羽夏看Linux核心——引導啟動(上)
寫在前面
此係列是本人一個字一個字碼出來的,包括範例和實驗截圖。如有好的建議,歡迎反饋。碼字不易,如果本篇文章有幫助你的,如有閒錢,可以打賞支援我的創作。如想轉載,請把我的轉載資訊附在文章後面,並宣告我的個人資訊和本人部落格地址即可,但必須事先通知我。
你如果是從中間插過來看的,請仔細閱讀 羽夏看Linux系統核心——簡述 ,方便學習本教學。
Linux 0.11 介紹
Linux 0.11 寫於 1991 年年底,那時很多計算機都是通過軟碟啟動的,故該程式碼是從軟碟啟動的。目前作業系統啟動都是通過硬碟,下面我們介紹它的啟動流程,仿製的時候改為從硬碟啟動。
在 16 位元型樣下,記憶體的使用是十分有限的,我再拿之前的表格:
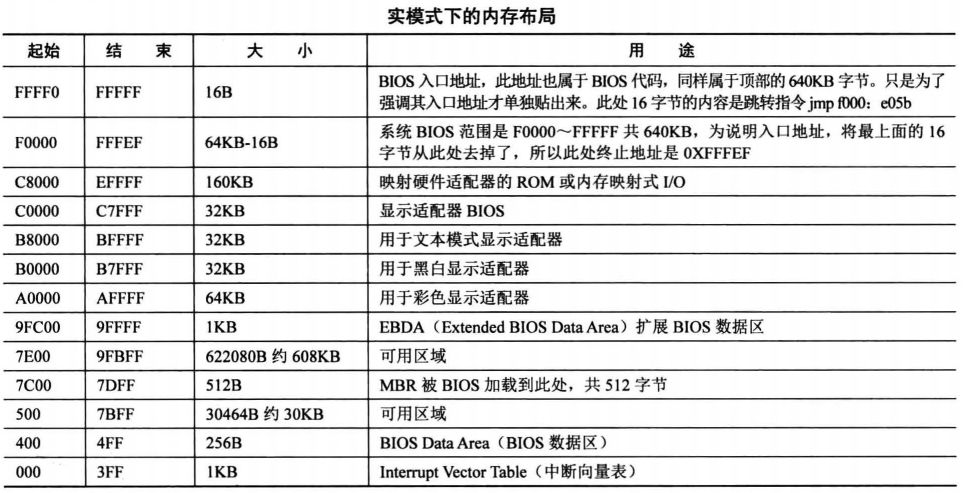
從圖中可以看出,我們可以在真真實模式下可以隨便動的記憶體區域是0x00500-0x9FBFF。注意,這裡可以隨便動是指我不影響真真實模式所用的東西的前提下可以動的區域。0x07C00-0x07DFF是BIOS把我們的第一個磁區載入到記憶體的程式碼,如果我們需要第一磁區的程式碼,這塊也不能亂動。
也就是說,在 16 位真真實模式下,我們拉起核心需要精打細算的利用好我們能夠用的記憶體,也不能在執行程式碼過程中覆蓋到我們所需的資料。說完這些,我們來看核心程式碼。
注:在之後的教學,我說核心原始碼所在目錄,我會用
linuxsrc表示,請悉知。
bootsect
學了之前的內容,我們知道BIOS會載入第一磁區的程式碼,而這個程式碼對應了linuxsrc/boot資料夾下的bootsect.s檔案,我們開啟看一下,首先看到了註釋:
! SYS_SIZE is the number of clicks (16 bytes) to be loaded.
! 0x3000 is 0x30000 bytes = 196kB, more than enough for current
! versions of linux
!
SYSSIZE = 0x3000
!
! bootsect.s (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
!
! bootsect.s is loaded at 0x7c00 by the bios-startup routines, and moves
! iself out of the way to address 0x90000, and jumps there.
!
! It then loads 'setup' directly after itself (0x90200), and the system
! at 0x10000, using BIOS interrupts.
