k8s驅逐篇(3)-kubelet節點壓力驅逐-原始碼分析篇
kubelet節點壓力驅逐-概述
kubelet監控叢集節點的 CPU、記憶體、磁碟空間和檔案系統的inode 等資源,根據kubelet啟動引數中的驅逐策略設定,當這些資源中的一個或者多個達到特定的消耗水平,kubelet 可以主動地驅逐節點上一個或者多個pod,以回收資源,降低節點資源壓力。
驅逐訊號
節點上的memory、nodefs、pid等資源都有驅逐訊號,kubelet通過將驅逐訊號與驅逐策略進行比較來做出驅逐決定;
驅逐策略
kubelet節點壓力驅逐包括了兩種,軟碟機逐和硬驅逐;
軟碟機逐
軟碟機逐機制表示,當node節點的memory、nodefs等資源達到一定的閾值後,需要持續觀察一段時間(寬限期),如果期間該資源又恢復到低於閾值,則不進行pod的驅逐,若高於閾值持續了一段時間(寬限期),則觸發pod的驅逐。
硬驅逐
硬驅逐策略沒有寬限期,當達到硬驅逐條件時,kubelet會立即觸發pod的驅逐,而不是優雅終止。
關於kubelet節點壓力驅逐的詳細介紹,可以檢視上一篇文章-kubelet節點壓力驅逐;
kubelet節點壓力驅逐-原始碼分析
負責kubelet節點壓力驅逐的是kubelet中的evictionManager;
基於kubernets v1.17.4
從kubelet的Run方法為入口,通過一系列的呼叫,呼叫了evictionManager.Start方法;
呼叫鏈:kubelet.Run() --> kubelet.updateRuntimeUp() --> kubelet.initializeRuntimeDependentModules() --> kubelet.evictionManager.Start()
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
func (kl *Kubelet) Run(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate) {
...
go wait.Until(kl.updateRuntimeUp, 5*time.Second, wait.NeverStop)
...
}
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
func (kl *Kubelet) updateRuntimeUp() {
...
kl.oneTimeInitializer.Do(kl.initializeRuntimeDependentModules)
...
}
evictionManager在沒有發生pod驅逐時,驅逐監測間隔時間為10s;
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
const (
...
evictionMonitoringPeriod = time.Second * 10
...
)
func (kl *Kubelet) initializeRuntimeDependentModules() {
...
kl.evictionManager.Start(kl.StatsProvider, kl.GetActivePods, kl.podResourcesAreReclaimed, evictionMonitoringPeriod)
...
}
1.evictionManager結構體分析
managerImpl struct
分析evictionManager.Start方法前,先來分析下eviction_manager的結構體managerImpl struct,看其有哪些比較重要的屬性:
(1)config:儲存著eviction_manager的相關設定,根據kubelet啟動引數設定值來初始化config;
(2)thresholdsMet:記錄已經達到驅逐閾值,但還沒有滿足驅逐策略條件,觸發驅逐的Threshold切片(Threshold後面做介紹);
(3)thresholdsFirstObservedAt:記錄各個Threshold的第一次發現時間點;
(4)lastObservations:記錄上一次調諧處理中,軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號的資源總量、資源可用量、探測時間;
(5)signalToRankFunc:儲存軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號所對應的排序函數,排序函數用於計算被驅逐pod的順序;
(6)killPodFunc:定義了驅逐pod的具體函數,在eviction_manager初始化的時候,該值被賦值為pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go-killPodNow()函數;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
type managerImpl struct {
...
config Config
thresholdsMet []evictionapi.Threshold
thresholdsFirstObservedAt thresholdsObservedAt
lastObservations signalObservations
signalToRankFunc map[evictionapi.Signal]rankFunc
killPodFunc KillPodFunc
...
}
1.1 Config struct
Config儲存著eviction_manager的相關設定,根據kubelet啟動引數設定值來初始化Config;
其中Config.Thresholds屬性儲存著設定的驅逐策略資訊;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/types.go
type Config struct {
...
Thresholds []evictionapi.Threshold
MaxPodGracePeriodSeconds int64
PressureTransitionPeriod time.Duration
...
}
1.2 evictionapi.Threshold
看到Threshold結構體,重要的幾個屬性如下:
(1)Signal:驅逐訊號;
(2)Operator:驅逐訊號對應資源的實際統計值與驅逐閾值之間的比較運運算元;
(3)Value:驅逐閾值;
(4)GracePeriod:驅逐訊號對應資源的實際統計值達到驅逐閾值之後需要持續GracePeriod時間後,才會觸發驅逐;
(5)MinReclaim:觸發驅逐後的資源最小回收值;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/api/types.go
type Threshold struct {
// Signal defines the entity that was measured.
Signal Signal
// Operator represents a relationship of a signal to a value.
Operator ThresholdOperator
// Value is the threshold the resource is evaluated against.
Value ThresholdValue
// GracePeriod represents the amount of time that a threshold must be met before eviction is triggered.
GracePeriod time.Duration
// MinReclaim represents the minimum amount of resource to reclaim if the threshold is met.
MinReclaim *ThresholdValue
}
1.3 thresholdsObservedAt
thresholdsObservedAt是個map型別,記錄各個Threshold及其第一次發現時間點;
type thresholdsObservedAt map[evictionapi.Threshold]time.Time
1.4 signalObservations
signalObservations是個map型別,記錄上一次調諧處理中,軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號的資源總量、資源可用量、探測時間;
type signalObservations map[evictionapi.Signal]signalObservation
type signalObservation struct {
// The resource capacity
capacity *resource.Quantity
// The available resource
available *resource.Quantity
// Time at which the observation was taken
time metav1.Time
}
1.5 rankFunc
rankFunc是排序函數,用於計算被驅逐pod的順序;
其函數入參為pod列表以及一個statsFunc,statsFunc是個函數,返回pod相關資源統計的一個函數;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/types.go
type statsFunc func(pod *v1.Pod) (statsapi.PodStats, bool)
type rankFunc func(pods []*v1.Pod, stats statsFunc)
// pkg/kubelet/apis/stats/v1alpha1/types.go
type PodStats struct {
// Reference to the measured Pod.
PodRef PodReference `json:"podRef"`
// The time at which data collection for the pod-scoped (e.g. network) stats was (re)started.
StartTime metav1.Time `json:"startTime"`
// Stats of containers in the measured pod.
Containers []ContainerStats `json:"containers" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"name"`
// Stats pertaining to CPU resources consumed by pod cgroup (which includes all containers' resource usage and pod overhead).
CPU *CPUStats `json:"cpu,omitempty"`
// Stats pertaining to memory (RAM) resources consumed by pod cgroup (which includes all containers' resource usage and pod overhead).
Memory *MemoryStats `json:"memory,omitempty"`
// Stats pertaining to network resources.
Network *NetworkStats `json:"network,omitempty"`
// Stats pertaining to volume usage of filesystem resources.
// VolumeStats.UsedBytes is the number of bytes used by the Volume
VolumeStats []VolumeStats `json:"volume,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"name"`
// EphemeralStorage reports the total filesystem usage for the containers and emptyDir-backed volumes in the measured Pod.
