如何使用VueRouter4.x?快速上手指南

Vue Router是Vue團隊的研發的一款與Vue.js核心深度整合的一款路由外掛,使Vue構建單頁面程式變得非常的簡單;Vue Router目前最新版本是4.X,也是Vue3推薦使用的版本,這篇文章我們就來學習一下Vue Router4.X。(學習視訊分享:)
URL.hash與History
Vue Router中存在兩種history(記錄歷史路由),分別是URL.hash和HTML5中提供的History兩種。
hash歷史記錄對於沒有主機的Web應用程式(例如file://),或當設定伺服器不能處理任意的URL時非常有用,但是hash的SEO非常差勁;
History歷史是HTML5中新增的,對於IE來說不是很友好,但是Vue3都放棄IE了,你也就不用考慮IE了;這種方式是目前最常見的一種方式,但是應用程式必須通過http協定被提供服務。
安裝與使用流程
首先我們安裝Vue Router,命令如下:
npm i vue-router
然後在main.js中寫入如下程式碼:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1 引入 createRouter
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 2 定義路由對映表
const routes = [
/* more router */
]
// 3 建立路由範例,並傳遞對應設定
const router = createRouter({
// history 模式 這裡使用createWebHistory
history: createWebHistory(),
// 傳遞路由對映表
routes
})
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')上面的程式碼中的routes如果多的話,可以定義一個router.js檔案,將其進行抽離,範例程式碼如下:
router.js
export default [ /* more router */ ]
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 2 引入路由對映表
import routes from './router'
// 1 引入 createRouter
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 3 建立路由範例,並傳遞對應設定
const router = createRouter({
// history 模式 這裡使用createWebHistory
history: createWebHistory(),
// 傳遞路由對映表
routes
})
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')或者**直接在****router.js中直接匯出一個路由範例,在main.js**中使用即可(這種方式更常用)。
router-link和router-view
router-link
<router-link>是Vue提供的自定義元件,用於建立連結,在Vue中並沒有使用原生的<a>,因為<a>改變URL後會重新載入頁面而<router-link>不會;關於<router-link>元件的細節支援哪些屬性,可以參考檔案。
router-view
<router-view>元件用於與URL對應的元件,例如下面這段程式碼:
<template>
<router-link to="/hello"
><img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png"
/></router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>然後我們的router.js的程式碼如下:
import RootComponent from './components/root.vue'
export default [
{
path: '/',
// 引入元件
component: RootComponent
},
{
