[spring]spring詳細總結
spring
1.spring簡介
-
Spring框架是一個開源的應用程式框架,是針對bean的生命週期進行管理的輕量級容器。
-
Spring解決了開發者在J2EE開發中遇到的許多常見的問題,提供了功能強大IOC、AOP及Web MVC等功能。
-
Spring可以單獨應用於構築應用程式,也可以和Struts、Webwork、Tapestry等眾多Web框架組合使用,並且可以與 Swing等桌面應用程式AP組合。
-
Spring不僅僅能應用於J2EE應用程式之中,也可以應用於桌面應用程式以及小應用程式之中。
-
Spring框架主要由七部分組成,分別是 Spring Core、 Spring AOP、 Spring ORM、 Spring DAO、Spring Context、 Spring Web和 Spring Web MVC。
官方檔案地址:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/4.3.9.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.2.0.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html
中文
https://www.docs4dev.com/docs/zh/spring-framework/5.1.3.RELEASE/reference/
優點:
- 開源免費
- 輕量級的非入侵式的
- 控制反轉(IOC),面向切面程式設計(aop)
- 支援事務處理
使用spring的jar包支援:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.22</version>
</dependency>
七大模組:
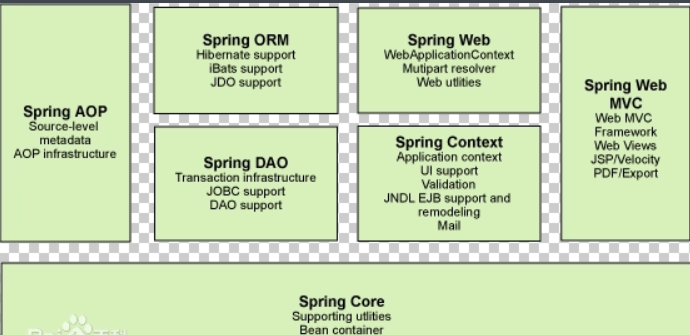
弊端:發展了太久後,設定越來越多,人稱「設定地獄」
2.IOC理論推導
在我們之前的業務中,使用者的需求可能會影響程式的程式碼,可能需要修改程式碼,如果程式的程式碼量十分大,修改一次的成本十分的昂貴!
原來的方式:
private UserMapper usermapper=new UserMapperImpl();
現在將物件的傳遞由new變成set動態注入
private UserMapper userMapper;
public void setUserMapper(UserMapper userMapper){
this.userMapper=userMapper;
}
原來是程式控制的,現在變成使用者控制了。
3.一個spring專案的快速搭建
(1)寫一個實體類
package com.pojo;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-23-21:40
*/
public class HelloSpring {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
(2)將實體類設定在spring容器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<!--使用spring來建立物件,在spring中被稱為bean -->
<!-- class="com.pojo.HelloSpring" 相當於在newHelloSpring
id="helloSpring" 相當於物件變數名字
name="name" 屬性
value="spring" 屬性值
-->
<bean id="helloSpring" class="com.pojo.HelloSpring">
<property name="name" value="spring"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
(3)測試
import com.pojo.HelloSpring;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-23-21:43
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "application.xml");
HelloSpring hello =(HelloSpring) context.getBean("helloSpring");
System.out.println(hello.toString());
}
}
4.IOC建立物件的過程
- 使用無參構造創造
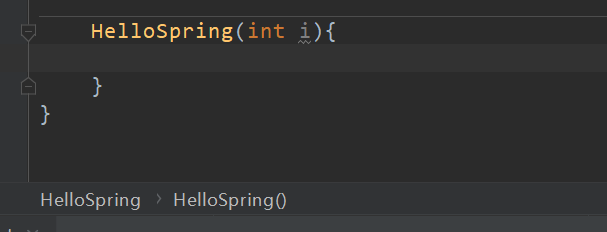
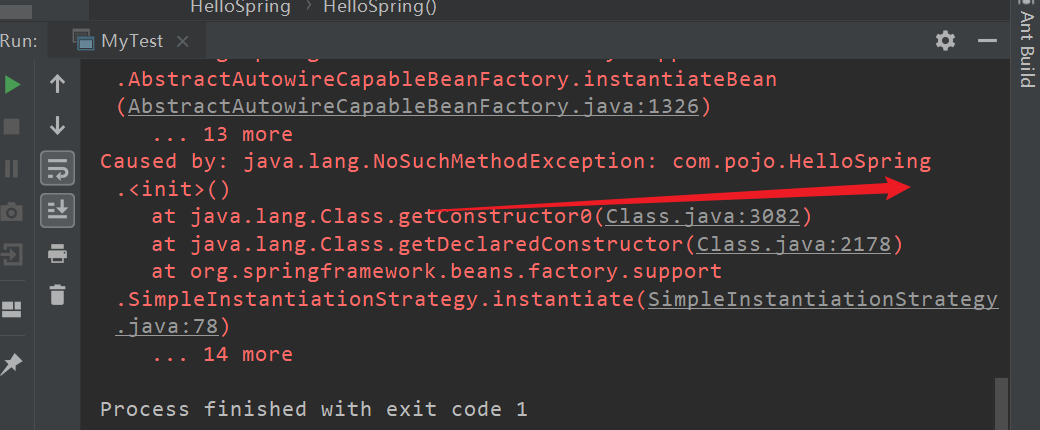
設定為有參後,就會報錯!