EphemeralStorage *FsStats `json:"ephemeral-storage,omitempty"`
}
2.evictionManager處理邏輯分析
evictionManager.Start
evictionManager.Start方法中包含了兩部分的啟動:
(1)實時驅逐:如果設定了KernelMemcgNotification(即kubelet啟動引數--experimental-kernel-memcg-notification設定為true,預設為false),則會針對memory記憶體資源,利用kernel memcg notification,根據核心實時通知,呼叫m.synchronize方法執行驅逐邏輯(暫不展開分析);
(2)輪詢驅逐:拉起一個goroutine,迴圈呼叫m.synchronize方法執行驅逐邏輯,如果被驅逐的pod不為空,則呼叫m.waitForPodsCleanup方法等待被驅逐的pod刪除成功,如果沒有pod被驅逐,則sleep 10秒後再回圈;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
func (m *managerImpl) Start(diskInfoProvider DiskInfoProvider, podFunc ActivePodsFunc, podCleanedUpFunc PodCleanedUpFunc, monitoringInterval time.Duration) {
thresholdHandler := func(message string) {
klog.Infof(message)
m.synchronize(diskInfoProvider, podFunc)
}
// 啟動實時驅逐
if m.config.KernelMemcgNotification {
for _, threshold := range m.config.Thresholds {
if threshold.Signal == evictionapi.SignalMemoryAvailable || threshold.Signal == evictionapi.SignalAllocatableMemoryAvailable {
notifier, err := NewMemoryThresholdNotifier(threshold, m.config.PodCgroupRoot, &CgroupNotifierFactory{}, thresholdHandler)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("eviction manager: failed to create memory threshold notifier: %v", err)
} else {
go notifier.Start()
m.thresholdNotifiers = append(m.thresholdNotifiers, notifier)
}
}
}
}
// 啟動輪詢驅逐
// start the eviction manager monitoring
go func() {
for {
if evictedPods := m.synchronize(diskInfoProvider, podFunc); evictedPods != nil {
klog.Infof("eviction manager: pods %s evicted, waiting for pod to be cleaned up", format.Pods(evictedPods))
m.waitForPodsCleanup(podCleanedUpFunc, evictedPods)
} else {
time.Sleep(monitoringInterval)
}
}
}()
}
2.1 m.synchronize
m.synchronize方法為kubelet節點壓力驅逐的核心處理方法,方法中會根據kubelet設定的驅逐策略,計算並判斷是否符合驅逐條件,符合則根據一定的優先順序來驅逐pod,然後返回被驅逐的pod(每次呼叫m.synchronize方法最多隻會驅逐一個pod);
且這裡說的驅逐pod,只是將pod.status.phase值更新為Failed,並附上驅逐reason:Evicted以及觸發驅逐的詳細資訊,不會刪除pod;而pod.status.phase值被更新為Failed後,replicaset controller會再次建立出新的pod呼叫到其他節點上,達到驅逐pod的效果;
方法主要邏輯為:
(1)從kubelet啟動引數中獲取驅逐策略設定,返回thresholds;
(2)判斷imageFs和rootfs是否為同一個,然後呼叫buildSignalToRankFunc函數來構建pod的排序函數(buildSignalToRankFunc函數返回軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號所對應的排序函數,排序函數用於計算被驅逐pod的順序),呼叫buildSignalToNodeReclaimFuncs函數構建節點資源回收函數(用於後續在執行驅逐pod之前,先呼叫節點資源回收函數來回收資源,如果回收的資源足夠,則不用走驅逐邏輯);
(3)呼叫podFunc,即呼叫kl.GetActivePods方法,獲取會被驅逐的pod列表-activePods;
(4)呼叫m.summaryProvider.Get,獲取各種統計資訊,如節點上各個資源的總量以及使用量情況、容器的資源宣告及使用量情況等;
(5)ThresholdNotifier相關的通知實現,ThresholdNotifier-基於觀察者模式實現對特殊資源驅逐管理的支援;
(6)呼叫makeSignalObservations函數,根據前面獲取到的節點資源總量及使用量等各種統計資訊,組裝返回observations,並返回獲取pod資源總量及使用量等統計資訊的方法statsFunc,該方法後面會用到;
(7)呼叫thresholdsMet函數,比較observations中的資源使用量和thresholds中的驅逐策略設定閾值之間的大小,將超過閾值的驅逐訊號(即memory.available、nodefs.available等)組裝成thresholds返回;
(8)判斷m.thresholdsMet(m.thresholdsMet記錄了已經達到驅逐閾值,但還沒有滿足驅逐策略條件,觸發驅逐的Threshold切片)長度是否大於0,大於0則呼叫mergeThresholds函數,將上面得到的thresholds與m.thresholdsMet合併;
(9)呼叫thresholdsFirstObservedAt函數,傳入thresholds與m.thresholdsFirstObservedAt(記錄各個Threshold的第一次發現時間點),記錄並更新各個驅逐訊號的第一次超過閾值的時間,返回thresholdsFirstObservedAt;
(10)呼叫nodeConditionsObservedSince函數,判斷距離上次更新nodeCondition時間是否已經超過了m.config.PressureTransitionPeriod(即kubelet啟動引數設定--eviction-pressure-transition-period),超過則更新nodeConditions並返回(這裡還沒有把nodeCondition更新到node物件中去);
(11)呼叫thresholdsMetGracePeriod函數,篩選出驅逐訊號達到驅逐閾值並持續了evictionSoftGracePeriod時間的(即kubelet啟動引數設定--eviction-soft-grace-period),組裝並返回thresholds,此時的thresholds是滿足驅逐策略即將觸發驅逐的thresholds;
(12)更新managerImpl的部分成員變數的值,如nodeConditions、thresholdsFirstObservedAt、nodeConditionsLastObservedAt、thresholdsMet、lastObservations;
(13)判斷LocalStorageCapacityIsolation即localStorage驅逐的featuregate是否開啟,是則先呼叫m.localStorageEviction處理localstorage驅逐,如果返回驅逐的pod列表不為空,則證明是localStorage觸發的驅逐,且已經處理完畢,直接return;
(14)判斷即將觸發驅逐的thresholds長度是否為0,是則代表沒有觸發驅逐,不需要執行驅逐邏輯,直接return;
(15)呼叫sort.Sort(byEvictionPriority(thresholds)),給thresholds排序,將記憶體排在所有其他資源訊號之前,並將沒有資源可回收的閾值排在最後;
(16)根據排序結果,呼叫getReclaimableThreshold,遍歷thresholds,從中獲取第一個可以被回收的threshold,返回thresholdToReclaim;
(17)呼叫m.reclaimNodeLevelResources,回收上面獲取到的節點級的資源thresholdToReclaim,如果回收的資源足夠,則直接return,不需要往下執行驅逐pod的邏輯;
(18)呼叫m.signalToRankFunc[thresholdToReclaim.Signal],獲取對應驅逐訊號的pod排序函數;
(19)判斷activePods長度是否為0,是則直接return,沒有可被驅逐的pod,無法執行驅逐邏輯;
(20)呼叫rank(activePods, statsFunc),根據之前獲取到的pod排序演演算法,給pod列表進行排序,再次得到activePods,用於後面驅逐pod;
(21)遍歷activePods列表,獲取pod的gracePeriod(硬驅逐為0,軟碟機逐則根據kubelet啟動引數--eviction-max-pod-grace-period設定值獲得),呼叫evictionMessage函數,構造驅逐message,後續更新到pod的event和status中,用於說明為什麼發生驅逐,最後呼叫m.evictPod,判斷pod能否被驅逐,能則開始驅逐pod;
但這裡要注意的是,每次呼叫m.synchronize方法,最多隻驅逐一個pod,驅逐成功一個pod則直接return;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
func (m *managerImpl) synchronize(diskInfoProvider DiskInfoProvider, podFunc ActivePodsFunc) []*v1.Pod {
// (1)獲取驅逐策略設定
// if we have nothing to do, just return
thresholds := m.config.Thresholds
if len(thresholds) == 0 && !utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.LocalStorageCapacityIsolation) {
return nil
}
klog.V(3).Infof("eviction manager: synchronize housekeeping")
// build the ranking functions (if not yet known)
// TODO: have a function in cadvisor that lets us know if global housekeeping has completed
if m.dedicatedImageFs == nil {
hasImageFs, ok := diskInfoProvider.HasDedicatedImageFs()
if ok != nil {
return nil
}
m.dedicatedImageFs = &hasImageFs
// (2)呼叫`buildSignalToRankFunc`函數來構建pod的排序函數(buildSignalToRankFunc函數返回軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號所對應的排序函數,排序函數用於計算被驅逐pod的順序)
m.signalToRankFunc = buildSignalToRankFunc(hasImageFs)
m.signalToNodeReclaimFuncs = buildSignalToNodeReclaimFuncs(m.imageGC, m.containerGC, hasImageFs)
}
// (3)呼叫`podFunc`,即呼叫`kl.GetActivePods`方法,獲取會被驅逐的pod列表-activePods
activePods := podFunc()
updateStats := true
// (4)獲取各種統計資訊,如節點上各個資源的總量以及使用量情況、容器的資源宣告及使用量情況等
summary, err := m.summaryProvider.Get(updateStats)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("eviction manager: failed to get summary stats: %v", err)
return nil
}
// (5)ThresholdNotifier相關的通知實現,ThresholdNotifier-基於觀察者模式實現對特殊資源驅逐管理的支援;
if m.clock.Since(m.thresholdsLastUpdated) > notifierRefreshInterval {
m.thresholdsLastUpdated = m.clock.Now()
for _, notifier := range m.thresholdNotifiers {
if err := notifier.UpdateThreshold(summary); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("eviction manager: failed to update %s: %v", notifier.Description(), err)
}
}
}
// (6)呼叫`makeSignalObservations`函數,根據前面獲取到的節點資源總量及使用量等各種統計資訊,組裝返回observations,並返回獲取pod資源總量及使用量等統計資訊的方法statsFunc,該方法後面會用到
// make observations and get a function to derive pod usage stats relative to those observations.