對於as86組合語法來說,在!或者;之後的表示註釋。這段註釋告訴我們,bootsect.s會被載入到0x7c00這個地址,那這個程式碼必定在第一磁區。之後這塊程式碼會移動到0x90000地址並跳轉到那裡,然後通過BIOS中斷拉起setup到0x10000。
與此同時,為了更加直觀的學習,我們可以使用已有的映象看看情況。現在 Linux 0.11 版本很難直接編譯通過,我調了半天雖然編譯成功了,但Bochs載入不了。不過我們網上已經有對應的映象,首先給個連結:
http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/bochs/
其實這些包個包是給在 Win 上學習準備的,這對於我們在 Deepin 等 Linux 發行版上進行學習就不太方便,這個組態檔沒法直接使用,會報錯。不過沒關係,我給製作了一個完整的包,並放到我的程式碼倉庫:
- Gitee : https://gitee.com/wingsummer/linuxbochs
- Gitea : https://code.gitlink.org.cn/wingsummer/Linuxbochs
你只需要clone一下到你的學習資料夾下即可。都是學核心的同志了,git clone應該都會,這裡就不贅述了。如果要啟動虛擬機器器,只需執行startLinux.sh指令碼即可。下面我們來看看開頭的程式碼:
BOOTSEG = 0x07c0 ! original address of boot-sector
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! setup starts here
