EFCore高階Saas系統下單DbContext如何支援不同資料庫的遷移
EFCore高階Saas系統下單DbContext如何支援不同資料庫的遷移
前言
隨著系統的不斷開發和迭代預設的efcore功能十分強大,但是隨著Saas系統的引進efcore基於表欄位的多租戶模式已經非常完美了,但是基於資料庫的多租戶也是可以用的,但是也存在缺點,缺點就是沒有辦法支援不同資料庫,migration support multi database provider with single dbcontext,本人不才,查詢了一下,官方檔案只說明瞭dbcontext的遷移如何實現多資料來源,但是缺不是單個dbcontext,這個就讓人很頭疼。所以秉著嘗試一下的原則進行了這篇部落格的編寫,因為本人只有mmsql和mysql所以這次就用這兩個資料庫來做測試
廣告時間
本人開發了一款efcore的分表分庫讀寫分離元件
https://github.com/dotnetcore/sharding-core
希望有喜歡的小夥伴給我點點star謝謝
那麼廢話不多說我們馬上開始migration support multi database provider with single dbcontext
新建專案
1.按裝依賴
2.新建一個User類
[Table(nameof(User))]
public class User
{
public string UserId { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
}
3.建立DbContext
public class MyDbContext:DbContext
{
public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; }
public MyDbContext(DbContextOptions<MyDbContext> options):base(options)
{
}
4.StartUp設定
var provider = builder.Configuration.GetValue("Provider", "UnKnown");
//Add-Migration InitialCreate -Context MyDbContext -OutputDir Migrations\SqlServer -Args "--provider SqlServer"
//Add-Migration InitialCreate -Context MyDbContext -OutputDir Migrations\MySql -Args "--provider MySql"
builder.Services.AddDbContext<MyDbContext>(options =>
{
_ = provider switch
{
"MySql" => options.UseMySql("server=127.0.0.1;port=3306;database=DBMultiDataBase;userid=root;password=L6yBtV6qNENrwBy7;", new MySqlServerVersion(new Version())),
"SqlServer" => options.UseSqlServer("Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=DBMultiDataBase;Integrated Security=True;"),
_ => throw new Exception($"Unsupported provider: {provider}")
};
});
遷移區分資料庫
新建一個遷移名稱空間提供者
public interface IMigrationNamespace
{
string GetNamespace();
}
mysql和sqlserver的實現分別是專案名稱遷移資料夾
public class MySqlMigrationNamespace:IMigrationNamespace
{
public string GetNamespace()
{
return "EFCoreMigrateMultiDatabase.Migrations.MySql";
}
}
public class SqlServerMigrationNamespace:IMigrationNamespace
{
public string GetNamespace()
{
return "EFCoreMigrateMultiDatabase.Migrations.SqlServer";
}
}
efcore擴充套件
新增efcore擴充套件
public class MigrationNamespaceExtension : IDbContextOptionsExtension
{
public IMigrationNamespace MigrationNamespace { get; }
public MigrationNamespaceExtension(IMigrationNamespace migrationNamespace)
{
MigrationNamespace = migrationNamespace;
}
public void ApplyServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton<IMigrationNamespace>(sp => MigrationNamespace);
}
public void Validate(IDbContextOptions options)
{
}
public DbContextOptionsExtensionInfo Info => new MigrationNamespaceExtensionInfo(this);
private class MigrationNamespaceExtensionInfo : DbContextOptionsExtensionInfo
{
private readonly MigrationNamespaceExtension _migrationNamespaceExtension;
public MigrationNamespaceExtensionInfo(IDbContextOptionsExtension extension) : base(extension)
{
_migrationNamespaceExtension = (MigrationNamespaceExtension)extension;
}
public override int GetServiceProviderHashCode() => _migrationNamespaceExtension.MigrationNamespace.GetNamespace().GetHashCode();
public override bool ShouldUseSameServiceProvider(DbContextOptionsExtensionInfo other) => true;
public override void PopulateDebugInfo(IDictionary<string, string> debugInfo)
{
}
public override bool IsDatabaseProvider => false;
public override string LogFragment => "MigrationNamespaceExtension";
}
}
重寫MigrationsAssembly支援多資料庫
public class EFCoreMultiDatabaseMigrationsAssembly: IMigrationsAssembly
{
public string MigrationNamespace { get; }
private readonly IMigrationsIdGenerator _idGenerator;
private readonly IDiagnosticsLogger<DbLoggerCategory.Migrations> _logger;
private IReadOnlyDictionary<string, TypeInfo>? _migrations;
private ModelSnapshot? _modelSnapshot;
private readonly Type _contextType;
/// <summary>
/// This is an internal API that supports the Entity Framework Core infrastructure and not subject to
/// the same compatibility standards as public APIs. It may be changed or removed without notice in
/// any release. You should only use it directly in your code with extreme caution and knowing that
/// doing so can result in application failures when updating to a new Entity Framework Core release.