物件在被註冊進去的時候,就被範例化了,直接使用就好。
5.IO注入
(1)前面的構造器注入
(2)set注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="cn.itnanls.User">
<!--構造注入——引數型別注入-->
<!--<constructor-arg type="java.lang.Integer" value="12"/>-->
<!--<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="Tom"/>-->
<!--構造注入——下標註入-->
<!--<constructor-arg index="0" value="tom"/>-->
<!--<constructor-arg index="1" value="12"/>-->
<!--構造注入——名字注入,最常用-->
<!--<constructor-arg name="name" value="lucy"/>-->
<!--<constructor-arg name="age" value="12"/>-->
<!--setter注入-->
<!--<property name="name" value="tom"/>-->
</bean>
</beans>
構造注入物件之間的關係為組合
set注入的物件之間的關係為聚合
(3)p名稱空間注入
- 使用set方式注入
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="helloSpring" class="com.pojo.HelloSpring">
<property name="name" value="spring"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="p-name" class="com.pojo.HelloSpring" p:name="ss">
</beans>
(4)c名稱空間注入
- 使用構造器方式注入,開啟構造器才能用
HelloSpring(String name){
this.name=name;
}
HelloSpring(){
}
<bean id="c-name" class="com.pojo.HelloSpring" c:name="cName"/>
注意匯入標頭檔案
xmlns:p = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
6.作用域
ScopeDescription
(Default) Scopes a single bean definition to a single object instance for each Spring IoC container.
Scopes a single bean definition to any number of object instances.
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a single HTTP request. That is, each HTTP request has its own instance of a bean created off the back of a single bean definition. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of an HTTP Session. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a ServletContext. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a WebSocket. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
- 單例
<bean id="accountService" class="com.DefaultAccountService"/>
*<!-- the following is equivalent, though redundant (singleton scope is the default) -->*
<bean id="accountService" class="com.DefaultAccountService" scope="singleton"/>
- 原型
<bean id="accountService" class="com.something.DefaultAccountService" scope="prototype"/>
7.bean的自動裝配
- 是spring滿足bean依賴的一種方式
- spring會在上下文中自動尋找,並自動給bean裝配屬性
spring的裝配方式:
(1)手動裝配
- 在people類中依賴了cat和dog物件,所以屬性中手動裝配他們的屬性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="cat" class="pojo.Cat">
<property name="voice" value="mom~"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dog" class="pojo.Dog">
<property name="voice" value="wow~"/>
</bean>
<bean id="people" class="pojo.People">
<property name="name" value="tata"/>
<property name="dog" ref="dog"/>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"/>
</bean>
</beans>
(2)自動裝配
通過byName自動裝配
- spring會自動去找people中的set後面相對應的cat和dog與bean中id對應
<bean id="people" class="pojo.People" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="tata"/>
</bean>
通過byType自動裝配
- spring會自動去找people中的物件依賴和bean中class類相同的對應
<bean id="people" class="pojo.People" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="tata"/>
</bean>
(3)使用註解實現自動裝配
使用之前匯入註解依賴的設定和支援
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
不再使用顯示參照物件依賴的其他屬性
<bean id="cat" class="pojo.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog" class="pojo.Dog"/>
<bean id="people" class="pojo.People"/>
@Autowired
直接在物件上面使用@Autowired註解
private String name;
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
如果裝配環境複雜的話,可以通過@Qualifier(value = "cat")指定bean注入
例如多個cat物件bean,屬性值不同的時候
<bean id="cat" class="pojo.Cat">
<property name="eat" value="fish"/>
</bean>
<bean id="cat11" class="pojo.Cat">
<property name="eat" value="cookie"/>
</bean>
就需要
@Qualifier
否則,只會spring會走第一個bean
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "cat11")
private Cat cat;
Resource
- 這個註解跟上面的@Autowired功能相似,但是它可以通過名字再通過型別裝配,都沒有才會報錯,要比@Autowired智慧一點,但使用較少。
@Resource(name="cat")
private Cat cat;
8.使用註解開發
1.bean
spring4以後,註解依賴於aop包,確保你的lib中有它
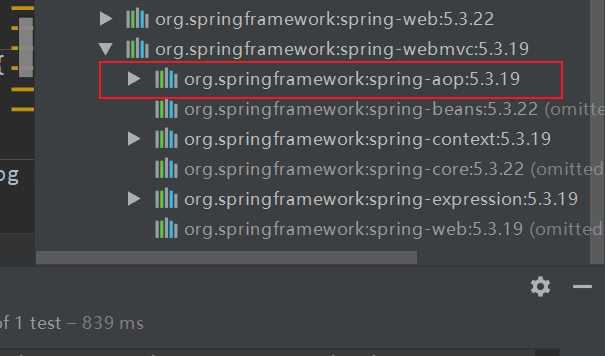
確保開啟了使用註解
