JDK自帶javap命令反編譯class檔案和Jad反編譯class檔案(推薦使用jad)
一、前言
我們在日常學習中,對一個java程式碼有問題,不知道jvm內部怎麼進行解析的時候;有個偉大壯舉就是反編譯,這樣就可以看到jvm內部怎麼進行對這個java檔案解析的!我們可以使用JDK自帶的javap命令來進行反編譯,反編譯出來的如果看不太明白,可以使用Jad工具來配合使用。還有就是把jar包完全反編譯為我們寫的程式碼的是GD-GUI,有興趣可以去官網看一下哈,小編這裡不做進一步說明。
我們今天以String string = new String("wang") + new String("zhen");,這條語句在底層是怎麼建立的來深入理解jvm底層,同時也對反編譯有進一步的瞭解哈!!話不多說,跟著小編一起學習吧。
二、編寫java檔案
public class JavaPTest {
String string = new String("學") + new String("Java");
}
三、科補程式碼理解
上面程式碼可是建立了5個物件哈,我們一步步的說哈!
首先,會先判斷字串常數池中是否存在"學"字串物件,如果不存在則在字串常數池中建立一個物件。當執行到new關鍵字在堆中建立一個"學"字串物件。後面的new String("Java"),也是這樣。
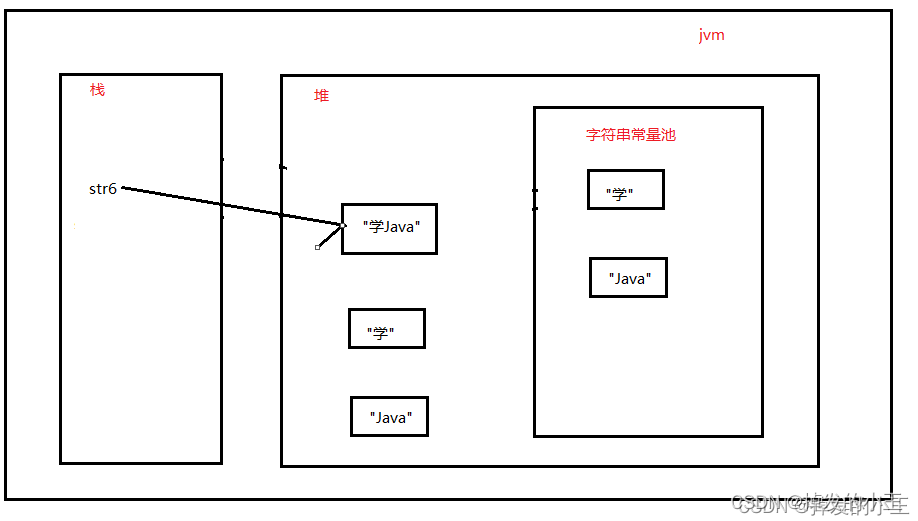
然後,當右邊完成時,會在堆中建立一個"學Java"字串物件。並把棧中的變數"str6"指向堆中的物件。
總結:一句程式碼建立了5個物件,但是有兩個在堆中是沒有參照的,按照垃圾回收的可達性分析,他們是垃圾就是"學"、"Java"這倆垃圾。
記憶體圖如下:
小編剛剛開始也是有疑問,為什麼是五個呢?下面我們進一步探究!!