start:
mov ax,#BOOTSEG
mov ds,ax
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov cx,#256
sub si,si
sub di,di
rep
movw
jmpi go,INITSEG
BOOTSEG是0x07c0,也就是被BIOS初始載入的地址。你可能會有疑問。 被BIOS初始載入的地址不是0x7c00嗎? 是的,但是這個是被載入到段暫存器的,如果偏移是0,且被16整除,只需要把地址地板除以16就是我們想要得到的結果。
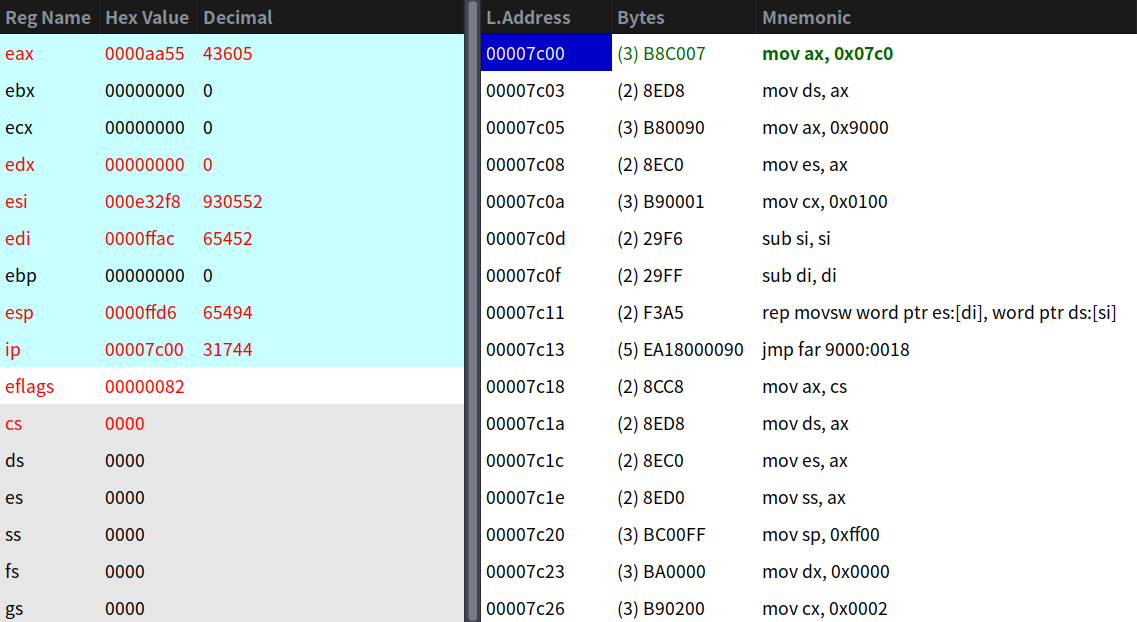
這段就是拷貝bootsect.s程式到0x90000這個地址。載入程式一共有512個位元組,由於一次移動一個字,所以給cx賦值256即可。我們可以看看Bochs的內容:
雖然有了 GUI ,但不能完全被代替,你還得需要知道一些基本的偵錯命令,這個不是本教學的重點,請自行補充。
拷貝完後,並執行跨段跳轉後的狀態:
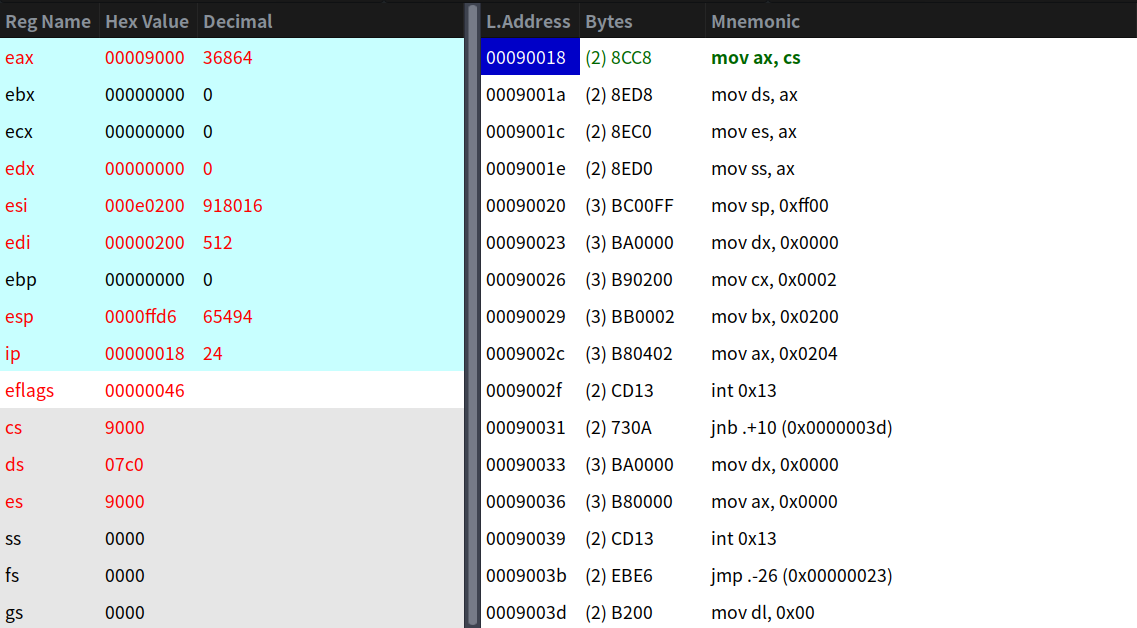
我們繼續:
go: mov ax,cs
mov ds,ax
mov es,ax
! put stack at 0x9ff00.
mov ss,ax
mov sp,#0xFF00 ! arbitrary value >>512
這塊是使用cs初始化段暫存器和棧空間,由於十分簡單就不贅述了。
! load the setup-sectors directly after the bootblock.
