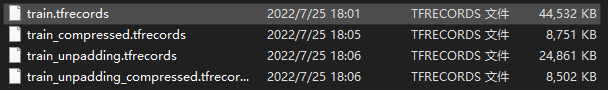
TFrecord寫入與讀取
Protocol buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data.
Protocol buffers是由Google設計的無關程式語言、平臺的、具有可延伸性機制的序列化資料結構。
The
tf.train.Examplemessage (or protosun) is a flexible message type that represents a{"string": value}mapping. It is designed for use with TensorFlow and is used throughout the higher-level APIs such as TFX.
tf.traom.Example是一種表示{「string」:value}對映關係的靈活的訊息型別。它被設計用於TensorFlow以及更加高階的API。
寫入
tf.train.Example
一個tf.train.Example的範例是構建的是數個{」string「: tf.train.Feature}對映。
其中,tf.train.Feature可以是以下三種,其他型別的資料格式可以通過一個或多個Feature組合描述:
- tf.train.BytesList
- tf.train.FloatList
- tf.train.Int64List
模板
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.io.TFRecordWriter("train.tfrecords","GZIP") as writer:
for i in range(200): # Assume there are 200 records
example_proto = tf.train.Example(
features=tf.train.Features(
feature= {
'feature0':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.int64List(value=feature0)),
'feature1':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=feature1)),
'feature2':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.BtyesList(value=feature2)),
'label':
tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.int64List(value=[label])),
}
)
)
writer.write(example_proto.SerializeToString())
讀取
tf.io.parse_single_example 和 tf.io.parse_example
One might see performance advantages by batching
Exampleprotos withparse_exampleinstead of using this function directly.
對Example protos分批並使用parse_example會比直接使用parse_single_example有效能優勢。
模板
# with map_func using tf.io.parse_single_example
def map_func(example):
# Create a dictionary describing the features.
feature_description = {
'feature0': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature0], tf.int64),
'feature1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature1], tf.float32),
'feature2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature2], tf.int64),
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64),
}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_single_example(example, features=feature_description)
feature0 = parsed_example["feature0"]
feature1 = parsed_example["feature1"]
feature2 = parsed_example["feature2"]
label = parsed_example["label"]
return image, label
raw_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("train.tfrecords","GZIP")
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.map(map_func=map_func)
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
以下程式碼和前者的區別在於map_func中使用tf.io.parse_example替換tf.io.parse_single_example,並在呼叫map方法前先呼叫batch方法。
# with map_func using tf.io.parse_example
def map_func(example):
# Create a dictionary describing the features.
feature_description = {
'feature0': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature0], tf.int64),
'feature1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature1], tf.float32),
'feature2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([len_feature2], tf.int64),
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64),
}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_example(example, features=feature_description)
# features can be modified here
feature0 = parsed_example["feature0"]
feature1 = parsed_example["feature1"]
feature2 = parsed_example["feature2"]
label = parsed_example["label"]
return image, label
raw_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(["./1.tfrecords", "./2.tfrecords"])
raw_dataset = raw_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.map(map_func=map_func)
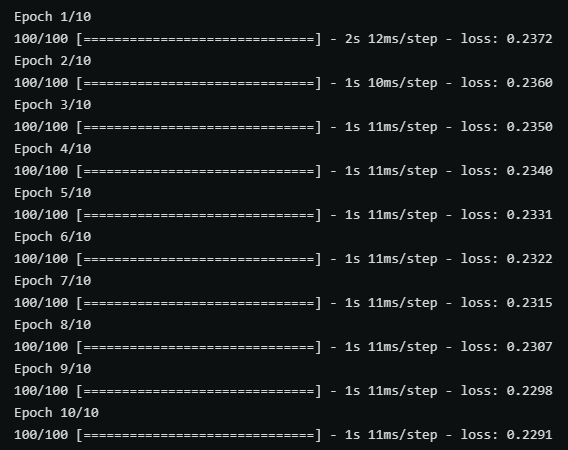
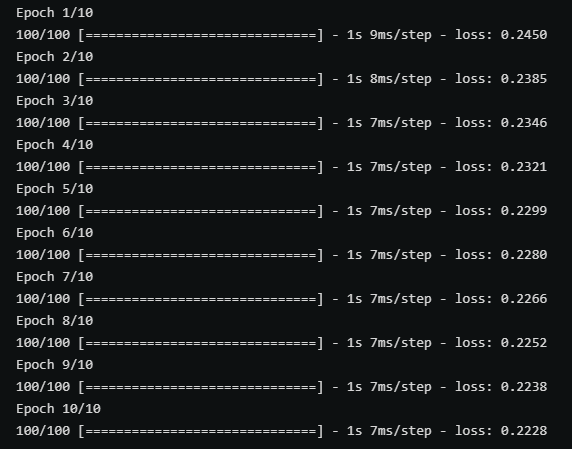
以上兩張圖分別時使用帶有parse_single_example和parse_example的map_func在訓練中的效能對比,後者(parse_example)明顯效能更優秀。
不定長資料的讀寫 RaggedFeature
對於不定長且未padding的資料,寫入過程中和定長資料沒有區別,但在讀取過程中需要使用tf.io.RaggedFeature替代tf.io.FixedLenFeature。
def map_func(example):
# Create a dictionary describing the features.
feature_description = {
'feature': tf.io.RaggedFeature(tf.float32),
'label': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64),
}
parsed_example = tf.io.parse_example(example, features=feature_description)
# feature = parsed_example["feature"]
feature = parsed_example["feature"].to_tensor(shape=[1,100])
label = parsed_example["label"]
return feature, label
raw_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("train_unpadding.tfrecords").batch(1000)
parsed_dataset = raw_dataset.map(map_func=map_func)
下圖對比了是否對不定長資料進行padding分別在壓縮和未壓縮的情況下的檔案大小。