四、javap命令
不知道有什麼命令的小夥伴,直接win+R輸入cmd 開啟的視窗輸入javap即可看到一下內容
C:\Users\Administrator>javap
用法: javap <options> <classes>
其中, 可能的選項包括:
-help --help -? 輸出此用法訊息
-version 版本資訊
-v -verbose 輸出附加資訊
-l 輸出行號和本地變數表
-public 僅顯示公共類和成員
-protected 顯示受保護的/公共類和成員
-package 顯示程式包/受保護的/公共類
和成員 (預設)
-p -private 顯示所有類和成員
-c 對程式碼進行反組合
-s 輸出內部型別簽名
-sysinfo 顯示正在處理的類的
系統資訊 (路徑, 大小, 日期, MD5 雜湊)
-constants 顯示最終常數
-classpath <path> 指定查詢使用者類檔案的位置
-cp <path> 指定查詢使用者類檔案的位置
心得:常用的就是javap -c -v class名字.class
例子:javap -c -v JavaPTest.class
五、執行javap命令
在IDEA的java類中按快捷鍵ctrl + f9編譯成class檔案,為反編譯做準備;
找到class檔案的位置
來到此目錄下,不用cd切換到這個目錄了哈
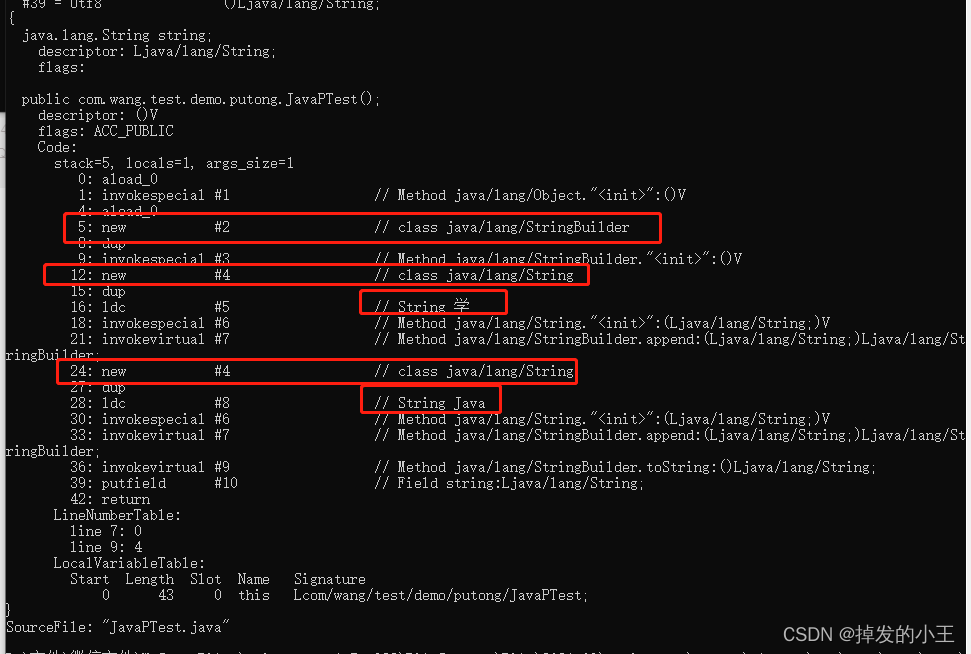
輸入javap -c -v JavaPTest.class,有反編譯後的可見,建立了5個物件。
六、下載Jad包
1. 網址下載
2. 解壓到指定目錄
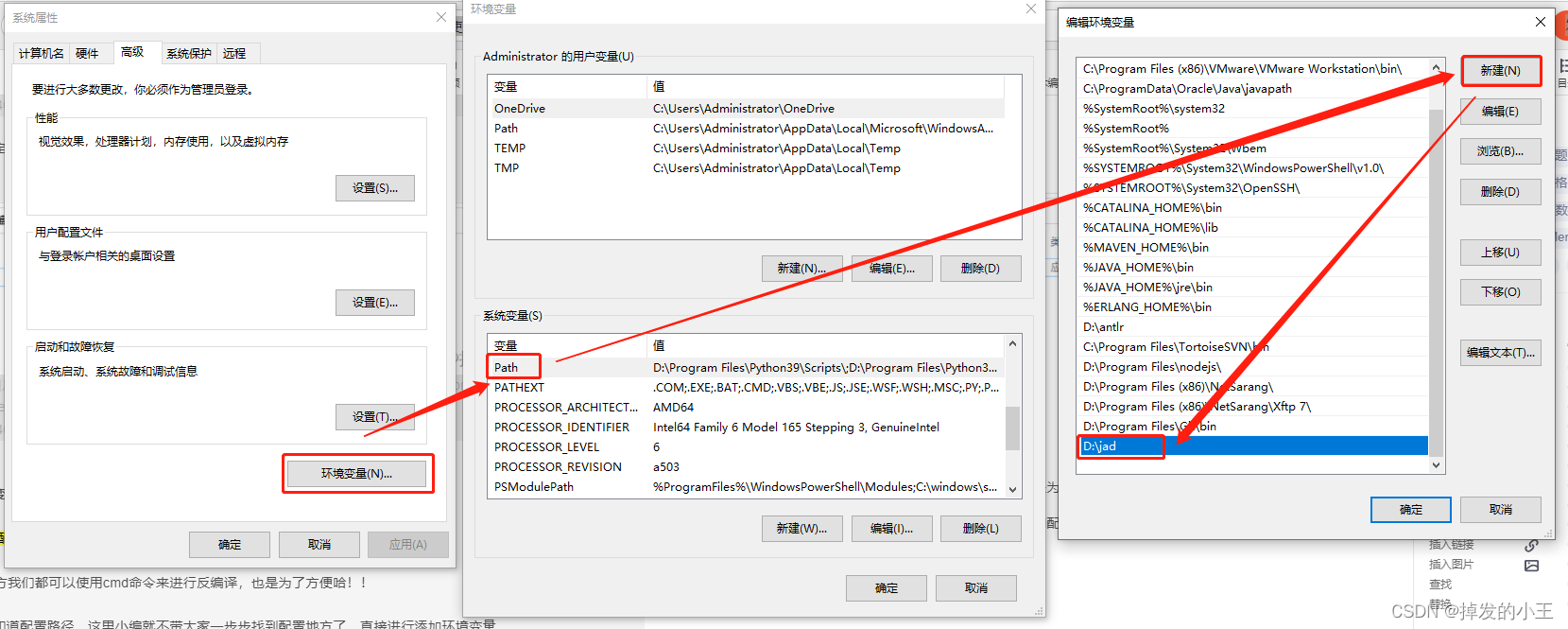
3. 設定環境變數
為什麼還要設定環境變數?
這樣在任何地方我們都可以使用cmd命令來進行反編譯,也是為了方便哈!!
PS:大家jdk都知道設定路徑,這裡小編就不帶大家一步步找到設定地方了,直接進行新增環境變數
4. 常用命令檢視
不知道有什麼命令的小夥伴,直接win+R輸入cmd 開啟的視窗輸入jad即可看到一下內容
C:\Users\Administrator>jad
Jad v1.5.8g. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov ([email protected]).
Usage: jad [option(s)] <filename(s)>
Options: -a - generate JVM instructions as comments (annotate)
-af - output fully qualified names when annotating
-b - generate redundant braces (braces)
-clear - clear all prefixes, including the default ones
-d <dir> - directory for output files
-dead - try to decompile dead parts of code (if there are any)
-dis - disassembler only (disassembler)
-f - generate fully qualified names (fullnames)
-ff - output fields before methods (fieldsfirst)
-i - print default initializers for fields (definits)
-l<num> - split strings into pieces of max <num> chars (splitstr)
-lnc - output original line numbers as comments (lnc)
-lradix<num>- display long integers using the specified radix
-nl - split strings on newline characters (splitstr)
-noconv - don't convert Java identifiers into valid ones (noconv)
-nocast - don't generate auxiliary casts