! Note that 'es' is already set up.
load_setup:
mov dx,#0x0000 ! drive 0, head 0
mov cx,#0x0002 ! sector 2, track 0
mov bx,#0x0200 ! address = 512, in INITSEG
mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN ! service 2, nr of sectors
int 0x13 ! read it
jnc ok_load_setup ! ok - continue
mov dx,#0x0000
mov ax,#0x0000 ! reset the diskette
int 0x13
j load_setup
0x13中斷是一個服務,用來對磁碟進行操作。我們簡單介紹一下各暫存器的功能。這塊程式碼是讀取磁區,如果使用該功能,需要AH=0x02,這也是為什麼mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN要加個0x0200。
| 暫存器 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| AL | 磁區數 |
| CH | 柱面 |
| CL | 磁區 |
| DH | 磁頭 |
| DL | 驅動器(00H - 7FH 為軟碟;80H - 0FFH 為硬碟) |
| ES:BX | 緩衝區的地址 |
既然是讀取操作,必然需要知道讀取結果。如果CF = 0,則表示成功,此時AH = 00H,AL = 傳輸的磁區數。如果失敗,AH是狀態碼。有關狀態碼這事情我就不贅述了,自己可以從網路進行查閱。
此時ES = 9000H,而讀取時BX = 0x0200,所以讀取後被放到0x90200這個地址。如果讀取成功,就會跳轉到ok_load_setup這個標籤,失敗重置磁碟狀態(AH = 0呼叫),重試直到成功。執行完int 0x13指令後,我們看看結果:
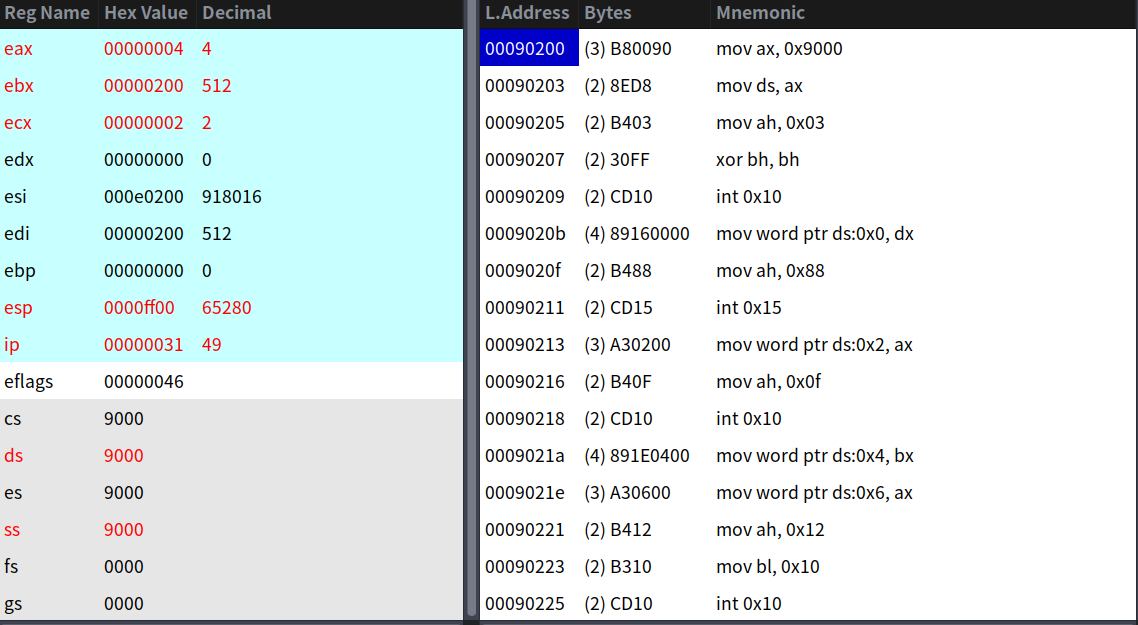
然後我們看看setup.s開頭幾行組合:
mov ax,#INITSEG ! this is done in bootsect already, but...
mov ds,ax
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos
xor bh,bh
int 0x10 ! save it in known place, con_init fetches
mov [0],dx ! it from 0x90000.
