範例程式碼之ES6箭頭函數實踐
2022-08-08 14:02:15

【相關推薦:、】
簡介
箭頭函數表示式的語法比函數表示式更簡潔,並且沒有自己的this,arguments,super或new.target。箭頭函數表示式更適用於那些本來需要匿名函數的地方,並且它不能用作建構函式。 ---- MDN
基礎用法
參數列示
(param1, param2, …, paramN) => { statements }
(param1, param2, …, paramN) => expression
//相當於:(param1, param2, …, paramN) =>{ return expression; }
// 當只有一個引數時,圓括號是可選的:
(singleParam) => { statements }
singleParam => { statements }
// 沒有引數的函數應該寫成一對圓括號。
() => { statements }返回值表示
let add1 = (num1, num2) => {
num1 + num2
};
let add2 = (num1, num2) => {
return num1 + num2
};
let add3 = (num1, num2) => (num1 + num2);
let add4 = (num1, num2) => num1 + num2;
console.log(add1(2, 3)); // undefined
console.log(add2(2, 3)); // 5
console.log(add3(2, 3)); // 5
console.log(add4(2, 3)); // 5進階
//加括號的函數體返回物件字面量表示式:
let func = () => ({foo: 'bar'})
console.log(func()); // {foo: 'bar'}
//支援剩餘引數和預設引數
(param1, param2, ...rest) => { statements }
(param1 = defaultValue1, param2, …, paramN = defaultValueN) => {
statements }
//同樣支援參數列解構
let f = ([a, b] = [1, 2], {x: c} = {x: a + b}) => a + b + c;
f(); // 6this
最佳實踐
- 如果必須使用匿名函數,或者inline 回撥函數,使用箭頭函數。eslint: prefer-arrow-callback, arrow-spacing
why?語法更簡潔,並且this更符合預期
如果函數邏輯相當複雜,應當使用命名函數
// bad[1, 2, 3].map(function (x) {
const y = x + 1;
return x * y;});// good[1, 2, 3].map((x) => {
const y = x + 1;
return x * y;});- 如果函數體只有一條語句,且該語句不會產生副作用。使用簡寫方式,隱式返回;或者使用完整寫法,顯式return。
eslint: arrow-parens, arrow-body-style
// bad
[1, 2, 3].map(number => {
const nextNumber = number + 1;
`A string containing the ${nextNumber}.`;
});
// good
[1, 2, 3].map(number => `A string containing the ${number}.`);
// good
[1, 2, 3].map((number) => {
const nextNumber = number + 1;
return `A string containing the ${nextNumber}.`;
});
// good
[1, 2, 3].map((number, index) => ({
[index]: number,
}));
