mybatis 攔截器
1.mybatis攔截器介紹
攔截器可在mybatis進行sql底層處理的時候執行額外的邏輯,最常見的就是分頁邏輯、對結果集進行處理過濾敏感資訊等。
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}從上面的程式碼可以看到mybatis支援的攔截型別只有四種(按攔截順序)
1.Executor 執行器介面
2.StatementHandler sql構建處理器
3.ParameterHandler 引數處理器
4.ResultSetHandler 結果集處理器
2.攔截器原理
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍歷定義的攔截器,對攔截的物件進行包裝
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
#Interceptor
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}mybatis攔截器本質上使用了jdk動態代理,interceptorChain攔截器鏈中儲存了使用者定義的攔截器,會遍歷進行對目標物件代理包裝。
使用者自定義攔截器類需要實現Interceptor介面,以及實現intercept方法,plugin和setProperties方法可重寫,plugin方法一般不會改動,該方法呼叫了Plugin的靜態方法wrap實現了對目標物件的代理
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
// 攔截目標物件
private final Object target;
// 攔截器物件-執行邏輯
private final Interceptor interceptor;
// 攔截介面和攔截方法的對映
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
// 獲取jdk代理物件
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 儲存攔截介面和攔截方法的對映
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 獲取攔截目標物件實現的介面,若為空則不代理
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 獲取需要攔截的方法集合,若不存在則使用目標物件執行
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// Invocation儲存了目標物件、攔截方法以及方法引數
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
// 獲取Intercepts註解值不能為空
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
// key 攔截的型別
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.computeIfAbsent(sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>());
try {
// 獲取攔截的方法
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
}@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Intercepts {
/**
* Returns method signatures to intercept.
*
* @return method signatures
*/
Signature[] value();
}
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Signature {
/**
* Returns the java type.
*
* @return the java type
*/
Class<?> type();
/**
* Returns the method name.
*
* @return the method name
*/
String method();
/**
* Returns java types for method argument.
* @return java types for method argument
*/
Class<?>[] args();
}可以看到,當被攔截的方法被執行時主要呼叫自定義攔截器的intercept方法,把攔截物件、方法以及方法引數封裝成Invocation物件傳遞過去。
在getSignatureMap方法中可以看到,自定義的攔截器類上需要新增Intercepts註解並且Signature需要有值,Signature註解中的type為需要攔截物件的介面(Executor.class/StatementHandler/ParameterHandler/ResultSetHandler),method為需要攔截的方法的方法名,args為攔截方法的方法引數型別。
3.參考例子
接下來舉一個攔截器實現對結果集下劃線轉駝峰的例子來簡要說明
/**
* @author dxu2
* @date 2022/7/14
* map結果轉駝峰
*/
@Intercepts(value = {@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class})})
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 呼叫目標方法
List<Object> result = (List<Object>) invocation.proceed();
for (Object o : result) {
if (o instanceof Map) {
processMap((Map<String, Object>) o);
} else {
break;
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
private void processMap(Map<String, Object> map) {
Set<String> keySet = new HashSet<>(map.keySet());
for (String key : keySet) {
if ((key.charAt(0) >= 'A' && key.charAt(0) <= 'Z') || key.indexOf("_") > 0) {
Object value = map.get(key);
map.remove(key);
map.put(camel(key), value);
}
}
}
// 下劃線轉駝峰
private String camel(String fieldName) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < fieldName.length(); i++) {
if (fieldName.charAt(i) == '_') {
if (stringBuffer.length() > 0) {
flag = true;
}
} else {
if (flag) {
stringBuffer.append(Character.toUpperCase(fieldName.charAt(i)));
flag = false;
} else {
stringBuffer.append(Character.toLowerCase(fieldName.charAt(i)));
}
}
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}這個例子攔截的是ResultSetHandler的handleResultSets方法,這個方法是用來對結果集處理的,看intercept方法首先呼叫了目標物件的方法接著強轉為List<Object>型別,這裡為什麼可以強轉呢,因為我們可以看到handleResultSets方法定義<E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException; 返回的是List型別,然後遍歷列表,若元素是map型別的再進行處理把key值轉化為駝峰形式重新put到map中。
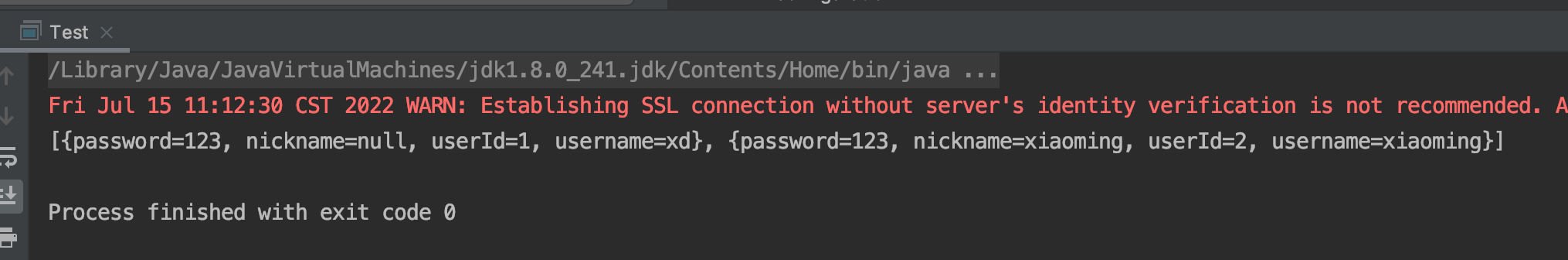
最後不要忘了把自定義的攔截器新增到設定中,這邊是使用xml設定的,新增完後接著執行測試程式碼,可以看到列user_id已經轉換成駝峰形式了。
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="org.apache.ibatis.study.interceptor.MyInterceptor">
</plugin>
</plugins>#mapper介面
List<Map> selectAllUsers();
#mapper.xml
<select id="selectAllUsers" resultType="map">
select user_id, username, password, nickname
from user
</select>
#java測試類
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")) {
// 構建session工廠 DefaultSqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(userMapper.selectAllUsers());
}
}
}