/// </summary>
public EFCoreMultiDatabaseMigrationsAssembly(
IMigrationNamespace migrationNamespace,
ICurrentDbContext currentContext,
IDbContextOptions options,
IMigrationsIdGenerator idGenerator,
IDiagnosticsLogger<DbLoggerCategory.Migrations> logger)
{
_contextType = currentContext.Context.GetType();
var assemblyName = RelationalOptionsExtension.Extract(options)?.MigrationsAssembly;
Assembly = assemblyName == null
? _contextType.Assembly
: Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(assemblyName));
MigrationNamespace = migrationNamespace.GetNamespace();
_idGenerator = idGenerator;
_logger = logger;
}
/// <summary>
/// This is an internal API that supports the Entity Framework Core infrastructure and not subject to
/// the same compatibility standards as public APIs. It may be changed or removed without notice in
/// any release. You should only use it directly in your code with extreme caution and knowing that
/// doing so can result in application failures when updating to a new Entity Framework Core release.
/// </summary>
public virtual IReadOnlyDictionary<string, TypeInfo> Migrations
{
get
{
IReadOnlyDictionary<string, TypeInfo> Create()
{
var result = new SortedList<string, TypeInfo>();
var items
= from t in Assembly.GetConstructibleTypes()
where t.IsSubclassOf(typeof(Migration))&& print(t)
&& t.Namespace.Equals(MigrationNamespace)
&& t.GetCustomAttribute<DbContextAttribute>()?.ContextType == _contextType
let id = t.GetCustomAttribute<MigrationAttribute>()?.Id
orderby id
select (id, t);
Console.WriteLine("Migrations:" + items.Count());
foreach (var (id, t) in items)
{
if (id == null)
{
_logger.MigrationAttributeMissingWarning(t);
continue;
}
result.Add(id, t);
}
return result;
}
return _migrations ??= Create();
}
}
private bool print(TypeInfo t)
{
Console.WriteLine(MigrationNamespace);
Console.WriteLine(t.Namespace);
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// This is an internal API that supports the Entity Framework Core infrastructure and not subject to
/// the same compatibility standards as public APIs. It may be changed or removed without notice in
/// any release. You should only use it directly in your code with extreme caution and knowing that
/// doing so can result in application failures when updating to a new Entity Framework Core release.
/// </summary>
public virtual ModelSnapshot? ModelSnapshot
=> GetMod();
private ModelSnapshot GetMod()
{
Console.WriteLine("_modelSnapshot:"+ _modelSnapshot);
if (_modelSnapshot == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("_modelSnapshot:null");
_modelSnapshot = (from t in Assembly.GetConstructibleTypes()
where t.IsSubclassOf(typeof(ModelSnapshot)) && print(t)
&& MigrationNamespace.Equals(t?.Namespace)
&& t.GetCustomAttribute<DbContextAttribute>()?.ContextType == _contextType
select (ModelSnapshot)Activator.CreateInstance(t.AsType())!)
.FirstOrDefault();
Console.WriteLine("_modelSnapshot:" + _modelSnapshot);
}
return _modelSnapshot;
}
/// <summary>
/// This is an internal API that supports the Entity Framework Core infrastructure and not subject to
/// the same compatibility standards as public APIs. It may be changed or removed without notice in
/// any release. You should only use it directly in your code with extreme caution and knowing that
/// doing so can result in application failures when updating to a new Entity Framework Core release.
/// </summary>
public virtual Assembly Assembly { get; }
/// <summary>
/// This is an internal API that supports the Entity Framework Core infrastructure and not subject to
/// the same compatibility standards as public APIs. It may be changed or removed without notice in
/// any release. You should only use it directly in your code with extreme caution and knowing that
/// doing so can result in application failures when updating to a new Entity Framework Core release.