<context:annotation-config/>
2.元件代替bean實現自動注入
在組態檔中自動掃描包下的所有類為bean
<context:component-scan base-package="pojo"/>
在類物件上加上註解@Component可以被掃描
- @component (把普通pojo範例化到spring容器中,相當於組態檔中的
)
@Component
使用註解給屬性注入值
package pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-9:52
*/
@Component
public class People {
private String name;
@Value("123")
public int age;
private Dog dog;
private Cat cat;
}
}
- 但是複雜的屬性設定還是建議使用xml統一管理注入
3.component衍生的註解
dao:@repository
service:@service
controller:@controller
跟component功能相同只是能夠使得分工更加的明確
小結:
xml與註解:
- xml更加萬能,適用於各種場合!維護簡單方便
- 註解 不是自己類使用不了,維護相對複雜
最佳實踐:
- xml用來管理bean
- 註解只負責屬性的注入
9.使用javaconfig實現代替xml設定
The central artifacts in Spring’s new Java-configuration support are @Configuration-annotated classes and @Bean-annotated methods.
根據官方檔案的說明,建立一個java—configuration的設定類,使用@configuration註解,再使用@Bean在方法上面就可以實現xml中的功能。
(1)建立一個java—configuration
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import pojo.User;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-11:24
*/
@Configuration
public class Java_config {
@Bean
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
}
(2)實體類
package pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-11:24
*/
@Component
public class User {
@Value("tata")
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
(3)測試
現在也可以拿到值
import config.Java_config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import pojo.User;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-11:28
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Java_config.class);
User user =(User) context.getBean("getUser");
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
}
這種java代替xml的實現方式,在springboot中大量使用。
10.代理模式
代理模式的分類:
- 靜態代理
- 動態代理
關係分析
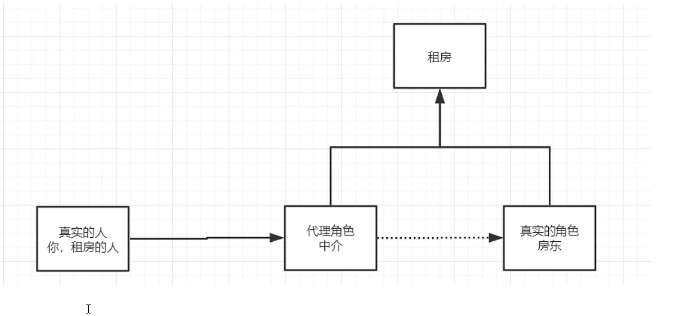
抽象角色:一般會使用介面或者抽象類
真實角色:被代理的角色
代理角色:代理真實的角色,做一些附屬的操作
客戶:存取代理物件的人
靜態代理
步驟:
抽象角色:
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-15:00
*/
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
真實角色:
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-15:01
*/
public class Host implements Rent {
public void rent() {
System.out.println("host would rent house");
}
}
代理角色:
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-15:02
*/
public class Proxy implements Rent {
private Host host;
public Proxy(){
}
public Proxy(Host host){
this.host=host;
}
public void rent() {
host.rent();
seeHouse();
}
//look house
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("look House");
}
}
客戶:
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-15:02
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Host host = new Host();
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(host);
proxy .rent();
}
}
動態代理
- 和靜態代理的角色一樣
- 動態生成,不是我們直接寫好了的
- 動態代理分為兩大類:基於介面的動態代理和基於類的動態代理
- 基於介面——jdbc
- 基於類——cglib
- 基於位元組碼
11.AOP切面程式設計
使用aop植入,需要匯入一個依賴包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
- 橫切關注點
- 切面
- 通知
- 目標
- 代理
- 切入點
- 連線點
在執行的方法前動態的新增一個紀錄檔輸出
方法一使用spring類實現
(1)介面
package service;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-16:09
*/
public interface Service {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void select();
}
(2)要代理的實現類
package service;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-16:09
*/
public class ServiceImpl implements Service {
public void add() {
System.out.println("add");
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println("delete");
}
public void update() {
System.out.println("update");
}
public void select() {
System.out.println("select");
}
}
(3)代理商
package log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-16:11
*/
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("excutor"+method.getName()+target);
}
}
<!--註冊bean -->
<bean id="userSer" class="service.ServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="log" class="log.Log"/>
