體驗SRCNN和FSRCNN兩種影象超分網路應用
摘要:影象超分即超解析度,將影象從模糊的狀態變清晰。
本文分享自華為雲社群《影象超分實驗:SRCNN/FSRCNN》,作者:zstar。
影象超分即超解析度,將影象從模糊的狀態變清晰。本文對BSDS500資料集進行超分實驗。
1.實驗目標
輸入大小為h×w的影象X,輸出為一個sh×sw的影象 Y,s為放大倍數。
2.資料集簡介
本次實驗採用的是 BSDS500 資料集,其中訓練集包含 200 張影象,驗證集包含 100 張影象,測試集包含 200 張影象。
資料集來源:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_42028424/11045313
3.資料預處理
資料預處理包含兩個步驟:
(1)將圖片轉換成YCbCr模式
由於RGB顏色模式色調、色度、飽和度三者混在一起難以分開,因此將其轉換成 YcbCr 顏色模式,Y是指亮度分量,Cb表示 RGB輸入訊號藍色部分與 RGB 訊號亮度值之間的差異,Cr 表示 RGB 輸入訊號紅色部分與 RGB 訊號亮度值之間的差異。
(2)將圖片裁剪成 300×300 的正方形
由於後面採用的神經網路輸入圖片要求長寬一致,而 BSDS500 資料集中的圖片長寬並不一致,因此需要對其進行裁剪。這裡採用的方式是先定位到每個圖片中心,然後以圖片中心為基準,向四個方向拓展 150 個畫素,從而將圖片裁剪成 300×300 的正方形。
相關程式碼:
def is_image_file(filename): return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in [".png", ".jpg", ".jpeg"]) def load_img(filepath): img = Image.open(filepath).convert('YCbCr') y, _, _ = img.split() return y CROP_SIZE = 300 class DatasetFromFolder(Dataset): def __init__(self, image_dir, zoom_factor): super(DatasetFromFolder, self).__init__() self.image_filenames = [join(image_dir, x) for x in listdir(image_dir) if is_image_file(x)] crop_size = CROP_SIZE - (CROP_SIZE % zoom_factor) # 從圖片中心裁剪成300*300 self.input_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.CenterCrop(crop_size), transforms.Resize( crop_size // zoom_factor), transforms.Resize( crop_size, interpolation=Image.BICUBIC), # BICUBIC 雙三次插值 transforms.ToTensor()]) self.target_transform = transforms.Compose( [transforms.CenterCrop(crop_size), transforms.ToTensor()]) def __getitem__(self, index): input = load_img(self.image_filenames[index]) target = input.copy() input = self.input_transform(input) target = self.target_transform(target) return input, target def __len__(self): return len(self.image_filenames)
4.網路結構
本次實驗嘗試了SRCNN和FSRCNN兩個網路。
4.1 SRCNN
SRCNN 由 2014 年 Chao Dong 等人提出,是深度學習在影象超分領域的開篇之作。其網路結構如下圖所示:
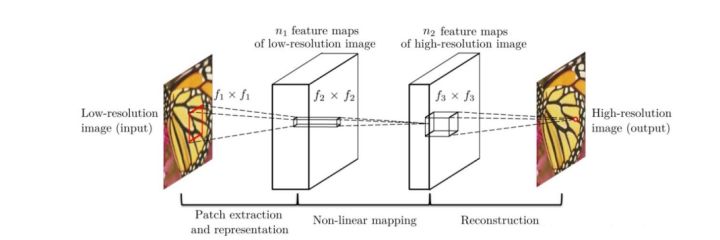
該網路對於一個低解析度影象,先使用雙三次插值將其放大到目標大小,再通過三層折積網路做非線性對映,得到的結果作為高解析度影象輸出。
作者對於這三層折積層的解釋:
(1)特徵塊提取和表示:此操作從低解析度影象Y中提取重疊特徵塊,並將每個特徵塊表示為一個高維向量。這些向量包括一組特徵圖,其數量等於向量的維數。
(2)非線性對映:該操作將每個高維向量非線性對映到另一個高維向量。每個對映向量在概念上都是高解析度特徵塊的表示。這些向量同樣包括另一組特徵圖。
(3)重建:該操作聚合上述高解析度patch-wise(介於畫素級別和影象級別的區域)表示,生成最終的高解析度影象。
各層結構:
- 輸入:處理後的低解析度影象
- 折積層 1:採用 9×9 的折積核
- 折積層 2:採用 1×1 的折積核
- 折積層 3:採用 5×5 的折積核
- 輸出:高解析度影象
模型結構程式碼:
class SRCNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, upscale_factor): super(SRCNN, self).__init__() self.relu = nn.ReLU() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(64, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, upscale_factor ** 2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(upscale_factor) self._initialize_weights() def _initialize_weights(self): init.orthogonal_(self.conv1.weight, init.calculate_gain('relu')) init.orthogonal_(self.conv2.weight, init.calculate_gain('relu')) init.orthogonal_(self.conv3.weight, init.calculate_gain('relu')) init.orthogonal_(self.conv4.weight) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.conv2(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.conv3(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.conv4(x) x = self.pixel_shuffle(x) return x
4.2 FSRCNN
FSRCNN 由 2016 年 Chao Dong 等人提出,與 SRCNN 是相同作者。其網路結構如下圖所示:
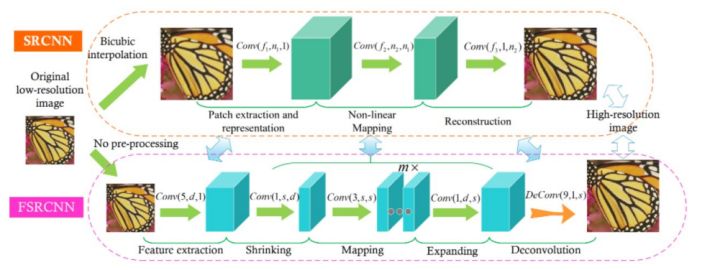
FSRCNN在SRCNN基礎上做了如下改變:
1.FSRCNN直接採用低分辨的影象作為輸入,不同於SRCNN需要先對低解析度的影象進行雙三次插值然後作為輸入;
2.FSRCNN在網路的最後採用反折積層實現上取樣;
3.FSRCNN中沒有非線性對映,相應地出現了收縮、對映和擴充套件;
4.FSRCNN選擇更小尺寸的濾波器和更深的網路結構。
各層結構:
- 輸入層:FSRCNN不使用bicubic插值來對輸入影象做上取樣,它直接進入特徵提取層
- 特徵提取層:採用1 × d × ( 5 × 5 )的折積層提取
- 收縮層:採用d × s × ( 1 × 1 ) 的折積層去減少通道數,來減少模型複雜度
- 對映層:採用s × s × ( 3 × 3 ) 折積層去增加模型非線性度來實現LR → SR 的對映
- 擴張層:該層和收縮層是對稱的,採用s × d × ( 1 × 1 ) 折積層去增加重建的表現力
- 反折積層:s × 1 × ( 9 × 9 )
- 輸出層:輸出HR影象
模型結構程式碼:
class FSRCNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, scale_factor, num_channels=1, d=56, s=12, m=4): super(FSRCNN, self).__init__() self.first_part = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(num_channels, d, kernel_size=5, padding=5//2), nn.PReLU(d) ) self.mid_part = [nn.Conv2d(d, s, kernel_size=1), nn.PReLU(s)] for _ in range(m): self.mid_part.extend([nn.Conv2d(s, s, kernel_size=3, padding=3//2), nn.PReLU(s)]) self.mid_part.extend([nn.Conv2d(s, d, kernel_size=1), nn.PReLU(d)]) self.mid_part = nn.Sequential(*self.mid_part) self.last_part = nn.ConvTranspose2d(d, num_channels, kernel_size=9, stride=scale_factor, padding=9//2, output_padding=scale_factor-1) self._initialize_weights() def _initialize_weights(self): for m in self.first_part: if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, mean=0.0, std=math.sqrt(2/(m.out_channels*m.weight.data[0][0].numel()))) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias.data) for m in self.mid_part: if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, mean=0.0, std=math.sqrt(2/(m.out_channels*m.weight.data[0][0].numel()))) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias.data) nn.init.normal_(self.last_part.weight.data, mean=0.0, std=0.001) nn.init.zeros_(self.last_part.bias.data) def forward(self, x): x = self.first_part(x) x = self.mid_part(x) x = self.last_part(x) return x
5.評估指標
本次實驗嘗試了 PSNR 和 SSIM 兩個指標。
5.1 PSNR