/// </summary>
public virtual string? FindMigrationId(string nameOrId)
=> Migrations.Keys
.Where(
_idGenerator.IsValidId(nameOrId)
// ReSharper disable once ImplicitlyCapturedClosure
? id => string.Equals(id, nameOrId, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)
: id => string.Equals(_idGenerator.GetName(id), nameOrId, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
.FirstOrDefault();
/// <summary>
/// This is an internal API that supports the Entity Framework Core infrastructure and not subject to
/// the same compatibility standards as public APIs. It may be changed or removed without notice in
/// any release. You should only use it directly in your code with extreme caution and knowing that
/// doing so can result in application failures when updating to a new Entity Framework Core release.
/// </summary>
public virtual Migration CreateMigration(TypeInfo migrationClass, string activeProvider)
{
Console.WriteLine(migrationClass.FullName);
var migration = (Migration)Activator.CreateInstance(migrationClass.AsType())!;
migration.ActiveProvider = activeProvider;
return migration;
}
}
編寫startup
參考 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/managing-schemas/migrations/providers?tabs=vs
//Add-Migration InitialCreate -Context MyDbContext -OutputDir Migrations\SqlServer -Args "--provider SqlServer"
//Add-Migration InitialCreate -Context MyDbContext -OutputDir Migrations\MySql -Args "--provider MySql"
//update-database -Args "--provider MySql"
//update-database -Args "--provider SqlServer"
builder.Services.AddDbContext<MyDbContext>(options =>
{
options.ReplaceService<IMigrationsAssembly, EFCoreMultiDatabaseMigrationsAssembly>();
_ = provider switch
{
"MySql" => options.UseMySql("server=127.0.0.1;port=3306;database=DBMultiDataBase;userid=root;password=L6yBtV6qNENrwBy7;", new MySqlServerVersion(new Version()))
.UseMigrationNamespace(new MySqlMigrationNamespace()),
"SqlServer" => options.UseSqlServer("Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=DBMultiDataBase;Integrated Security=True;")
.UseMigrationNamespace(new SqlServerMigrationNamespace()),
_ => throw new Exception($"Unsupported provider: {provider}")
};
});
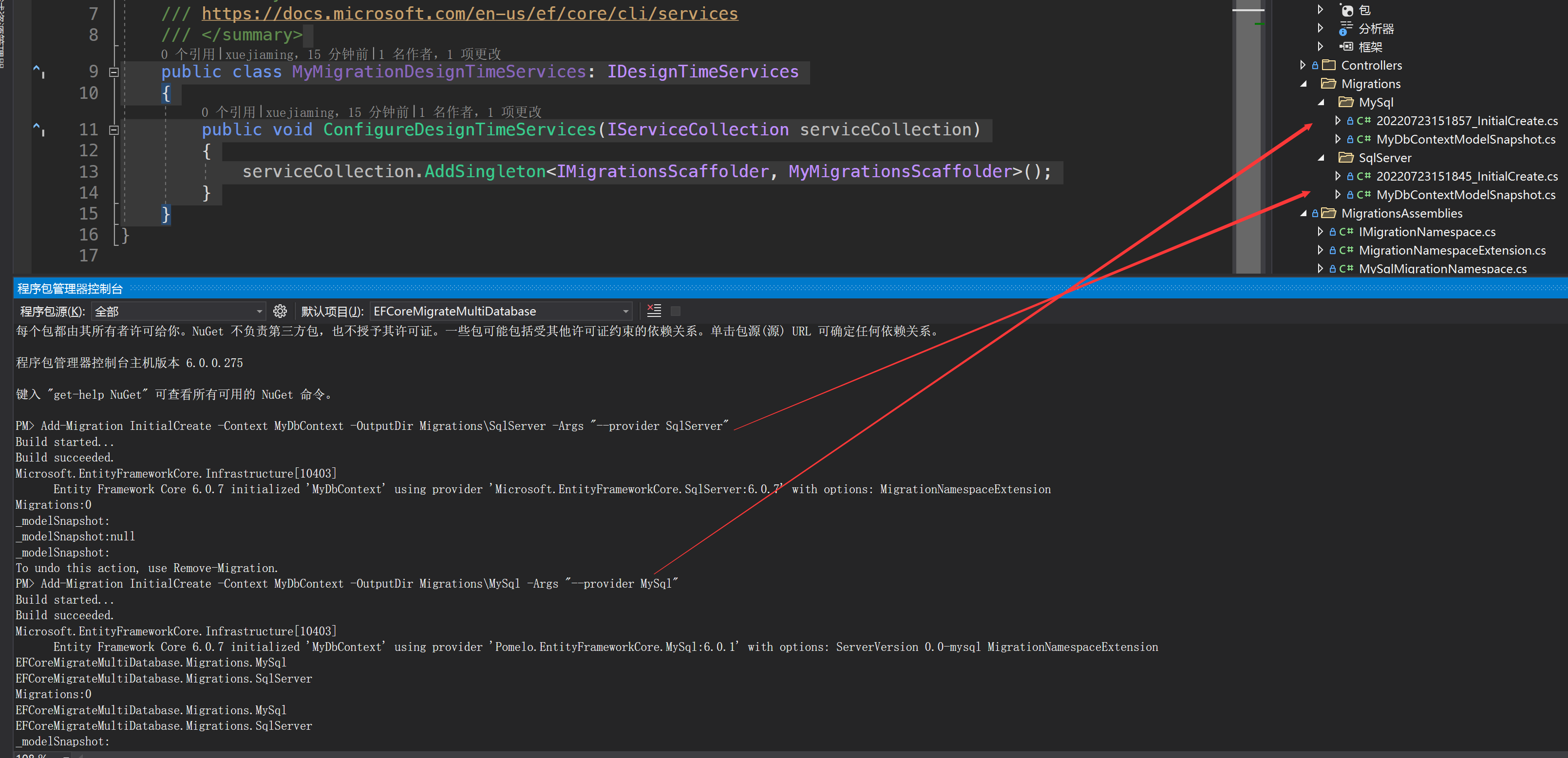
到此為止我這邊想我們應該已經實現了把,但是如果我們分別執行兩個遷移命令會導致前一個遷移命令被覆蓋掉,經過一整個下午的debug偵錯最後發現是因為在遷移指令碼生成寫入檔案的時候會判斷當前DbContext'的ModelSnapshot,同一個dbcontext生成的檔案是一樣的,所以我們這邊有兩個選擇
- 1.讓生成的檔名不一樣
- 2.讓ModelSnapshot不進行深度查詢只在當前目錄下處理
這邊選了第二種
public class MyMigrationsScaffolder: MigrationsScaffolder
{
private readonly Type _contextType;
public MyMigrationsScaffolder(MigrationsScaffolderDependencies dependencies) : base(dependencies)
{
_contextType = dependencies.CurrentContext.Context.GetType();
}
protected override string GetDirectory(string projectDir, string? siblingFileName, string subnamespace)