// No implicit return with side effects
function foo(callback) {
const val = callback();
if (val === true) {
// Do something if callback returns true
}
}
let bool = false;
// bad
foo(() => bool = true);
// good
foo(() => {
bool = true;
});- 當表示式佔多行時,使用括號括起來增強可讀性
why?函數開頭和結束更明確
// bad['get', 'post', 'put'].map(httpMethod => Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(
httpMagicObjectWithAVeryLongName,
httpMethod,
));// good['get', 'post', 'put'].map(httpMethod => (
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(
httpMagicObjectWithAVeryLongName,
httpMethod,
)));- 如果函數只有一個引數,省略括號,省略花括號。否則,一直使用完整寫法,保持一致性。eslint: arrow-parens
// bad[1, 2, 3].map((x) => x * x);// good[1, 2, 3].map(x => x * x);// good[1, 2, 3].map(number => (
`A long string with the ${number}. It’s so long that we don’t want it to take up space on the .map line!`));// bad[1, 2, 3].map(x => {
const y = x + 1;
return x * y;});// good[1, 2, 3].map((x) => {
const y = x + 1;
return x * y;});- 使用無歧義的=>語法,與<=,>=區分開。eslint: no-confusing-arrow
// badconst itemHeight = item => item.height > 256 ? item.largeSize : item.smallSize;// badconst itemHeight = (item) => item.height > 256 ? item.largeSize : item.smallSize;// goodconst itemHeight = item => (item.height > 256 ? item.largeSize : item.smallSize);// goodconst itemHeight = (item) => {
const { height, largeSize, smallSize } = item;
return height > 256 ? largeSize : smallSize;簡單結論
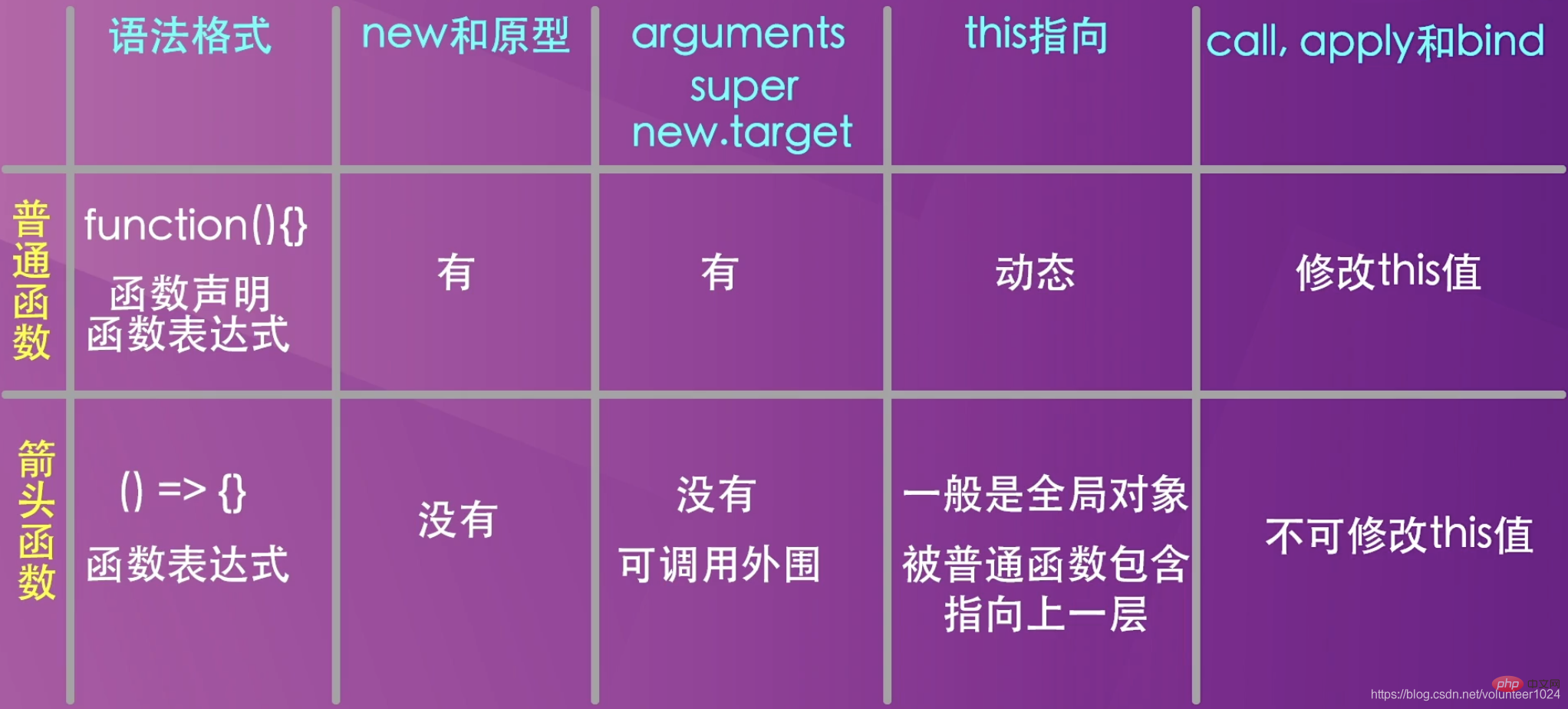
箭頭函數不能用new來建立建構函式的範例,普通函數可以(因為箭頭函數建立的時候程式不會為它建立construct方法,也就是沒有構造能力,用完就丟掉了,不像普通函數重複利用,因此也不需要建構函式原型,也就是不會自動生成prototype屬性)
程式不會給箭頭函數建立arguments物件
普通函數中的this是動態的,而箭頭函數中的this指向的是緊緊包裹箭頭函數的那個物件(定義時決定的)
箭頭函數不能通過bind、call、apply來改變this的值,但依然可以呼叫這幾個方法(只是this的值不受這幾個方法控制)
【相關推薦:、】
以上就是範例程式碼之ES6箭頭函數實踐的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!