可以看到完全一致。我們接著繼續:
ok_load_setup:
! Get disk drive parameters, specifically nr of sectors/track
mov dl,#0x00
mov ax,#0x0800 ! AH=8 is get drive parameters
int 0x13
mov ch,#0x00
seg cs
mov sectors,cx
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
! Print some inane message
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#24
mov bx,#0x0007 ! page 0, attribute 7 (normal)
mov bp,#msg1
mov ax,#0x1301 ! write string, move cursor
int 0x10
當AH = 0x08時,呼叫int 0x13是獲取磁碟大小資訊。其中DL為驅動器,如果成功CF = 0,BL會獲得1-4的數值,為磁碟大小,含義如下:
| BL 值 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 360 KB |
| 2 | 1.2 MB |
| 3 | 720 KB |
| 4 | 1.44 MB |
與此同時,CH代表柱面數的低八位;CL的高兩位代表柱面數的高兩位,CL剩餘的位代表磁區數;DH代表柱頭數;DL代表驅動器數;ES:DI指向的是磁碟驅動器參數列地址。
在呼叫完int 0x13之後,將區塊的磁區數目放到了sectors中。緊接著後面我們又遇到了一箇中斷int 0x10,這個是用於顯示的服務,可以往螢幕上寫字串操作。將msg1寫到螢幕上,我們來看看這是什麼:
msg1:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Loading system ..."
.byte 13,10,13,10
確認鍵的ASCII是13,換行鍵的ASCII是10,如果組合起來就是回車換行,就是C/C++的\n。
接下來我們繼續下一部分程式碼:
! ok, we've written the message, now
! we want to load the system (at 0x10000)
mov ax,#SYSSEG
mov es,ax ! segment of 0x010000
call read_it
call kill_motor
這部分就是載入system模組了,system模組就是核心模組,包含庫模組lib、記憶體管理模組mm、核心模組kernel、main.c和head.s程式,後面將會詳細介紹。read_it就是讀取函數,將模組讀取到0x010000這個地址。kill_motor函數是關閉驅動器馬達,以知道驅動器狀態。為什麼可以看註釋:
/*
* This procedure turns off the floppy drive motor, so
* that we enter the kernel in a known state, and
* don't have to worry about it later.
*/
kill_motor:
我們來粗略簡單看看read_it函數:
read_it:
mov ax,es
test ax,#0x0fff
die:· jne die ! es must be at 64kB boundary
xor bx,bx ! bx is starting address within segment
rp_read:
mov ax,es
cmp ax,#ENDSEG ! have we loaded all yet?
jb ok1_read
ret
ok1_read:
seg cs
mov ax,sectors
sub ax,sread
mov cx,ax
shl cx,#9
add cx,bx
jnc ok2_read
je ok2_read
xor ax,ax
sub ax,bx
shr ax,#9
ok2_read:
call read_track
mov cx,ax
add ax,sread
seg cs
cmp ax,sectors
jne ok3_read
mov ax,#1
sub ax,head
jne ok4_read