observations, statsFunc := makeSignalObservations(summary)
debugLogObservations("observations", observations)
// (7)呼叫thresholdsMet函數,比較observations中的資源使用量和thresholds中的驅逐策略設定閾值之間的大小,將超過閾值的驅逐訊號(即`memory.available`、`nodefs.available`等)組裝成`thresholds`返回
// determine the set of thresholds met independent of grace period
thresholds = thresholdsMet(thresholds, observations, false)
debugLogThresholdsWithObservation("thresholds - ignoring grace period", thresholds, observations)
// (8)判斷`m.thresholdsMet`(`m.thresholdsMet`記錄了已經達到驅逐閾值,但還沒有滿足驅逐策略條件,觸發驅逐的`Threshold`切片)長度是否大於0,大於0則呼叫mergeThresholds函數,將上面得到的`thresholds`與`m.thresholdsMet`合併
// determine the set of thresholds previously met that have not yet satisfied the associated min-reclaim
if len(m.thresholdsMet) > 0 {
thresholdsNotYetResolved := thresholdsMet(m.thresholdsMet, observations, true)
thresholds = mergeThresholds(thresholds, thresholdsNotYetResolved)
}
debugLogThresholdsWithObservation("thresholds - reclaim not satisfied", thresholds, observations)
// (9)呼叫`thresholdsFirstObservedAt`函數,傳入`thresholds`與`m.thresholdsFirstObservedAt`(記錄各個`Threshold`的第一次發現時間點),記錄並更新各個驅逐訊號的第一次超過閾值的時間,返回`thresholdsFirstObservedAt`
// track when a threshold was first observed
now := m.clock.Now()
thresholdsFirstObservedAt := thresholdsFirstObservedAt(thresholds, m.thresholdsFirstObservedAt, now)
// the set of node conditions that are triggered by currently observed thresholds
nodeConditions := nodeConditions(thresholds)
if len(nodeConditions) > 0 {
klog.V(3).Infof("eviction manager: node conditions - observed: %v", nodeConditions)
}
// (10)呼叫nodeConditionsObservedSince函數,判斷距離上次更新nodeCondition時間是否已經超過了`m.config.PressureTransitionPeriod`(即kubelet啟動引數設定`--eviction-pressure-transition-period`),超過則更新nodeConditions並返回(這裡還沒有把nodeCondition更新到node物件中去)
// track when a node condition was last observed
nodeConditionsLastObservedAt := nodeConditionsLastObservedAt(nodeConditions, m.nodeConditionsLastObservedAt, now)
// node conditions report true if it has been observed within the transition period window
nodeConditions = nodeConditionsObservedSince(nodeConditionsLastObservedAt, m.config.PressureTransitionPeriod, now)
if len(nodeConditions) > 0 {
klog.V(3).Infof("eviction manager: node conditions - transition period not met: %v", nodeConditions)
}
// (11)呼叫`thresholdsMetGracePeriod`函數,篩選出驅逐訊號達到驅逐閾值並持續了`evictionSoftGracePeriod`時間的(即kubelet啟動引數設定`--eviction-soft-grace-period`),組裝並返回`thresholds`,此時的`thresholds`是滿足驅逐策略即將觸發驅逐的thresholds;
// determine the set of thresholds we need to drive eviction behavior (i.e. all grace periods are met)
thresholds = thresholdsMetGracePeriod(thresholdsFirstObservedAt, now)
debugLogThresholdsWithObservation("thresholds - grace periods satisfied", thresholds, observations)
// (12)更新`managerImpl`的部分成員變數的值,如`nodeConditions`、`thresholdsFirstObservedAt`、`nodeConditionsLastObservedAt`、`thresholdsMet`、`lastObservations`
// update internal state
m.Lock()
m.nodeConditions = nodeConditions
m.thresholdsFirstObservedAt = thresholdsFirstObservedAt
m.nodeConditionsLastObservedAt = nodeConditionsLastObservedAt
m.thresholdsMet = thresholds
// determine the set of thresholds whose stats have been updated since the last sync
thresholds = thresholdsUpdatedStats(thresholds, observations, m.lastObservations)
debugLogThresholdsWithObservation("thresholds - updated stats", thresholds, observations)
m.lastObservations = observations
m.Unlock()
// (13)判斷`LocalStorageCapacityIsolation`即localStorage驅逐的featuregate是否開啟,是則先呼叫`m.localStorageEviction`處理localstorage驅逐,如果返回驅逐的pod列表不為空,則證明是localStorage觸發的驅逐,且已經處理完畢,直接return
// evict pods if there is a resource usage violation from local volume temporary storage
// If eviction happens in localStorageEviction function, skip the rest of eviction action
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.LocalStorageCapacityIsolation) {
if evictedPods := m.localStorageEviction(summary, activePods); len(evictedPods) > 0 {
return evictedPods
}
}
// (14)判斷即將觸發驅逐的`thresholds`長度是否為0,是則代表沒有觸發驅逐,不需要執行驅逐邏輯,直接return
if len(thresholds) == 0 {
klog.V(3).Infof("eviction manager: no resources are starved")
return nil
}
// (15)呼叫`sort.Sort(byEvictionPriority(thresholds))`,給`thresholds`排序,將記憶體排在所有其他資源訊號之前,並將沒有資源可回收的閾值排在最後
// rank the thresholds by eviction priority
sort.Sort(byEvictionPriority(thresholds))
// (16)根據排序結果,呼叫`getReclaimableThreshold`,遍歷`thresholds`,從中獲取第一個可以被回收的`threshold`,返回`thresholdToReclaim`
thresholdToReclaim, resourceToReclaim, foundAny := getReclaimableThreshold(thresholds)
if !foundAny {
return nil
}
klog.Warningf("eviction manager: attempting to reclaim %v", resourceToReclaim)
// record an event about the resources we are now attempting to reclaim via eviction
m.recorder.Eventf(m.nodeRef, v1.EventTypeWarning, "EvictionThresholdMet", "Attempting to reclaim %s", resourceToReclaim)
// (17)呼叫`m.reclaimNodeLevelResources`,回收上面獲取到的節點級的資源`thresholdToReclaim`,如果回收的資源足夠,則直接return,不需要往下執行驅逐pod的邏輯
// check if there are node-level resources we can reclaim to reduce pressure before evicting end-user pods.
