範例詳解Pytorch中的tensor資料結構
php零基礎到就業直播視訊課:進入學習
【相關推薦:Python3視訊教學 】
torch.Tensor
torch.Tensor 是一種包含單一資料型別元素的多維矩陣,類似於 numpy 的 array。
Tensor 可以使用 torch.tensor() 轉換 Python 的 list 或序列資料生成,生成的是dtype 預設是 torch.FloatTensor。
注意
torch.tensor()總是拷貝 data。如果你有一個 Tensor data 並且僅僅想改變它的requires_grad屬性,可用requires_grad_()或者detach()來避免拷貝。如果你有一個numpy陣列並且想避免拷貝,請使用torch.as_tensor()。
1,指定資料型別的 Tensor 可以通過傳遞引數 torch.dtype 和/或者 torch.device 到建構函式生成:
注意為了改變已有的 tensor 的 torch.device 和/或者 torch.dtype, 考慮使用
to()方法.
>>> torch.ones([2,3], dtype=torch.float64, device="cuda:0")
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64)
>>> torch.ones([2,3], dtype=torch.float32)
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])2,Tensor 的內容可以通過 Python索引或者切片存取以及修改:
>>> matrix = torch.tensor([[2,3,4],[5,6,7]])
>>> print(matrix[1][2])
tensor(7)
>>> matrix[1][2] = 9
>>> print(matrix)
tensor([[2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 9]])3,使用 torch.Tensor.item() 或者 int() 方法從只有一個值的 Tensor中獲取 Python Number:
>>> x = torch.tensor([[4.5]]) >>> x tensor([[4.5000]]) >>> x.item() 4.5 >>> int(x) 4
4,Tensor可以通過引數 requires_grad=True 建立, 這樣 torch.autograd 會記錄相關的運算實現自動求導:
>>> x = torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., 1.]], requires_grad=True) >>> out = x.pow(2).sum() >>> out.backward() >>> x.grad tensor([[ 2.0000, -2.0000], [ 2.0000, 2.0000]])
5,每一個 tensor都有一個相應的 torch.Storage 儲存其資料。tensor 類提供了一個多維的、strided 檢視, 並定義了數值操作。
Tensor 資料型別
Torch 定義了七種 CPU tensor 型別和八種 GPU tensor 型別:
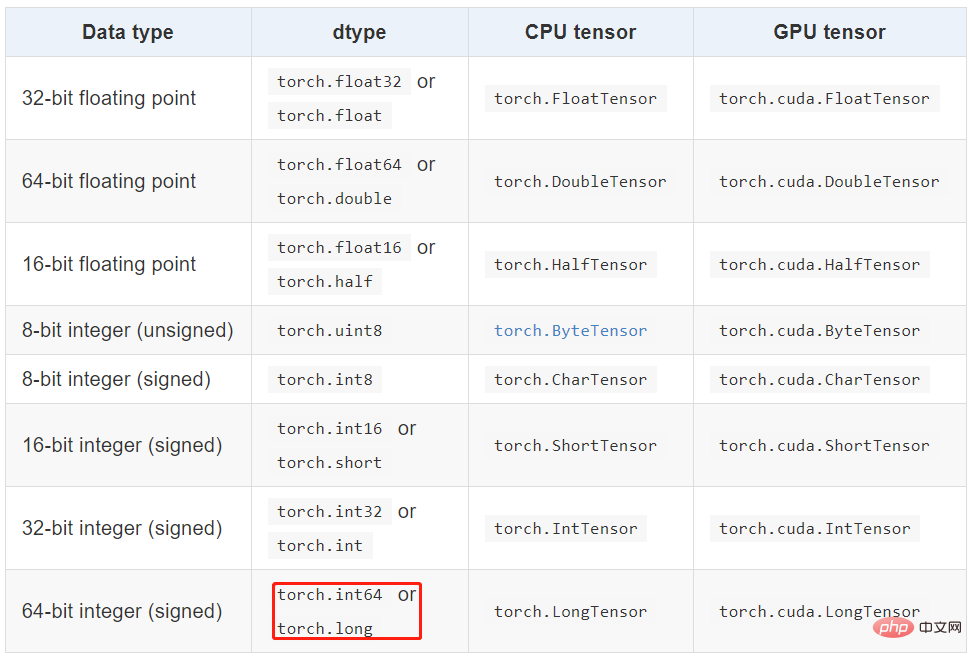
torch.Tensor 是預設的 tensor 型別(torch.FloatTensor)的簡稱,即 32 位浮點數資料型別。
Tensor 的屬性
Tensor 有很多屬性,包括資料型別、Tensor 的維度、Tensor 的尺寸。
- 資料型別:可通過改變 torch.tensor() 方法的 dtype 引數值,來設定不同的 tensor 資料型別。
- 維度:不同型別的資料可以用不同維度(dimension)的張量來表示。標量為 0 維張量,向量為 1 維張量,矩陣為 2 維張量。彩色影象有 rgb 三個通道,可以表示為 3 維張量。視訊還有時間維,可以表示為 4 維張量,有幾個中括號 [ 維度就是幾。可使用 dim() 方法 獲取 tensor 的維度。
- 尺寸:可以使用 shape屬性或者 size()方法檢視張量在每一維的長度,可以使用 view()方法或者reshape() 方法改變張量的尺寸。
樣例程式碼如下:
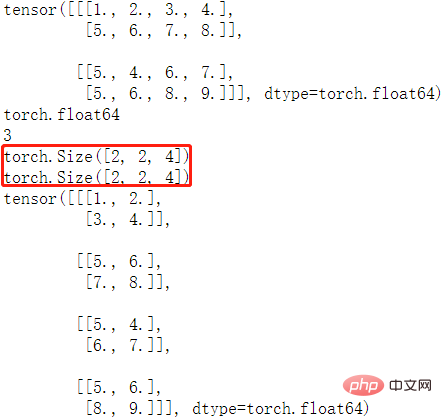
matrix = torch.tensor([[[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]],
[[5,4,6,7], [5,6,8,9]]], dtype = torch.float64)
print(matrix) # 列印 tensor
print(matrix.dtype) # 列印 tensor 資料型別
print(matrix.dim()) # 列印 tensor 維度
print(matrix.size()) # 列印 tensor 尺寸
print(matrix.shape) # 列印 tensor 尺寸
matrix2 = matrix.view(4, 2, 2) # 改變 tensor 尺寸
print(matrix2)程式輸出結果如下:
view 和 reshape 的區別
兩個方法都是用來改變 tensor 的 shape,view() 只適合對滿足連續性條件(contiguous)的 tensor 進行操作,而 reshape() 同時還可以對不滿足連續性條件的 tensor 進行操作。在滿足 tensor 連續性條件(contiguous)時,a.reshape() 返回的結果與a.view() 相同,都不會開闢新記憶體空間;不滿足 contiguous 時, 直接使用 view() 方法會失敗,reshape() 依然有用,但是會重新開闢記憶體空間,不與之前的 tensor 共用記憶體,即返回的是 」副本「(等價於先呼叫 contiguous() 方法再使用 view() 方法)。
更多理解參考這篇文章
Tensor 與 ndarray
1,張量和 numpy 陣列。可以用 .numpy() 方法從 Tensor 得到 numpy 陣列,也可以用 torch.from_numpy 從 numpy 陣列得到Tensor。這兩種方法關聯的 Tensor 和 numpy 陣列是共用資料記憶體的。可以用張量的 clone方法拷貝張量,中斷這種關聯。
arr = np.random.rand(4,5) print(type(arr)) tensor1 = torch.from_numpy(arr) print(type(tensor1)) arr1 = tensor1.numpy() print(type(arr1)) """ <class 'numpy.ndarray'> <class 'torch.Tensor'> <class 'numpy.ndarray'> """
2,item() 方法和 tolist() 方法可以將張量轉換成 Python 數值和數值列表
# item方法和tolist方法可以將張量轉換成Python數值和數值列表 scalar = torch.tensor(5) # 標量 s = scalar.item() print(s) print(type(s)) tensor = torch.rand(3,2) # 矩陣 t = tensor.tolist() print(t) print(type(t)) """ 1.0 <class 'float'> [[0.8211846351623535, 0.20020723342895508], [0.011571824550628662, 0.2906131148338318]] <class 'list'> """
建立 Tensor
建立 tensor ,可以傳入資料或者維度,torch.tensor() 方法只能傳入資料,torch.Tensor() 方法既可以傳入資料也可以傳維度,強烈建議 tensor() 傳資料,Tensor() 傳維度,否則易搞混。
傳入維度的方法
| 方法名 | 方法功能 | 備註 |
|---|---|---|
torch.rand(*sizes, out=None) → Tensor | 返回一個張量,包含了從區間 [0, 1) 的均勻分佈中抽取的一組亂數。張量的形狀由引數sizes定義。 | 推薦 |
torch.randn(*sizes, out=None) → Tensor | 返回一個張量,包含了從標準正態分佈(均值為0,方差為1,即高斯白噪聲)中抽取的一組亂數。張量的形狀由引數sizes定義。 | 不推薦 |
torch.normal(means, std, out=None) → Tensor | 返回一個張量,包含了從指定均值 means 和標準差 std 的離散正態分佈中抽取的一組亂數。標準差 std 是一個張量,包含每個輸出元素相關的正態分佈標準差。 | 多種形式,建議看原始碼 |
torch.rand_like(a) | 根據資料 a 的 shape 來生成亂資料 | 不常用 |
torch.randint(low=0, high, size) | 生成指定範圍(low, hight)和 size 的隨機整數資料 | 常用 |
torch.full([2, 2], 4) | 生成給定維度,全部資料相等的資料 | 不常用 |
torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1, *, out=None) | 生成指定間隔的資料 | 易用常用 |
torch.ones(*size, *, out=None) | 生成給定 size 且值全為1 的矩陣資料 | 簡單 |
zeros()/zeros_like()/eye() | 全 0 的 tensor 和 對角矩陣 | 簡單 |
樣例程式碼:
>>> torch.rand([1,1,3,3])
tensor([[[[0.3005, 0.6891, 0.4628],
[0.4808, 0.8968, 0.5237],
[0.4417, 0.2479, 0.0175]]]])
>>> torch.normal(2, 3, size=(1, 4))
tensor([[3.6851, 3.2853, 1.8538, 3.5181]])
>>> torch.full([2, 2], 4)
tensor([[4, 4],
[4, 4]])
>>> torch.arange(0,10,2)
tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
>>> torch.eye(3,3)
tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]])【相關推薦:Python3視訊教學 】
以上就是範例詳解Pytorch中的tensor資料結構的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!