inc track
ok4_read:
mov head,ax
xor ax,ax
ok3_read:
mov sread,ax
shl cx,#9
add bx,cx
jnc rp_read
mov ax,es
add ax,#0x1000
mov es,ax
xor bx,bx
jmp rp_read
read_track:
push ax
push bx
push cx
push dx
mov dx,track
mov cx,sread
inc cx
mov ch,dl
mov dx,head
mov dh,dl
mov dl,#0
and dx,#0x0100
mov ah,#2
int 0x13
jc bad_rt
pop dx
pop cx
pop bx
pop ax
ret
這些都是對磁碟進行大量讀寫的操作,以0x100位元組作為塊一次一次讀取。我們來看一下執行結果:
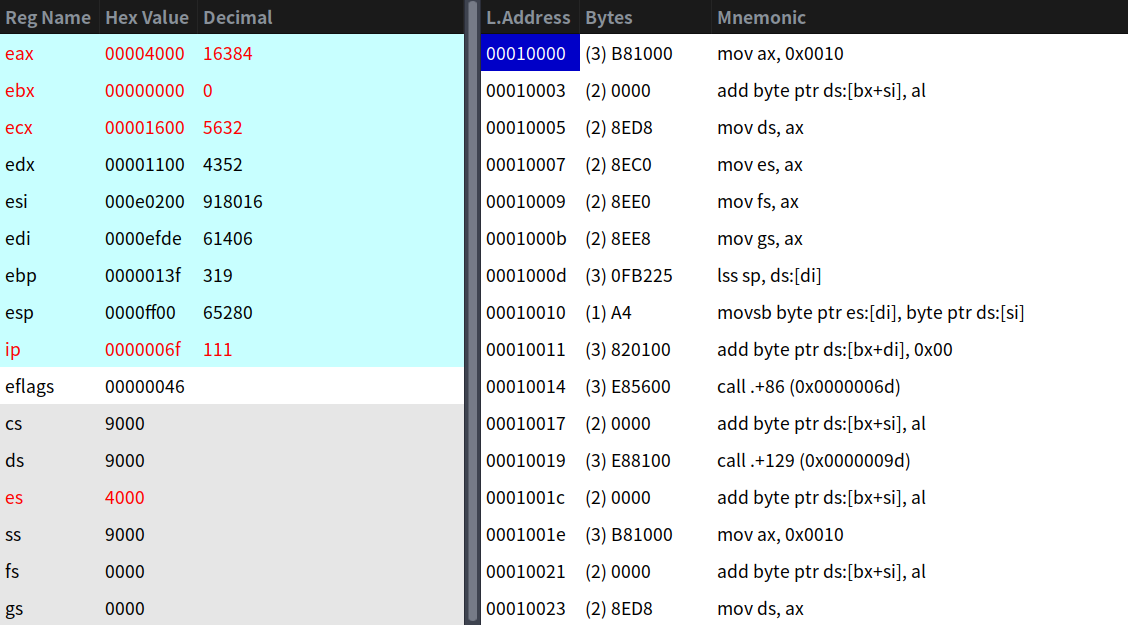
剩下的最後一塊bootsect.s程式:
! After that we check which root-device to use. If the device is
! defined (!= 0), nothing is done and the given device is used.
! Otherwise, either /dev/PS0 (2,28) or /dev/at0 (2,8), depending
! on the number of sectors that the BIOS reports currently.
seg cs
mov ax,root_dev
cmp ax,#0
jne root_defined
seg cs
mov bx,sectors
mov ax,#0x0208 ! /dev/ps0 - 1.2Mb
cmp bx,#15
je root_defined
mov ax,#0x021c ! /dev/PS0 - 1.44Mb
cmp bx,#18
je root_defined
undef_root:
jmp undef_root
root_defined:
seg cs
mov root_dev,ax
! after that (everyting loaded), we jump to
! the setup-routine loaded directly after
! the bootblock:
jmpi 0,SETUPSEG
root_dev是一個變數,它指向一個字大小的宏ROOT_DEV,它的值為0x306。
root_dev:
.word ROOT_DEV
為什麼是這個值呢?如果該值為0,根檔案系統裝置與引導使用同樣的軟碟機裝置;如果是0x301,則為第一個硬碟的第一個分割區上,這個被稱為裝置號。裝置號 = 主裝置號 * 256 + 次裝置號,舉個例子:
- 0x300 - /dev/hd0 代表第一個硬碟
- 0x301 - /dev/hd1 代表第一個硬碟的第一個分割區
- ……
- 0x304 - /dev/hd4 代表第一個硬碟的第四個分割區
- 0x305 - /dev/hd5 代表第二個硬碟
- ……
於是該核心使用的是第二個硬碟的第一個分割區,作為根檔案系統裝置。
接下來兩個cmp可能看不懂,咱們給個解釋:sectors是我們之前儲存的每磁軌磁區數目,如果是 15 ,那麼就是 1.2 MB 的驅動器;如果是 18 ,那麼就是 1.44 MB 的,也就是引導驅動器的裝置號。如果正常找到,將會執行jmpi 0,SETUPSEG,該部分程式結束;否則,直接死迴圈。
setup
下面開始setup.s程式碼的講解,這個程式十分重要,它是作業系統載入程式。先看開頭:
! ok, the read went well so we get current cursor position and save it for
! posterity.
mov ax,#INITSEG ! this is done in bootsect already, but...
mov ds,ax
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos
xor bh,bh
int 0x10 ! save it in known place, con_init fetches
mov [0],dx ! it from 0x90000.