if m.reclaimNodeLevelResources(thresholdToReclaim.Signal, resourceToReclaim) {
klog.Infof("eviction manager: able to reduce %v pressure without evicting pods.", resourceToReclaim)
return nil
}
klog.Infof("eviction manager: must evict pod(s) to reclaim %v", resourceToReclaim)
// (18)呼叫`m.signalToRankFunc[thresholdToReclaim.Signal]`,獲取對應驅逐訊號的pod排序函數
// rank the pods for eviction
rank, ok := m.signalToRankFunc[thresholdToReclaim.Signal]
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("eviction manager: no ranking function for signal %s", thresholdToReclaim.Signal)
return nil
}
// (19)判斷`activePods`長度是否為0,是則直接return,沒有可被驅逐的pod,無法執行驅逐邏輯
// the only candidates viable for eviction are those pods that had anything running.
if len(activePods) == 0 {
klog.Errorf("eviction manager: eviction thresholds have been met, but no pods are active to evict")
return nil
}
// (20)呼叫`rank(activePods, statsFunc)`,根據之前獲取到的pod排序演演算法,給pod列表進行排序,再次得到`activePods`,用於後面驅逐pod
// rank the running pods for eviction for the specified resource
rank(activePods, statsFunc)
klog.Infof("eviction manager: pods ranked for eviction: %s", format.Pods(activePods))
//record age of metrics for met thresholds that we are using for evictions.
for _, t := range thresholds {
timeObserved := observations[t.Signal].time
if !timeObserved.IsZero() {
metrics.EvictionStatsAge.WithLabelValues(string(t.Signal)).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(timeObserved.Time))
metrics.DeprecatedEvictionStatsAge.WithLabelValues(string(t.Signal)).Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(timeObserved.Time))
}
}
// (21)遍歷`activePods`列表,獲取pod的`gracePeriod`(硬驅逐為0,軟碟機逐則根據kubelet啟動引數`--eviction-max-pod-grace-period`設定值獲得),呼叫`m.evictPod`,判斷pod能否被驅逐,能則開始驅逐pod,但這裡要注意的是,每次呼叫`m.synchronize`方法,最多隻驅逐一個pod,驅逐成功一個pod則直接return
// we kill at most a single pod during each eviction interval
for i := range activePods {
pod := activePods[i]
gracePeriodOverride := int64(0)
if !isHardEvictionThreshold(thresholdToReclaim) {
gracePeriodOverride = m.config.MaxPodGracePeriodSeconds
}
// 呼叫`evictionMessage`函數,構造驅逐message,後續更新到pod的event和status中,用於說明為什麼發生驅逐
message, annotations := evictionMessage(resourceToReclaim, pod, statsFunc)
if m.evictPod(pod, gracePeriodOverride, message, annotations) {
metrics.Evictions.WithLabelValues(string(thresholdToReclaim.Signal)).Inc()
return []*v1.Pod{pod}
}
}
klog.Infof("eviction manager: unable to evict any pods from the node")
return nil
}
2.1.1 m.config.Thresholds
m.config.Thresholds屬性儲存著設定的驅逐策略資訊,在kubelet初始化的時候呼叫eviction.ParseThresholdConfig函數,根據函數返回被賦值;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/types.go
type Config struct {
...
Thresholds []evictionapi.Threshold
...
}
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
func NewMainKubelet(...) {
...
thresholds, err := eviction.ParseThresholdConfig(enforceNodeAllocatable, kubeCfg.EvictionHard, kubeCfg.EvictionSoft, kubeCfg.EvictionSoftGracePeriod, kubeCfg.EvictionMinimumReclaim)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
evictionConfig := eviction.Config{
PressureTransitionPeriod: kubeCfg.EvictionPressureTransitionPeriod.Duration,
MaxPodGracePeriodSeconds: int64(kubeCfg.EvictionMaxPodGracePeriod),
Thresholds: thresholds,
KernelMemcgNotification: experimentalKernelMemcgNotification,
PodCgroupRoot: kubeDeps.ContainerManager.GetPodCgroupRoot(),
}
...
}
呼叫eviction.ParseThresholdConfig函數時的入參kubeCfg.EvictionHard、kubeCfg.EvictionSoft、kubeCfg.EvictionSoftGracePeriod、kubeCfg.EvictionMinimumReclaim等值都來源於kubelet的啟動引數設定;
// cmd/kubelet/app/options/options.go
func AddKubeletConfigFlags(mainfs *pflag.FlagSet, c *kubeletconfig.KubeletConfiguration) {
...
fs.Var(cliflag.NewLangleSeparatedMapStringString(&c.EvictionHard), "eviction-hard", "A set of eviction thresholds (e.g. memory.available<1Gi) that if met would trigger a pod eviction.")
fs.Var(cliflag.NewLangleSeparatedMapStringString(&c.EvictionSoft), "eviction-soft", "A set of eviction thresholds (e.g. memory.available<1.5Gi) that if met over a corresponding grace period would trigger a pod eviction.")
fs.Var(cliflag.NewMapStringString(&c.EvictionSoftGracePeriod), "eviction-soft-grace-period", "A set of eviction grace periods (e.g. memory.available=1m30s) that correspond to how long a soft eviction threshold must hold before triggering a pod eviction.")
fs.Var(cliflag.NewMapStringString(&c.EvictionMinimumReclaim), "eviction-minimum-reclaim", "A set of minimum reclaims (e.g. imagefs.available=2Gi) that describes the minimum amount of resource the kubelet will reclaim when performing a pod eviction if that resource is under pressure.")
...
}
eviction.ParseThresholdConfig
eviction.ParseThresholdConfig函數中對軟碟機逐、硬驅逐相關的設定值進行處理並最終合併返回儲存著驅逐策略資訊的[]evictionapi.Threshold結構體;
從方法中也可以看到,軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中的每個驅逐訊號,都會生成一個evictionapi.Threshold,所以最終方法返回是[]evictionapi.Threshold;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/helpers.go
func ParseThresholdConfig(allocatableConfig []string, evictionHard, evictionSoft, evictionSoftGracePeriod, evictionMinimumReclaim map[string]string) ([]evictionapi.Threshold, error) {
results := []evictionapi.Threshold{}
hardThresholds, err := parseThresholdStatements(evictionHard)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
results = append(results, hardThresholds...)
softThresholds, err := parseThresholdStatements(evictionSoft)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
gracePeriods, err := parseGracePeriods(evictionSoftGracePeriod)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
minReclaims, err := parseMinimumReclaims(evictionMinimumReclaim)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
for i := range softThresholds {
signal := softThresholds[i].Signal
period, found := gracePeriods[signal]
if !found {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("grace period must be specified for the soft eviction threshold %v", signal)
}
softThresholds[i].GracePeriod = period
}
results = append(results, softThresholds...)
