深入剖析(JDK)ArrayQueue原始碼
深入剖析(JDK)ArrayQueue原始碼
前言
在本篇文章當中主要給大家介紹一個比較簡單的JDK為我們提供的容器ArrayQueue,這個容器主要是用陣列實現的一個單向佇列,整體的結構相對其他容器來說就比較簡單了。
ArrayQueue內部實現
在談ArrayQueue的內部實現之前我們先來看一個ArrayQueue的使用例子:
public void testQueue() {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>(10);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0); // 這個引數只能為0 表示刪除佇列當中第一個元素,也就是隊頭元素
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0);
System.out.println(queue);
}
// 輸出結果
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4]
首先ArrayQueue內部是由迴圈陣列實現的,可能保證增加和刪除資料的時間複雜度都是\(O(1)\),不像ArrayList刪除資料的時間複雜度為\(O(n)\)。在ArrayQueue內部有兩個整型資料head和tail,這兩個的作用主要是指向佇列的頭部和尾部,它的初始狀態在記憶體當中的佈局如下圖所示:

因為是初始狀態head和tail的值都等於0,指向陣列當中第一個資料。現在我們向ArrayQueue內部加入5個資料,那麼他的記憶體佈局將如下圖所示:
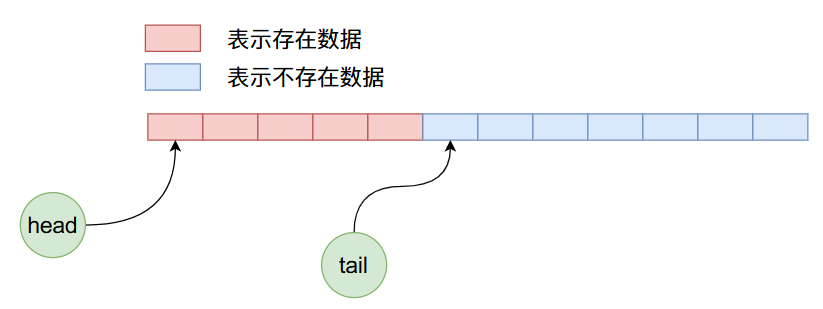
現在我們刪除4個資料,那麼上圖經過4次刪除操作之後,ArrayQueue內部資料佈局如下:

在上面的狀態下,我們繼續加入8個資料,那麼佈局情況如下:

我們知道上圖在加入資料的時候不僅將陣列後半部分的空間使用完了,而且可以繼續使用前半部分沒有使用過的空間,也就是說在ArrayQueue內部實現了一個迴圈使用的過程。
ArrayQueue原始碼剖析
建構函式
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
this.queue = newArray(capacity + 1);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}
上面的建構函式的程式碼比較容易理解,主要就是根據使用者輸入的陣列空間長度去申請陣列,不過他具體在申請陣列的時候會多申請一個空間。
add函數
public boolean add(T o) {
queue[tail] = o;
// 迴圈使用陣列
int newtail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
if (newtail == head)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
tail = newtail;
return true; // we did add something
}
上面的程式碼也相對比較容易看懂,在上文當中我們已經提到了ArrayQueue可以迴圈將資料加入到陣列當中去,這一點在上面的程式碼當中也有所體現。
remove函數
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (head == tail)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}
從上面的程式碼當中可以看出,在remove函數當中我們必須傳遞引數0,否則會丟擲異常。而在這個函數當中我們只會刪除當前head下標所在位置的資料,然後將head的值進行迴圈加1操作。
get函數
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}
get函數的參數列示得到第i個資料,這個第i個資料並不是陣列位置的第i個資料,而是距離head位置為i的位置的資料,瞭解這一點,上面的程式碼是很容易理解的。
resize函數
public void resize(int newcapacity) {
int size = size();
if (newcapacity < size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Resizing would lose data");
newcapacity++;
if (newcapacity == this.capacity)
return;
T[] newqueue = newArray(newcapacity);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
newqueue[i] = get(i);
this.capacity = newcapacity;
this.queue = newqueue;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = size;
}
在resize函數當中首先申請新長度的陣列空間,然後將原陣列的資料一個一個的拷貝到新的陣列當中,注意在這個拷貝的過程當中,重新更新了head與tail,而且並不是簡單的陣列拷貝,因為在之前的操作當中head可能已經不是了0,因此新的拷貝需要我們一個一個的從就陣列拿出來,然後放到新陣列當中。下圖可以很直觀的看出這個過程:

總結
在本篇文章當中主要給大家介紹了ArrayQueue的內部實現過程和原理,並且看了ArrayQueue的原始碼,有圖的輔助整個閱讀的過程應該是比較清晰的,ArrayQueue也是一個比較簡單的容器,JDK對他的實現也比較簡單。
以上就是本文所有的內容了,希望大家有所收穫,我是LeHung,我們下期再見!!!(記得點贊收藏哦!)
更多精彩內容合集可存取專案:https://github.com/Chang-LeHung/CSCore
關注公眾號:一無是處的研究僧,瞭解更多計算機(Java、Python、計算機系統基礎、演演算法與資料結構)知識。