<!--方式一:使用原生的spring api介面 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入點expression要切入的位置-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* service.ServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--執行環繞增加 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
(4)客戶呼叫
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import service.Service;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-16:28
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
//注意,代理的是介面型別
Service ser = (Service) context.getBean("userSer");
ser.add();
}
}
方法二 使用自定義類實現
(1)自定義一個類,是被橫切進去的內容
package dir;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-17:00
*/
public class PointMethod {
public void after(){
System.out.println("執行方法之後切入……");
}
public void before(){
System.out.println("執行方法之前切入……");
}
}
(2)在組態檔中使用aop切入
<!--方式二 自定義類切入 -->
<bean id="in" class="dir.PointMethod"/>
<aop:config>
<!--自定義切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="in">
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* service.ServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
(3)測試
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import service.Service;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-16:28
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
//注意,代理的是介面型別
Service ser = (Service) context.getBean("userSer");
ser.add();
}
}
方式三 使用註解實現aop
(1)在要被切入的地方使用@Aspect和@After等註解標識切面和切點等
package dir;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-17:00
*/
@Aspect
public class PointMethod {
@After("execution(* service.ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("執行方法之後切入……");
}
@Before("execution(* service.ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("執行方法之前切入……");
}
}
(2)將此類設定到spring中,別忘了開啟註解支援
<!--方式三 註解 -->
<bean id="in1" class="dir.PointMethod"/>
<!--一定要開啟 否則註解不生效 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
(3)測試
同上面一樣的測試,不再贅述
12.spring和mybatis整合
1.導包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.29</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.19</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.將mybatis中的設定到spring中
mybatis被spring接管後,他自己的組態檔只需要寫別名和紀錄檔,事務和資料庫連線交給spring
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.pang.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
</configuration>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--整合mybatis的資料庫 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123123"/>
</bean>
<!--整合mybatis的SQLSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--繫結mybatis組態檔 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis_config.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<!--只能用構造器注入 沒有set方法 -->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="user" class="mapper.UserMapperImpl">
<property name="session" ref="sqlSession"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.介面實現類
package mapper;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-18:42
*/
public class UserMapperImpl implements UserMapper {
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
public void setSession(SqlSessionTemplate session) {
this.sqlSession = session;
}
public List<User> user() {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
return mapper.user();
}
}
測試
import mapper.UserMapper;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author panglili
* @create 2022-07-24-18:01
*/
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void Test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
UserMapper user1 = context.getBean("user", UserMapper.class);
List<User> list = user1.user();
for(User u :list){
System.out.println(u);
}
}
}
13.事務支援
只需要在spring中簡單的設定兩點就可以實現
<tx:advice id="txAdvice">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
注意代理的是介面不是類!!!
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="serviceOperation"
expression="execution(* service..*Service.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor pointcut-ref="serviceOperation" advice-ref="txAdvice"/>
</aop:config>