for i := range results {
if minReclaim, ok := minReclaims[results[i].Signal]; ok {
results[i].MinReclaim = &minReclaim
}
}
for _, key := range allocatableConfig {
if key == kubetypes.NodeAllocatableEnforcementKey {
results = addAllocatableThresholds(results)
break
}
}
return results, nil
}
2.1.2 buildSignalToRankFunc
buildSignalToRankFunc函數返回map[evictionapi.Signal]rankFunc,其代表了軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號所對應的排序函數,排序函數用於計算被驅逐pod的順序;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/helpers.go
func buildSignalToRankFunc(withImageFs bool) map[evictionapi.Signal]rankFunc {
signalToRankFunc := map[evictionapi.Signal]rankFunc{
evictionapi.SignalMemoryAvailable: rankMemoryPressure,
evictionapi.SignalAllocatableMemoryAvailable: rankMemoryPressure,
evictionapi.SignalPIDAvailable: rankPIDPressure,
}
// usage of an imagefs is optional
if withImageFs {
// with an imagefs, nodefs pod rank func for eviction only includes logs and local volumes
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsAvailable] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsLogs, fsStatsLocalVolumeSource}, v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage)
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsInodesFree] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsLogs, fsStatsLocalVolumeSource}, resourceInodes)
// with an imagefs, imagefs pod rank func for eviction only includes rootfs
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsAvailable] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsRoot}, v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage)
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsInodesFree] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsRoot}, resourceInodes)
} else {
// without an imagefs, nodefs pod rank func for eviction looks at all fs stats.
// since imagefs and nodefs share a common device, they share common ranking functions.
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsAvailable] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsRoot, fsStatsLogs, fsStatsLocalVolumeSource}, v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage)
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsInodesFree] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsRoot, fsStatsLogs, fsStatsLocalVolumeSource}, resourceInodes)
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsAvailable] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsRoot, fsStatsLogs, fsStatsLocalVolumeSource}, v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage)
signalToRankFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsInodesFree] = rankDiskPressureFunc([]fsStatsType{fsStatsRoot, fsStatsLogs, fsStatsLocalVolumeSource}, resourceInodes)
}
return signalToRankFunc
}
因記憶體資源緊張導致的驅逐比較常見,所以這裡對其中記憶體的pod排序函數來做一下分析;
rankMemoryPressure
可以看到記憶體資源的pod排序邏輯為:
(1)先根據pod的記憶體使用量是否超過記憶體request排序,超過的排在前面;
(2)再根據pod的priority值大小排序,值小的排在前面;
(3)最後根據pod記憶體request值減去pod的記憶體使用量的值,得到值小的排在前面;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/helpers.go
func rankMemoryPressure(pods []*v1.Pod, stats statsFunc) {
orderedBy(exceedMemoryRequests(stats), priority, memory(stats)).Sort(pods)
}
從這個排序函數也可以看出,當因為宿主記憶體資源緊張發生驅逐時,什麼樣的pod會最先被驅逐;
關於pod的priority詳細介紹,可以檢視官方檔案:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/pod-priority-preemption/
2.1.3 buildSignalToNodeReclaimFuncs
buildSignalToNodeReclaimFuncs用於構建節點資源回收函數,回收函數用於後續在執行驅逐pod之前,先呼叫節點資源回收函數來回收資源,如果回收的資源足夠,則不用走驅逐邏輯;
可以看到只有nodefs.available、nodefs.inodesfree、imagefs.available、imagefs.inodesfree四個驅逐訊號有回收函數,其餘驅逐訊號均沒有;且當有專門的imageFs時,nodefs.available、nodefs.inodesfree也不會有回收函數;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/helpers.go
func buildSignalToNodeReclaimFuncs(imageGC ImageGC, containerGC ContainerGC, withImageFs bool) map[evictionapi.Signal]nodeReclaimFuncs {
signalToReclaimFunc := map[evictionapi.Signal]nodeReclaimFuncs{}
// usage of an imagefs is optional
if withImageFs {
// with an imagefs, nodefs pressure should just delete logs
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsAvailable] = nodeReclaimFuncs{}
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsInodesFree] = nodeReclaimFuncs{}
// with an imagefs, imagefs pressure should delete unused images
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsAvailable] = nodeReclaimFuncs{containerGC.DeleteAllUnusedContainers, imageGC.DeleteUnusedImages}
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsInodesFree] = nodeReclaimFuncs{containerGC.DeleteAllUnusedContainers, imageGC.DeleteUnusedImages}
} else {
// without an imagefs, nodefs pressure should delete logs, and unused images
// since imagefs and nodefs share a common device, they share common reclaim functions
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsAvailable] = nodeReclaimFuncs{containerGC.DeleteAllUnusedContainers, imageGC.DeleteUnusedImages}
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsInodesFree] = nodeReclaimFuncs{containerGC.DeleteAllUnusedContainers, imageGC.DeleteUnusedImages}
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsAvailable] = nodeReclaimFuncs{containerGC.DeleteAllUnusedContainers, imageGC.DeleteUnusedImages}
signalToReclaimFunc[evictionapi.SignalImageFsInodesFree] = nodeReclaimFuncs{containerGC.DeleteAllUnusedContainers, imageGC.DeleteUnusedImages}
}
return signalToReclaimFunc
}
2.1.4 kl.GetActivePods
kl.GetActivePods方法用於獲取能被驅逐的pod列表,過濾掉以下情形的pod之後,返回的pod列表即為能被驅逐的pod列表:
(1)failed狀態;
(2)succeeded狀態;
(3)pod的DeletionTimestamp不為空,且notRunning函數返回true;
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet_pods.go
func (kl *Kubelet) GetActivePods() []*v1.Pod {
allPods := kl.podManager.GetPods()
activePods := kl.filterOutTerminatedPods(allPods)
return activePods
}
func (kl *Kubelet) filterOutTerminatedPods(pods []*v1.Pod) []*v1.Pod {
var filteredPods []*v1.Pod
for _, p := range pods {
if kl.podIsTerminated(p) {
continue
}
filteredPods = append(filteredPods, p)
}
return filteredPods
}
func (kl *Kubelet) podIsTerminated(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
// Check the cached pod status which was set after the last sync.
status, ok := kl.statusManager.GetPodStatus(pod.UID)
if !ok {
// If there is no cached status, use the status from the
// apiserver. This is useful if kubelet has recently been
// restarted.
status = pod.Status
}
return status.Phase == v1.PodFailed || status.Phase == v1.PodSucceeded || (pod.DeletionTimestamp != nil && notRunning(status.ContainerStatuses))
}
func notRunning(statuses []v1.ContainerStatus) bool {
for _, status := range statuses {
if status.State.Terminated == nil && status.State.Waiting == nil {
return false
}
}
return true
}
2.1.5 m.summaryProvider.Get
m.summaryProvider.Get方法從各個途徑獲取各種統計資訊,然後組裝並返回,各種統計資訊如節點上各種資源的總量以及使用量情況、容器的資源宣告及使用量情況等;
(1)sp.provider.GetNode(),最終是從client-go informer的本地快取中獲取node物件;
(2)sp.provider.GetNodeConfig(),最終是從container_manager中獲取NodeConfig結構體;
(3)sp.provider.GetCgroupStats(),從cadvisor中獲取根目錄「/」下的cgroup的統計資訊;
(4)sp.provider.RootFsStats(),從cadvisor中獲取root檔案系統的統計資訊;
(5)sp.provider.ImageFsStats(),獲取image檔案系統的統計資訊,其有兩個實現,一個是criStatsProvider,另一個是cadvisorStatsProvider;
(6)sp.provider.ListPodStatsAndUpdateCPUNanoCoreUsage(),更新所有容器的cpu usage資訊並獲取所有pod的啟動時間、容器狀態、cpu使用量、記憶體使用量等統計資訊,其有兩個實現,一個是criStatsProvider,另一個是cadvisorStatsProvider;
(7)sp.provider.ListPodStats(),獲取所有pod的啟動時間、容器狀態、cpu使用量、記憶體使用量等統計資訊,其有兩個實現,一個是criStatsProvider,另一個是cadvisorStatsProvider;
(8)sp.provider.RlimitStats(),獲取pid限制資訊;
// pkg/kubelet/server/stats/summary.go
func (sp *summaryProviderImpl) Get(updateStats bool) (*statsapi.Summary, error) {
// TODO(timstclair): Consider returning a best-effort response if any of
// the following errors occur.