! Get memory size (extended mem, kB)
mov ah,#0x88
int 0x15
mov [2],ax
! Get video-card data:
mov ah,#0x0f
int 0x10
mov [4],bx ! bh = display page
mov [6],ax ! al = video mode, ah = window width
! check for EGA/VGA and some config parameters
mov ah,#0x12
mov bl,#0x10
int 0x10
mov [8],ax
mov [10],bx
mov [12],cx
! Get hd0 data
mov ax,#0x0000
mov ds,ax
lds si,[4*0x41]
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0080
mov cx,#0x10
rep
movsb
! Get hd1 data
mov ax,#0x0000
mov ds,ax
lds si,[4*0x46]
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0090
mov cx,#0x10
rep
movsb
! Check that there IS a hd1 :-)
mov ax,#0x01500
mov dl,#0x81
int 0x13
jc no_disk1
cmp ah,#3
je is_disk1
no_disk1:
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov di,#0x0090
mov cx,#0x10
mov ax,#0x00
rep
stosb
這塊程式碼首先獲取了遊標位置,然後作為一個字存到了0x90000。同理,獲取了擴充套件記憶體的大小、一些顯示類的資訊和硬碟參數列。
硬碟參數列是什麼?在PC機中BIOS設定的中斷向量表中int 0x41的中斷向量位置存放的並不是中斷程式的地址,而是第一個硬碟的基本參數列。對於BIOS來說,這裡存放著硬碟參數列陣列的首地址0xFE401。第二個硬碟的基本參數列入口地址存於int 0x46中斷向量位置處。每個硬碟參數列有16個位元組大小。這些是硬體的相關知識,瞭解明白即可。
接下來就是讓你激動的時刻,開始進入保護模式。先看第一部分程式碼:
! now we want to move to protected mode ...
cli ! no interrupts allowed !
! first we move the system to it's rightful place
mov ax,#0x0000
cld ! 'direction'=0, movs moves forward
do_move:
mov es,ax ! destination segment
add ax,#0x1000
cmp ax,#0x9000
jz end_move
mov ds,ax ! source segment
sub di,di
sub si,si
mov cx,#0x8000
rep
movsw
jmp do_move
end_move:
首先使用cli指令遮蔽中斷,準備開始乾坤大挪移,將system模組移動到想要的位置(記憶體0地址處)。
但是0地址附近正是BIOS相關資料區,我們再把上面的表格拿下來:

也就是說,原來的BIOS的中斷和資料被覆蓋了,也就是被捨棄掉了。由於當時system假設模組的最大長度不會超過0x80000,也就是512 KB,即末尾不會超過0x90000這個地址。
移動完後,就開始進入保護模式的準備工作了。
在Intel的保護模式下,段描述符存在於GDT和IDT表中(LDT不使用)。段暫存器需要GDT表,而呼叫中斷需要IDT表,所以我們需要設定這兩張表:
! then we load the segment descriptors
end_move:
mov ax,#SETUPSEG ! right, forgot this at first. didn't work :-)
mov ds,ax
lidt idt_48 ! load idt with 0,0
lgdt gdt_48 ! load gdt with whatever appropriate
我們來看看這所謂的IDT和GDT表:
idt_48:
.word 0 ! idt limit=0
.word 0,0 ! idt base=0L
gdt_48:
.word 0x800 ! gdt limit=2048, 256 GDT entries
.word 512+gdt,0x9 ! gdt base = 0X9xxxx
下一步開啟A20地址線,開始蛻變:
! that was painless, now we enable A20
call empty_8042
mov al,#0xD1 ! command write
out #0x64,al
call empty_8042
mov al,#0xDF ! A20 on
out #0x60,al
call empty_8042
這裡得注意一下:A20地址線並不是開啟保護模式的關鍵,只是在保護模式下,不開啟A20地址線,你將無法存取到所有的記憶體。 這個又是為了保持相容性出的么蛾子。empty_8042這個函數的作用是測試8042狀態暫存器。這塊程式碼涉及硬體的相關東西太多,這裡就簡單介紹,感興趣可自行科普。
! well, that went ok, I hope. Now we have to reprogram the interrupts :-(
! we put them right after the intel-reserved hardware interrupts, at
! int 0x20-0x2F. There they won't mess up anything. Sadly IBM really
! messed this up with the original PC, and they haven't been able to
! rectify it afterwards. Thus the bios puts interrupts at 0x08-0x0f,
! which is used for the internal hardware interrupts as well. We just
! have to reprogram the 8259's, and it isn't fun.