path: '/hello',
// 路由懶載入引入元件
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue')
}
]關於其他設定項,可以參考檔案。
程式碼執行結果如下所示:

路由懶載入
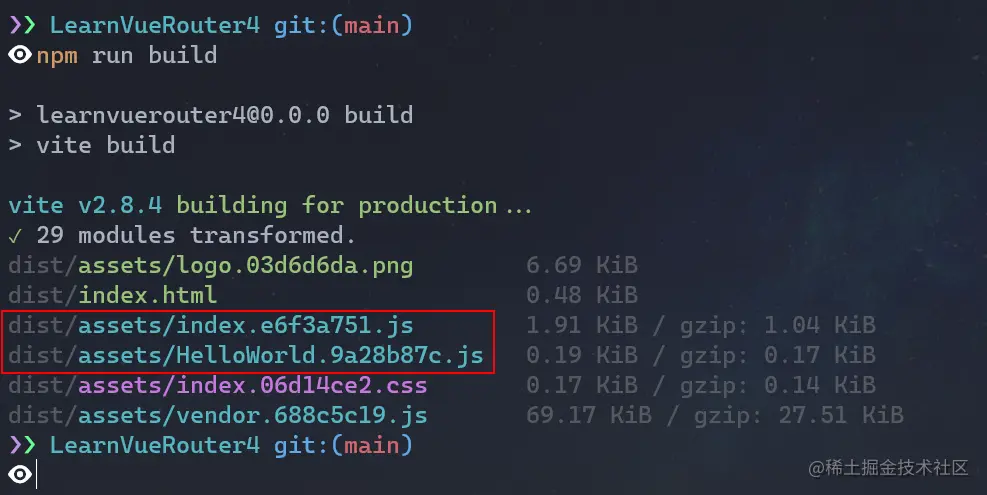
當我們的應用越來越大時,打包後的JavaScript程式碼也會特別的大,這個時候需要我們將整個應用拆分為不同的塊,而Vue Router就支援這個功能,我們只需要使用動態匯入替換靜態匯入即可,就比如上面那段程式碼:
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue')然後打包(webpack、Vite)工具就會將這些動態匯入的元件單獨打包,如下圖所示:
動態路由
VueRouter允許我們動態的去設定路由匹配規則,例如我們現在有一個User元件,元件的內容會根據不同的ID展示不同的內容,設定方法只需要通過:引數名的形式去設定即可。
例如:
{
path: '/user/:id',
component: () => import('@/components/User')
}在模板中跳轉如下:
<router-link to="/user/10010"></router-link>
或者通過useRouter這個hook提供的push方法,例如:
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router'
const {push} = useRouter()
push({
path: '/user',
params: { id: 10010 }
})
// 或者
let id = 10010
push('/user/' + id)獲取路由地址可以通過useRoute這個hook,用法與useRouter一致。
匹配所有路由
VueRouter的動態路由允許我們匹配哪些沒有匹配到的路由,範例程式碼如下:
{
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)',
component: () => import('./components/Page404.vue'),
},當前面的路由匹配未成功時,就會匹配這個路由。
路由巢狀
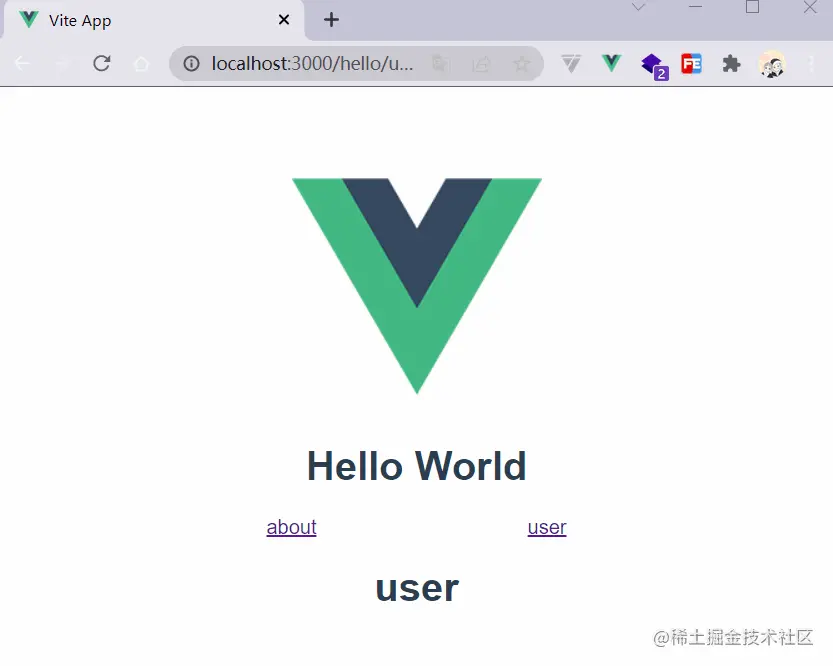
現在我們有一個需求,就是在HelloWorld元件下存兩個元件,需要切換著兩個元件。
這個時候路由巢狀的就發揮作用了,其實路由巢狀比較簡單,就是通過路由設定中的一個children屬性來實現,範例程式碼如下:
HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<div
style="
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 240px;
margin: 0 auto;
"
>
<router-link to="about">about</router-link>
<router-link to="user">user</router-link>
</div>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>router.js
{
path: '/hello',
// 路由懶載入引入元件
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'about',
component: () => import('./components/about.vue'),
},
{
path: 'user',
component: () => import('./components/user.vue'),
},
],
},子元件比較簡單,只有一個<h1>標籤,最終效果如下:
寫在最後
這篇文章到這就結束了,總的來說比較簡單沒有什麼太深入的東西,比較適合入門。
【相關視訊教學推薦:、】
以上就是如何使用VueRouter4.x?快速上手指南的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!