// 從client-go informer的本地快取中獲取node物件
node, err := sp.provider.GetNode()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get node info: %v", err)
}
// 從container_manager中獲取NodeConfig結構體
nodeConfig := sp.provider.GetNodeConfig()
// 從cadvisor中獲取根目錄「/」下的cgroup的統計資訊
rootStats, networkStats, err := sp.provider.GetCgroupStats("/", updateStats)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get root cgroup stats: %v", err)
}
// 從cadvisor中獲取root檔案系統的統計資訊
rootFsStats, err := sp.provider.RootFsStats()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get rootFs stats: %v", err)
}
// 獲取image檔案系統的統計資訊
imageFsStats, err := sp.provider.ImageFsStats()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get imageFs stats: %v", err)
}
var podStats []statsapi.PodStats
if updateStats {
// 更新所有容器的cpu usage資訊並獲取所有pod的啟動時間、容器狀態、cpu使用量、記憶體使用量等統計資訊
podStats, err = sp.provider.ListPodStatsAndUpdateCPUNanoCoreUsage()
} else {
// 獲取所有pod的啟動時間、容器狀態、cpu使用量、記憶體使用量等統計資訊
podStats, err = sp.provider.ListPodStats()
}
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to list pod stats: %v", err)
}
// 獲取pid限制資訊
rlimit, err := sp.provider.RlimitStats()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get rlimit stats: %v", err)
}
// 組裝以上的統計資訊並返回
nodeStats := statsapi.NodeStats{
NodeName: node.Name,
CPU: rootStats.CPU,
Memory: rootStats.Memory,
Network: networkStats,
StartTime: sp.systemBootTime,
Fs: rootFsStats,
Runtime: &statsapi.RuntimeStats{ImageFs: imageFsStats},
Rlimit: rlimit,
SystemContainers: sp.GetSystemContainersStats(nodeConfig, podStats, updateStats),
}
summary := statsapi.Summary{
Node: nodeStats,
Pods: podStats,
}
return &summary, nil
}
2.1.6 byEvictionPriority
該排序方法將記憶體排在所有其他資源訊號之前,並將沒有資源可回收的閾值排在最後;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/helpers.go
func (a byEvictionPriority) Less(i, j int) bool {
_, jSignalHasResource := signalToResource[a[j].Signal]
return a[i].Signal == evictionapi.SignalMemoryAvailable || a[i].Signal == evictionapi.SignalAllocatableMemoryAvailable || !jSignalHasResource
}
2.1.7 getReclaimableThreshold
getReclaimableThreshold函數遍歷thresholds,從中獲取第一個可以被回收的threshold並返回;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/helpers.go
func getReclaimableThreshold(thresholds []evictionapi.Threshold) (evictionapi.Threshold, v1.ResourceName, bool) {
for _, thresholdToReclaim := range thresholds {
if resourceToReclaim, ok := signalToResource[thresholdToReclaim.Signal]; ok {
return thresholdToReclaim, resourceToReclaim, true
}
klog.V(3).Infof("eviction manager: threshold %s was crossed, but reclaim is not implemented for this threshold.", thresholdToReclaim.Signal)
}
return evictionapi.Threshold{}, "", false
}
func init() {
...
signalToResource = map[evictionapi.Signal]v1.ResourceName{}
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalMemoryAvailable] = v1.ResourceMemory
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalAllocatableMemoryAvailable] = v1.ResourceMemory
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalImageFsAvailable] = v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalImageFsInodesFree] = resourceInodes
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsAvailable] = v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalNodeFsInodesFree] = resourceInodes
signalToResource[evictionapi.SignalPIDAvailable] = resourcePids
}
2.1.8 m.reclaimNodeLevelResources
m.reclaimNodeLevelResources方法用於提前回收節點資源,並判斷是否需要繼續走驅逐pod的邏輯,方法返回true則代表回收節點資源已足夠,無需再執行驅逐pod邏輯,返回false則代表需要繼續執行驅逐pod的邏輯;
方法主要邏輯為:
(1)根據驅逐訊號,獲取對應的節點資源回收函數,遍歷並呼叫回收函數來回收資源;
(2)如果回收函數為空,直接return false;
(3)呼叫m.summaryProvider.Get獲取實時的資源統計資訊;
(4)判斷呼叫回收函數回收節點資源過後,現在的各個資源使用情況是否還是超過設定的各個驅逐閾值,沒有超過則返回true,否則返回false;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
func (m *managerImpl) reclaimNodeLevelResources(signalToReclaim evictionapi.Signal, resourceToReclaim v1.ResourceName) bool {
nodeReclaimFuncs := m.signalToNodeReclaimFuncs[signalToReclaim]
for _, nodeReclaimFunc := range nodeReclaimFuncs {
// attempt to reclaim the pressured resource.
if err := nodeReclaimFunc(); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("eviction manager: unexpected error when attempting to reduce %v pressure: %v", resourceToReclaim, err)
}
}
if len(nodeReclaimFuncs) > 0 {
summary, err := m.summaryProvider.Get(true)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("eviction manager: failed to get summary stats after resource reclaim: %v", err)
return false
}
// make observations and get a function to derive pod usage stats relative to those observations.
observations, _ := makeSignalObservations(summary)
debugLogObservations("observations after resource reclaim", observations)
// determine the set of thresholds met independent of grace period
thresholds := thresholdsMet(m.config.Thresholds, observations, false)
debugLogThresholdsWithObservation("thresholds after resource reclaim - ignoring grace period", thresholds, observations)
if len(thresholds) == 0 {
return true
}
}
return false
}
2.1.9 m.evictPod
m.evictPod方法主要邏輯:
(1)呼叫kubelettypes.IsCriticalPod,判斷是否是critical pod,是則返回false,說明該pod不能是被驅逐的物件;
(2)呼叫m.recorder.AnnotatedEventf,上報驅逐event;
(3)呼叫m.killPodFunc,驅逐pod;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
func (m *managerImpl) evictPod(pod *v1.Pod, gracePeriodOverride int64, evictMsg string, annotations map[string]string) bool {
// If the pod is marked as critical and static, and support for critical pod annotations is enabled,
// do not evict such pods. Static pods are not re-admitted after evictions.