-noclass - don't convert .class operators
-nocode - don't generate the source code for methods
-noctor - suppress the empty constructors
-nodos - turn off check for class files written in DOS mode
-nofd - don't disambiguate fields with the same names (nofldis)
-noinner - turn off the support of inner classes
-nolvt - ignore Local Variable Table entries (nolvt)
-nonlb - don't insert a newline before opening brace (nonlb)
-o - overwrite output files without confirmation
-p - send all output to STDOUT (for piping)
-pa <pfx>- prefix for all packages in generated source files
-pc <pfx>- prefix for classes with numerical names (default: _cls)
-pe <pfx>- prefix for unused exception names (default: _ex)
-pf <pfx>- prefix for fields with numerical names (default: _fld)
-pi<num> - pack imports into one line using .* (packimports)
-pl <pfx>- prefix for locals with numerical names (default: _lcl)
-pm <pfx>- prefix for methods with numerical names (default: _mth)
-pp <pfx>- prefix for method parms with numerical names (default:_prm)
-pv<num> - pack fields with the same types into one line (packfields)
-r - restore package directory structure
-radix<num>- display integers using the specified radix (8, 10, or 16)
-s <ext> - output file extension (default: .jad)
-safe - generate additional casts to disambiguate methods/fields
-space - output space between keyword (if, while, etc) and expression
-stat - show the total number of processed classes/methods/fields
-t<num> - use <num> spaces for indentation (default: 4)
-t - use tabs instead of spaces for indentation
-v - show method names while decompiling
-8 - convert Unicode strings into ANSI strings (ansi)
-& - redirect STDERR to STDOUT
小編這裡就翻譯了哈,常用的就是jad -o -p class檔名稱
-o:無需確認直接覆蓋輸出
-p: 直接反編譯程式碼到輸出到命令下(直接在介面顯示)
5.實踐命令
輸入:jad -o JavaPTest,會在class檔案所在同一級命令生成.jad檔案,看的也比較清晰,我們使用工具開啟:
// Decompiled by Jad v1.5.8g. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov.