mov al,#0x11 ! initialization sequence
out #0x20,al ! send it to 8259A-1
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb ! jmp $+2, jmp $+2
out #0xA0,al ! and to 8259A-2
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x20 ! start of hardware int's (0x20)
out #0x21,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x28 ! start of hardware int's 2 (0x28)
out #0xA1,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x04 ! 8259-1 is master
out #0x21,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x02 ! 8259-2 is slave
out #0xA1,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0x01 ! 8086 mode for both
out #0x21,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
out #0xA1,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
mov al,#0xFF ! mask off all interrupts for now
out #0x21,al
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
out #0xA1,al
這塊程式碼相當奇奇怪怪。這個是對中斷重新程式設計,放到Intel保留中斷之後。這個又涉及硬體層面的東西,感興趣自行科普825A晶片的相關知識。
這些程式碼看起來真沒勁,生澀而且難看。不過所幸的是,我們終於可以真正的踏入保護模式了:
! Well, now's the time to actually move into protected mode. To make
! things as simple as possible, we do no register set-up or anything,
! we let the gnu-compiled 32-bit programs do that. We just jump to
! absolute address 0x00000, in 32-bit protected mode.
mov ax,#0x0001 ! protected mode (PE) bit
lmsw ax ! This is it!
jmpi 0,8 ! jmp offset 0 of segment 8 (cs)
我們先看一張圖:
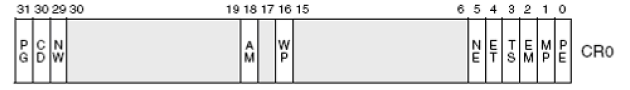
CR0的最後一位PE,控制著是否開啟保護模式,如果置1,則麼表示開啟,此時CPU將開始進入全新的模式。但為什麼用lmsw ax載入程式狀態字的形式進行而不直接用mov cr0,ax呢?這又是該死的歷史的包袱,僅僅是為了相容罷了。
有關引導啟動還剩最後一塊
練習與思考
本節的答案將會在下一節進行講解,務必把本節練習做完後看下一個講解內容。不要偷懶,實驗是學習本教學的捷徑。
俗話說得好,光說不練假把式,如下是本節相關的練習。如果練習沒做成功,就不要看下一節教學了。
- 繪製執行進入保護模式的時候的記憶體佈局狀態。
- 用表格的形式展示
setup.s程式在記憶體中儲存的資料。 .word 0x00eb,0x00eb的作用是啥?- 介紹到最後的
jmpi 0,8程式碼最終跳到了哪個地址?為什麼?
下一篇
羽夏看Linux核心——引導啟動(下)
本文來自部落格園,作者:寂靜的羽夏 ,一個熱愛計算機技術的菜鳥
轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/wingsummer/p/16576792.html