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/40573 has more details.
if kubelettypes.IsCriticalPod(pod) {
klog.Errorf("eviction manager: cannot evict a critical pod %s", format.Pod(pod))
return false
}
status := v1.PodStatus{
Phase: v1.PodFailed,
Message: evictMsg,
Reason: Reason,
}
// record that we are evicting the pod
m.recorder.AnnotatedEventf(pod, annotations, v1.EventTypeWarning, Reason, evictMsg)
// this is a blocking call and should only return when the pod and its containers are killed.
err := m.killPodFunc(pod, status, &gracePeriodOverride)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("eviction manager: pod %s failed to evict %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
} else {
klog.Infof("eviction manager: pod %s is evicted successfully", format.Pod(pod))
}
return true
}
IsCriticalPod
IsCriticalPod函數判斷一個pod是否是critical pod;
是static pod,是mirror pod,pod.Spec.Priority屬性不為空且其值大於等於2000000000,三個條件均符合則方法返回true,否則返回false;
// pkg/kubelet/types/pod_update.go
func IsCriticalPod(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
if IsStaticPod(pod) {
return true
}
if IsMirrorPod(pod) {
return true
}
if pod.Spec.Priority != nil && IsCriticalPodBasedOnPriority(*pod.Spec.Priority) {
return true
}
return false
}
IsStaticPod
看到IsStaticPod函數,可以知道是否是static pod是根據pod annotation中是否有key:"kubernetes.io/config.source",且其值為"api",滿足條件則為static pod;
// pkg/kubelet/types/pod_update.go
const (
ConfigSourceAnnotationKey = "kubernetes.io/config.source"
ApiserverSource = "api"
)
func IsStaticPod(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
source, err := GetPodSource(pod)
return err == nil && source != ApiserverSource
}
func GetPodSource(pod *v1.Pod) (string, error) {
if pod.Annotations != nil {
if source, ok := pod.Annotations[ConfigSourceAnnotationKey]; ok {
return source, nil
}
}
return "", fmt.Errorf("cannot get source of pod %q", pod.UID)
}
IsCriticalPodBasedOnPriority
// pkg/kubelet/types/pod_update.go
func IsCriticalPodBasedOnPriority(priority int32) bool {
return priority >= scheduling.SystemCriticalPriority
}
// pkg/apis/scheduling/types.go
const (
HighestUserDefinablePriority = int32(1000000000)
SystemCriticalPriority = 2 * HighestUserDefinablePriority
)
2.1.10 m.killPodFunc
m.killPodFunc主要是停止pod中的所有業務容器以及sandbox容器;
前面的分析講過,在eviction_manager初始化的時候,m.killPodFunc被賦值為pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go-killPodNow()函數,所以接下來直接看到killPodNow函數的分析;
killPodNow函數主要邏輯:獲取gracePeriod,拼湊UpdatePodOptions,並呼叫podWorkers.UpdatePod來kill Pod(這裡的kill pod最終只是停止了pod中的所有業務容器以及sandbox容器,沒有做任何刪除操作);
// pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go
func killPodNow(podWorkers PodWorkers, recorder record.EventRecorder) eviction.KillPodFunc {
return func(pod *v1.Pod, status v1.PodStatus, gracePeriodOverride *int64) error {
// determine the grace period to use when killing the pod
gracePeriod := int64(0)
if gracePeriodOverride != nil {
gracePeriod = *gracePeriodOverride
} else if pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds != nil {
gracePeriod = *pod.Spec.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds
}
// we timeout and return an error if we don't get a callback within a reasonable time.
// the default timeout is relative to the grace period (we settle on 10s to wait for kubelet->runtime traffic to complete in sigkill)
timeout := int64(gracePeriod + (gracePeriod / 2))
minTimeout := int64(10)
if timeout < minTimeout {
timeout = minTimeout
}
timeoutDuration := time.Duration(timeout) * time.Second
// open a channel we block against until we get a result
type response struct {
err error
}
ch := make(chan response, 1)
podWorkers.UpdatePod(&UpdatePodOptions{
Pod: pod,
UpdateType: kubetypes.SyncPodKill,
OnCompleteFunc: func(err error) {
ch <- response{err: err}
},
KillPodOptions: &KillPodOptions{
PodStatusFunc: func(p *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus) v1.PodStatus {
return status
},
PodTerminationGracePeriodSecondsOverride: gracePeriodOverride,
},
})
// wait for either a response, or a timeout
select {
case r := <-ch:
return r.err
case <-time.After(timeoutDuration):
recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.ExceededGracePeriod, "Container runtime did not kill the pod within specified grace period.")
return fmt.Errorf("timeout waiting to kill pod")
}
}
}
podWorkers.UpdatePod方法這裡不展開分析,給出方法呼叫鏈,可自行檢視;
podWorkers.UpdatePod() --> p.managePodLoop() --> kl.syncPod() --> kl.killPod() --> kl.containerRuntime.KillPod() --> kl.containerRuntime.killContainersWithSyncResult()/kl.containerRuntime.runtimeService.StopPodSandbox()
2.2 m.waitForPodsCleanup
m.waitForPodsCleanup方法會迴圈呼叫podCleanedUpFunc,等待pod的相關資源被清理、回收(pod的所有業務容器停止並被刪除、volume被清理),清理完成後return;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
func (m *managerImpl) waitForPodsCleanup(podCleanedUpFunc PodCleanedUpFunc, pods []*v1.Pod) {
timeout := m.clock.NewTimer(podCleanupTimeout)
defer timeout.Stop()
ticker := m.clock.NewTicker(podCleanupPollFreq)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-timeout.C():
klog.Warningf("eviction manager: timed out waiting for pods %s to be cleaned up", format.Pods(pods))
return
case <-ticker.C():
for i, pod := range pods {
if !podCleanedUpFunc(pod) {
break
}
if i == len(pods)-1 {
klog.Infof("eviction manager: pods %s successfully cleaned up", format.Pods(pods))
return
}
}
}
}
}
podCleanedUpFunc
podCleanedUpFunc實際上是podResourcesAreReclaimed方法,podResourcesAreReclaimed方法呼叫了kl.PodResourcesAreReclaimed方法做進一步處理;
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet_pods.go
func (kl *Kubelet) podResourcesAreReclaimed(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
status, ok := kl.statusManager.GetPodStatus(pod.UID)
if !ok {
status = pod.Status
}
return kl.PodResourcesAreReclaimed(pod, status)
}
從PodResourcesAreReclaimed方法中可以看出,會等待pod的所有業務容器停止執行並被刪除,等待pod的volume被清理完成,等待pod的cgroup sandbox被清理完成;
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet_pods.go
func (kl *Kubelet) PodResourcesAreReclaimed(pod *v1.Pod, status v1.PodStatus) bool {
if !notRunning(status.ContainerStatuses) {
// We shouldn't delete pods that still have running containers
klog.V(3).Infof("Pod %q is terminated, but some containers are still running", format.Pod(pod))
return false
}
// pod's containers should be deleted
runtimeStatus, err := kl.podCache.Get(pod.UID)
if err != nil {
klog.V(3).Infof("Pod %q is terminated, Error getting runtimeStatus from the podCache: %s", format.Pod(pod), err)
return false
}
if len(runtimeStatus.ContainerStatuses) > 0 {
var statusStr string
for _, status := range runtimeStatus.ContainerStatuses {
statusStr += fmt.Sprintf("%+v ", *status)
}
klog.V(3).Infof("Pod %q is terminated, but some containers have not been cleaned up: %s", format.Pod(pod), statusStr)
return false
}
if kl.podVolumesExist(pod.UID) && !kl.keepTerminatedPodVolumes {
// We shouldn't delete pods whose volumes have not been cleaned up if we are not keeping terminated pod volumes
klog.V(3).Infof("Pod %q is terminated, but some volumes have not been cleaned up", format.Pod(pod))
return false
}
if kl.kubeletConfiguration.CgroupsPerQOS {
pcm := kl.containerManager.NewPodContainerManager()
if pcm.Exists(pod) {
klog.V(3).Infof("Pod %q is terminated, but pod cgroup sandbox has not been cleaned up", format.Pod(pod))
return false
}
}
return true
}
總結
kubelet節點壓力驅逐中包括了兩部分,一個是實時驅逐,一個是輪詢驅逐;
// pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go
func (m *managerImpl) Start(diskInfoProvider DiskInfoProvider, podFunc ActivePodsFunc, podCleanedUpFunc PodCleanedUpFunc, monitoringInterval time.Duration) {
thresholdHandler := func(message string) {
klog.Infof(message)
m.synchronize(diskInfoProvider, podFunc)
}
// 啟動實時驅逐
if m.config.KernelMemcgNotification {
for _, threshold := range m.config.Thresholds {
if threshold.Signal == evictionapi.SignalMemoryAvailable || threshold.Signal == evictionapi.SignalAllocatableMemoryAvailable {
notifier, err := NewMemoryThresholdNotifier(threshold, m.config.PodCgroupRoot, &CgroupNotifierFactory{}, thresholdHandler)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("eviction manager: failed to create memory threshold notifier: %v", err)
} else {
go notifier.Start()
m.thresholdNotifiers = append(m.thresholdNotifiers, notifier)
}
}
}
}
// 啟動輪詢驅逐
// start the eviction manager monitoring
go func() {
for {
if evictedPods := m.synchronize(diskInfoProvider, podFunc); evictedPods != nil {
klog.Infof("eviction manager: pods %s evicted, waiting for pod to be cleaned up", format.Pods(evictedPods))
m.waitForPodsCleanup(podCleanedUpFunc, evictedPods)
} else {
time.Sleep(monitoringInterval)
}
}
}()
}
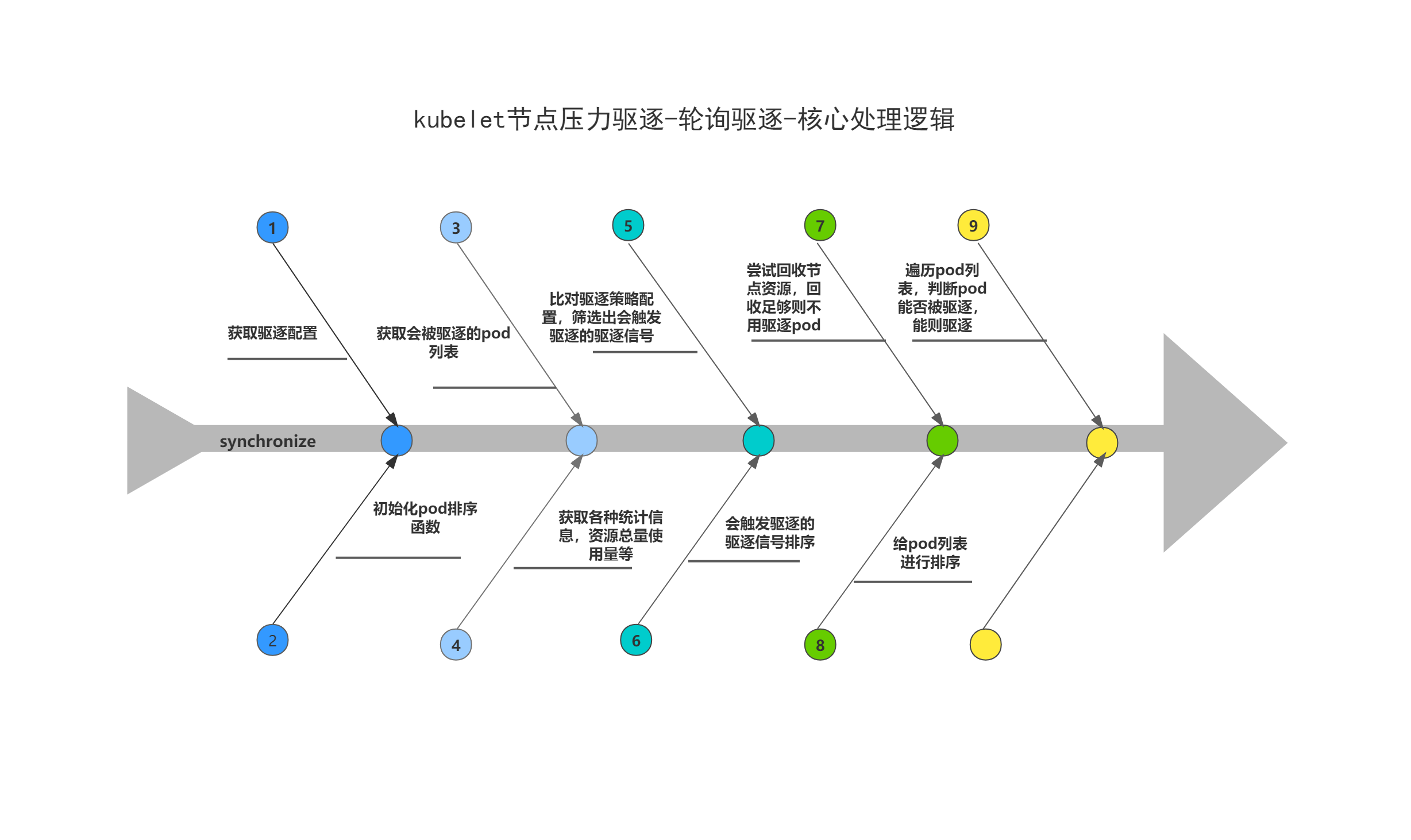
這裡主要對輪詢驅逐做一下分析總結,m.synchronize方法為驅逐核心邏輯所在;
m.synchronize方法驅逐邏輯概要總結:
(1)根據kubelet啟動引數設定,獲取驅逐策略設定;
(2)初始化軟碟機逐、硬驅逐中各個驅逐訊號的pod排序函數;
(3)獲取會被驅逐的pod列表-activePods;
(4)從cAdvisor、CRIRuntimes獲取各種統計資訊,如節點上各個資源的總量以及使用量情況、容器的資源宣告及使用量情況等;
(5)比對驅逐策略設定以及上述的各種資源統計資訊,篩選出會觸發驅逐的驅逐訊號;
(6)將上面篩選出來的驅逐訊號做排序,將記憶體驅逐訊號排在所有其他訊號之前,並將沒有資源可回收的驅逐訊號排在最後,並從排序後的結果中取出第一個驅逐訊號;
(7)呼叫m.reclaimNodeLevelResources,回收上面獲取到的驅逐訊號的節點級資源,如果回收的資源足夠,則直接return,不需要往下執行驅逐pod的邏輯;
(8)獲取上述取出的驅逐訊號對應的pod排序函數,給pod列表進行排序;
(9)遍歷排序後的pod列表,呼叫m.evictPod,判斷pod能否被驅逐,能則開始驅逐pod;
驅逐邏輯三個注意點:
(1)每次呼叫m.synchronize方法,即每次的驅逐邏輯,最多隻驅逐一個pod;
(2)如果呼叫m.synchronize方法沒有驅逐pod,則會等待10s後再進行下一次的m.synchronize方法輪詢呼叫,也就是說輪詢驅逐會有一定的時延;
(3)驅逐pod,只是將pod.status.phase值更新為Failed,並附上驅逐reason:Evicted以及觸發驅逐的詳細資訊,不會刪除pod;而pod.status.phase值被更新為Failed後,replicaset controller會再次建立出新的pod呼叫到其他節點上,達到驅逐pod的效果;