// Jad home page: http://www.kpdus.com/jad.html
// Decompiler options: packimports(3)
// Source File Name: JavaPTest.java
package com.wang.test.demo.putong;
public class JavaPTest
{
public JavaPTest()
{
string = (new StringBuilder()).append(new String("wang"))
.append(new String("zhjen")).toString();
}
String string;
}
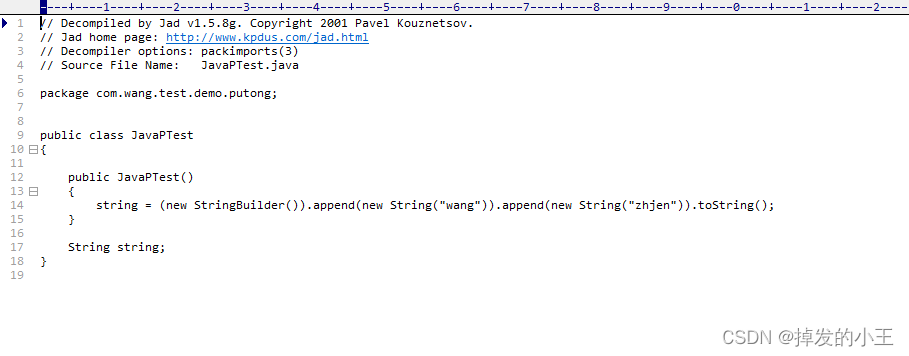
輸入:jad -o -p JavaPTest,也是五個物件更加簡單版的,不需要向上面一樣要開啟檔案才可以看
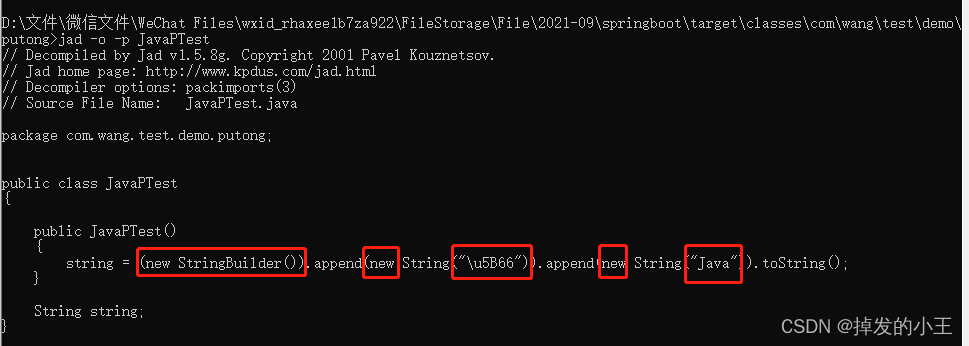
七、總結
這樣我們就完成了class檔案反編譯了,兩種方法有利有弊,大家根據實際情況來進行反編譯。總而言之,這兩種方法都是要必須掌握的!
看到這裡了,還不給小編三連一波哈!!謝謝大家嘍!!
有緣人才可以看得到的哦!!!
歡迎關注小編的微信公眾號:
