flutter系列之:flutter中常用的container layout詳解
簡介
在上一篇文章中,我們列舉了flutter中的所有layout類,並且詳細介紹了兩個非常常用的layout:Row和Column。
掌握了上面兩個基本的layout還是不夠的,如果需要應付日常的layout使用,我們還需要掌握多一些layout元件。今天我們會介紹一個功能強大的layout:Container layout。
Container的使用
Container是一個空白的容器,通常可以用Container來封裝其他的widget。那麼為什麼還需要把widget封裝在Container中呢?這是因為Container中包含了一些特殊的功能。
比如Container中可以設定背景顏色或者背景圖片,並且可以設定padding, margins和borders。這就為元件的自定義提供了諸多空間。
首先看一下Container的定義和建構函式:
class Container extends StatelessWidget {
Container({
Key? key,
this.alignment,
this.padding,
this.color,
this.decoration,
this.foregroundDecoration,
double? width,
double? height,
BoxConstraints? constraints,
this.margin,
this.transform,
this.transformAlignment,
this.child,
this.clipBehavior = Clip.none,
})
可以看到Container是一個StatelessWidget,它的建構函式可以傳入多個非常有用的屬性,用來控制Container的表現。
Container中有padding,decoration,constraints和margin這些和位置相關的一些屬性,他們有什麼關係呢?
container首先將child用padding包裹起來,padding可以用decoration進行填充。
填充後的padding又可以應用constraints來進行限制(比如width和height),然後這個元件又可以使用margin空白包裹起來。
接下來我們看一個簡單的Container中包含Column和Row的例子。
首先構造一個container widget,它包含一個Column:
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
),
child: Column(
children: [
buildBoxRow(),
buildBoxRow(),
],
),
);
}
這裡給Container設定了一個BoxDecoration,用於指定Container的背景顏色。
在Child中給定了一個Column widget,它的child是一個Row物件。
Widget buildBoxRow() => Row(
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
children: [
Container(
width: 100,
child: Image.asset("images/head.jpg")
)
],
);
這裡的Row中又是一個包含了Image的Container物件。
最後執行,我們可以得到下面的介面:
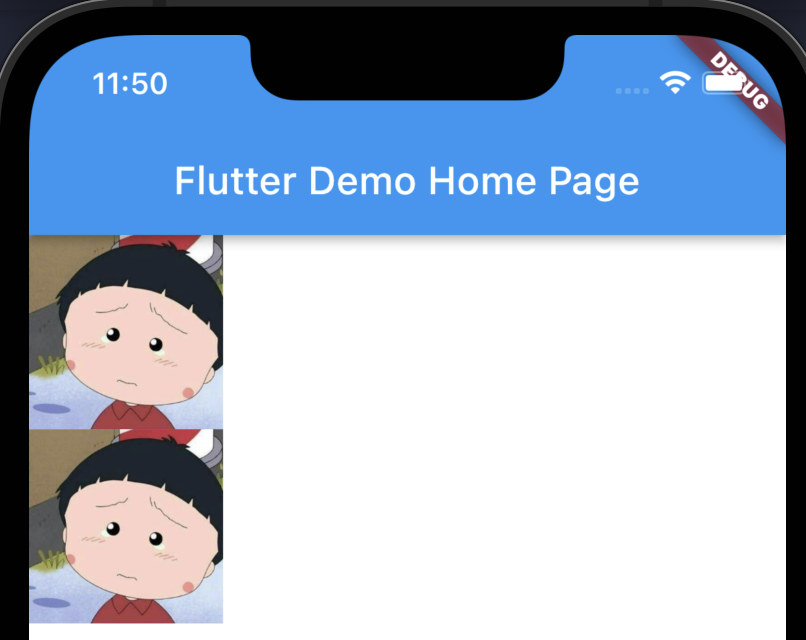
Container中包含兩行,每行包含一個Image物件。
旋轉Container
預設情況下Container是一個正常佈局的widget,但是有時候我們可能需要實現一些特殊效果,比如說元件的旋轉,Container提供的transform屬性可以很方便的做到這一點。
對於Container來說,transform是在元件繪製中最先被應用的,transform之後會進行decoration的繪製,然後進行child的繪製,最後進行foregroundDecoration的繪製。
還是上面的例子,我們試一下transform屬性是如何工作的,我們在包含image的container中加入transform屬性:
Widget buildBoxRow() => Row(
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
children: [
Container(
transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.2),
width: 100,
child: Image.asset("images/head.jpg")
)
],
);
最後生成的APP如下:
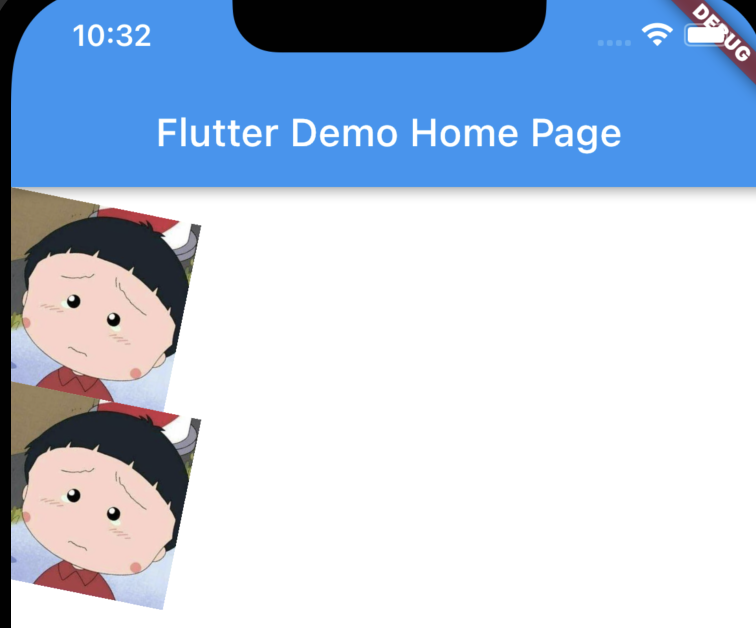
可以看到圖片已經沿Z軸進行了旋轉。
這裡的旋轉使用的是Matrix4.rotationZ,也就是沿Z軸選擇,當然你可以可以使用rotationX或者rotationY,分別沿X軸或者Y軸旋轉。
如果選擇rotationX,那麼看起來的影象應該是這樣的:
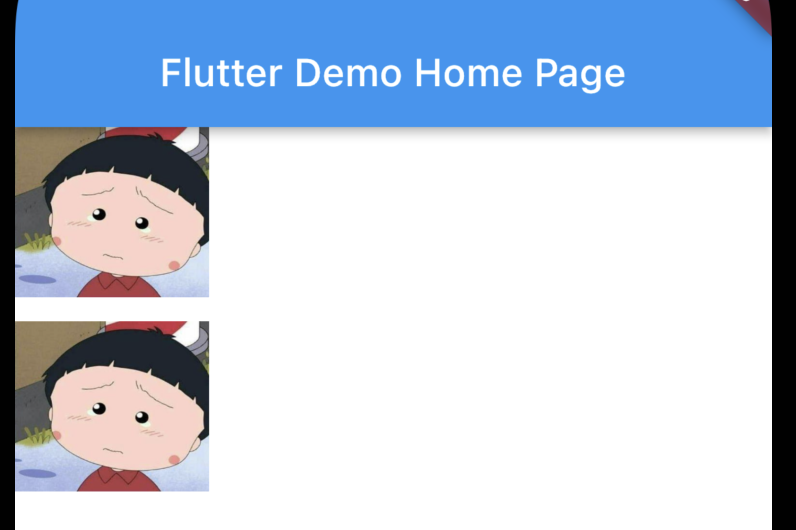
事實上,Matrix4不僅僅可以沿單獨的軸進行旋轉,還可以選擇特定的向量方向進行選擇。
比如下面的兩個方法:
/// Translation matrix.
factory Matrix4.translation(Vector3 translation) => Matrix4.zero()
..setIdentity()
..setTranslation(translation);
/// Translation matrix.
factory Matrix4.translationValues(double x, double y, double z) =>
Matrix4.zero()
..setIdentity()
..setTranslationRaw(x, y, z);
Matrix4還可以沿三個方向進行進行放大縮寫,如下面的方法:
/// Scale matrix.
factory Matrix4.diagonal3Values(double x, double y, double z) =>
Matrix4.zero()
.._m4storage[15] = 1.0
.._m4storage[10] = z
.._m4storage[5] = y
.._m4storage[0] = x;
感興趣的朋友可以自行嘗試。
Container中的BoxConstraints
在Container中設定Constraints的時候,我們使用的是BoxConstraints。BoxConstraints有四個包含數位的屬性,分別是minWidth,maxWidth,minHeight和maxHeight。
所以BoxConstraints提供了這四個值的建構函式:
const BoxConstraints({
this.minWidth = 0.0,
this.maxWidth = double.infinity,
this.minHeight = 0.0,
this.maxHeight = double.infinity,
}) : assert(minWidth != null),
assert(maxWidth != null),
assert(minHeight != null),
assert(maxHeight != null);
BoxConstraints還有兩個建構函式分別是loose和tight:
BoxConstraints.loose(Size size)
BoxConstraints.tight(Size size)
這兩個有什麼區別呢?如果一個axis的最小值是0的話,那麼這個BoxConstraints就是loose。
如果一個axis的最大值和最小值是相等的情況,那麼這個BoxConstraints就是tight。
BoxConstraints中還有一個非常常用的方法如下:
BoxConstraints.expand({double? width, double? height})
expand的意思就是最大值和最小值都是infinity的,具體的定義可以從方法的實現中看出:
const BoxConstraints.expand({
double? width,
double? height,
}) : minWidth = width ?? double.infinity,
maxWidth = width ?? double.infinity,
minHeight = height ?? double.infinity,
maxHeight = height ?? double.infinity;
總結
Container是一個非常常用的layout元件,大家可以熟練的使用起來。
本文的例子:https://github.com/ddean2009/learn-flutter.git
更多內容請參考 http://www.flydean.com/08-flutter-ui-layout-container/
最通俗的解讀,最深刻的乾貨,最簡潔的教學,眾多你不知道的小技巧等你來發現!
歡迎關注我的公眾號:「程式那些事」,懂技術,更懂你!