)
testing = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=batch_size)
for X, y in testing:
print(f"Shape of X: {X.shape}")
print(f"Shape of y: {y.shape}")
break
Shape of X: torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
Shape of y: torch.Size([64])
for X,y in training:
print(torch.max(X))
print(torch.min(X))
break
tensor(1.)
tensor(0.)
我們不需要擴充套件,因為 DataLoader會處理這個問題。
class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNetwork,self).__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.build_model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28,512), #28*28 is input shape
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512,512), #hidden layer
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512,10) #output layer
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.flatten(x)
dnn = self.build_model(x)
return dnn
model = NeuralNetwork()
# compile model - Loss Function and Optimizer
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-5)
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
model.train()
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
# Compute prediction error
pred = model(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
# Backpropagation
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch % 100 == 0:
loss, current = loss.item(), batch * len(X)
print(f"loss: {loss:>7f} [{current:>5d}/{size:>5d}]")
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
model.eval()
test_loss, correct = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
correct += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_loss /= num_batches
correct /= size
print(f"Test Error: \n Accuracy: {(100*correct):>0.1f}%, Avg loss: {test_loss:>8f} \n")
for epoch in range(5):
print(f"Epochs {epoch+1}")
train(training, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
test(testing, model, loss_fn)
print("Done!")
Epochs 1
loss: 0.473322 [ 0/60000]
loss: 0.569312 [ 6400/60000]
loss: 0.383823 [12800/60000]
loss: 0.613123 [19200/60000]
loss: 0.511312 [25600/60000]
loss: 0.534981 [32000/60000]
loss: 0.519904 [38400/60000]
loss: 0.663009 [44800/60000]
loss: 0.595559 [51200/60000]
loss: 0.510713 [57600/60000]
Test Error:
Accuracy: 81.6%, Avg loss: 0.523760
Epochs 2
loss: 0.441475 [ 0/60000]
loss: 0.541651 [ 6400/60000]
loss: 0.362368 [12800/60000]
loss: 0.587903 [19200/60000]
loss: 0.489257 [25600/60000]
loss: 0.512706 [32000/60000]
loss: 0.496316 [38400/60000]
loss: 0.658995 [44800/60000]
loss: 0.588307 [51200/60000]
loss: 0.486178 [57600/60000]
Test Error:
Accuracy: 82.2%, Avg loss: 0.507999
Epochs 3
loss: 0.414868 [ 0/60000]
loss: 0.520754 [ 6400/60000]
loss: 0.345219 [12800/60000]
loss: 0.567657 [19200/60000]
loss: 0.470389 [25600/60000]
loss: 0.493463 [32000/60000]
loss: 0.477664 [38400/60000]
loss: 0.654533 [44800/60000]
loss: 0.580627 [51200/60000]
loss: 0.466487 [57600/60000]
Test Error:
Accuracy: 82.7%, Avg loss: 0.495437
Epochs 4
loss: 0.391931 [ 0/60000]
loss: 0.504477 [ 6400/60000]
loss: 0.331017 [12800/60000]
loss: 0.550430 [19200/60000]
loss: 0.453982 [25600/60000]
loss: 0.477417 [32000/60000]
loss: 0.462027 [38400/60000]
loss: 0.649069 [44800/60000]
loss: 0.573334 [51200/60000]
loss: 0.450685 [57600/60000]
Test Error:
Accuracy: 83.0%, Avg loss: 0.485073
Epochs 5
loss: 0.372204 [ 0/60000]
loss: 0.491510 [ 6400/60000]
loss: 0.318891 [12800/60000]
loss: 0.536430 [19200/60000]
loss: 0.440059 [25600/60000]
loss: 0.463519 [32000/60000]
loss: 0.449640 [38400/60000]
loss: 0.642708 [44800/60000]
loss: 0.565997 [51200/60000]
loss: 0.438368 [57600/60000]
Test Error:
Accuracy: 83.2%, Avg loss: 0.476352
Done!
我們將在下一個筆電序列中探討更多關於神經網路的問題。
Notebook:瞭解PytorchGet Started with PyTorch | Kaggle
原文作者:孤飛-部落格園
我的個人部落格:https://blog.onefly.top