{
var defaultDirectory = Path.Combine(projectDir, Path.Combine(subnamespace.Split('.')));
if (siblingFileName != null)
{
if (!siblingFileName.StartsWith(_contextType.Name + "ModelSnapshot."))
{
var siblingPath = TryGetProjectFile(projectDir, siblingFileName);
if (siblingPath != null)
{
var lastDirectory = Path.GetDirectoryName(siblingPath)!;
if (!defaultDirectory.Equals(lastDirectory, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
Dependencies.OperationReporter.WriteVerbose(DesignStrings.ReusingNamespace(siblingFileName));
return lastDirectory;
}
}
}
}
return defaultDirectory;
}
}
新增designservices
public class MyMigrationDesignTimeServices: IDesignTimeServices
{
public void ConfigureDesignTimeServices(IServiceCollection serviceCollection)
{
serviceCollection.AddSingleton<IMigrationsScaffolder, MyMigrationsScaffolder>();
}
}
遷移
分別執行兩個遷移命令
執行更新資料庫命令
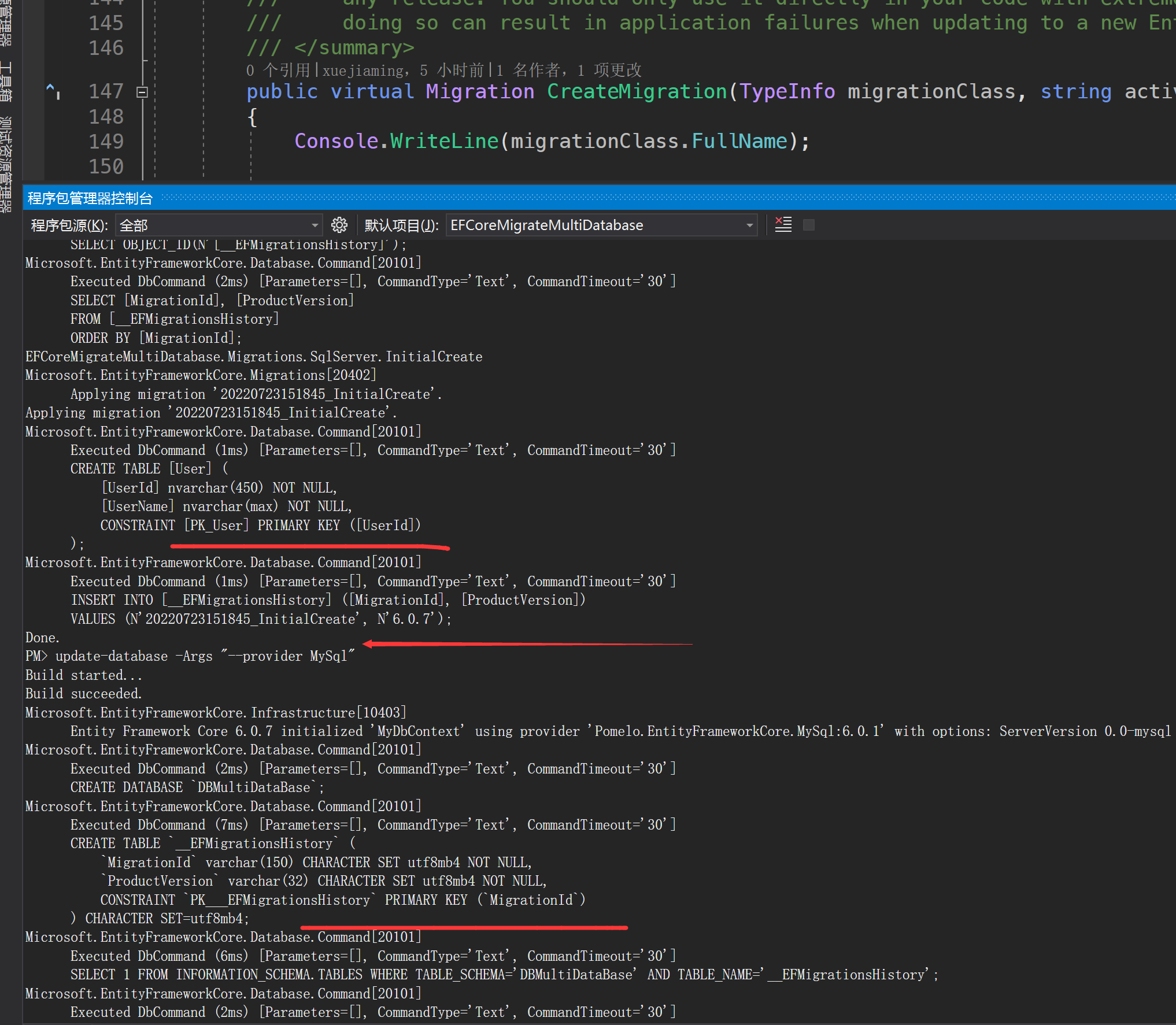
記得我們需要在引數裡面新增選項
下期預告
下期我們將實現efcore在Saas系統下的多租戶+code-first(遷移)+分表+分庫+讀寫分離+動態分表+動態分庫+動態讀寫分離+動態新增多租戶 全程零sql指令碼的解決方案
是不是buffer疊滿
最後的最後
附上demo:EFCoreMigrateMultiDatabase https://github.com/xuejmnet/EFCoreMigrateMultiDatabase
您都看到這邊了確定不點個star或者贊嗎,一款.Net不得不學的分庫分表解決方案,簡單理解為sharding-jdbc在.net中的實現並且支援更多特性和更優秀的資料聚合,擁有原生效能的97%,並且無業務侵入性,支援未分片的所有efcore原生查詢
- github地址 https://github.com/xuejmnet/sharding-core
- gitee地址 https://gitee.com/dotnetchina/sharding-core