PSNR(Peak Signal to Noise Ratio)為峰值訊雜比,計算公式如下:
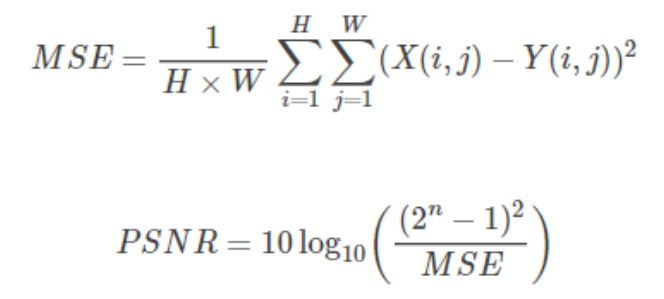
其中,n為每畫素的位元數。
PSNR 的單位是dB,數值越大表示失真越小,一般認為 PSNR 在 38 以上的時候,人眼就無法區分兩幅圖片了。
相關程式碼:
def psnr(loss): return 10 * log10(1 / loss.item())
5.2 SSIM
SSIM(Structural Similarity)為結構相似性,由三個對比模組組成:亮度、對比度、結構。
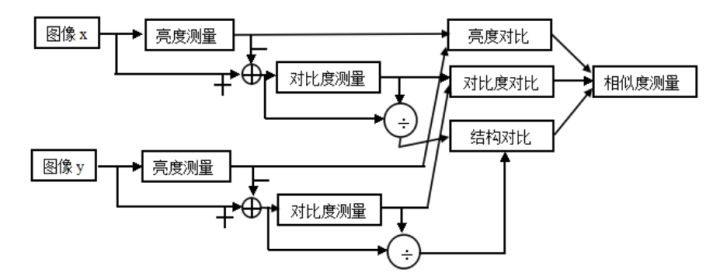
亮度對比函數
影象的平均灰度計算公式:
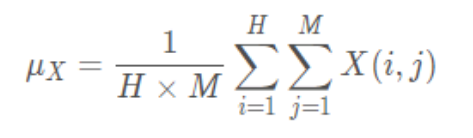
亮度對比函數計算公式:

對比度對比函數
影象的標準差計算公式:
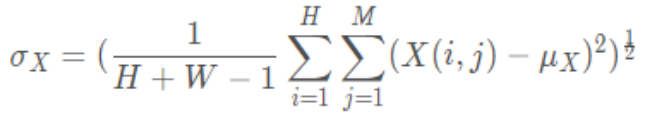
對比度對比函數計算公式:
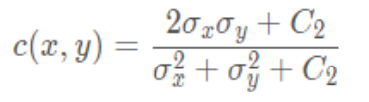
結構對比函數
結構對比函數計算公式:

綜合上述三個部分,得到 SSIM 計算公式:
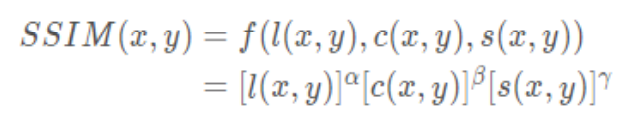
其中,\alphaα,\betaβ,\gammaγ > 0,用來調整這三個模組的重要性。
SSIM 函數的值域為[0, 1], 值越大說明影象失真越小,兩幅影象越相似。
相關程式碼:
由於pytorch沒有類似tensorflow類似tf.image.ssim這樣計算SSIM的介面,因此根據公式進行自定義函數用來計算
""" 計算ssim函數 """ # 計算一維的高斯分佈向量 def gaussian(window_size, sigma): gauss = torch.Tensor( [exp(-(x - window_size//2)**2/float(2*sigma**2)) for x in range(window_size)]) return gauss/gauss.sum() # 建立高斯核,通過兩個一維高斯分佈向量進行矩陣乘法得到 # 可以設定channel引數拓展為3通道 def create_window(window_size, channel=1): _1D_window = gaussian(window_size, 1.5).unsqueeze(1) _2D_window = _1D_window.mm( _1D_window.t()).float().unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) window = _2D_window.expand( channel, 1, window_size, window_size).contiguous() return window # 計算SSIM # 直接使用SSIM的公式,但是在計算均值時,不是直接求畫素平均值,而是採用歸一化的高斯核折積來代替。 # 在計算方差和協方差時用到了公式Var(X)=E[X^2]-E[X]^2, cov(X,Y)=E[XY]-E[X]E[Y]. def ssim(img1, img2, window_size=11, window=None, size_average=True, full=False, val_range=None): # Value range can be different from 255. Other common ranges are 1 (sigmoid) and 2 (tanh). if val_range is None: if torch.max(img1) > 128: max_val = 255 else: max_val = 1 if torch.min(img1) < -0.5: min_val = -1 else: min_val = 0 L = max_val - min_val else: L = val_range padd = 0 (_, channel, height, width) = img1.size() if window is None: real_size = min(window_size, height, width) window = create_window(real_size, channel=channel).to(img1.device) mu1 = F.conv2d(img1, window, padding=padd, groups=channel) mu2 = F.conv2d(img2, window, padding=padd, groups=channel) mu1_sq = mu1.pow(2) mu2_sq = mu2.pow(2) mu1_mu2 = mu1 * mu2 sigma1_sq = F.conv2d(img1 * img1, window, padding=padd, groups=channel) - mu1_sq sigma2_sq = F.conv2d(img2 * img2, window, padding=padd, groups=channel) - mu2_sq sigma12 = F.conv2d(img1 * img2, window, padding=padd, groups=channel) - mu1_mu2 C1 = (0.01 * L) ** 2 C2 = (0.03 * L) ** 2 v1 = 2.0 * sigma12 + C2 v2 = sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2 cs = torch.mean(v1 / v2) # contrast sensitivity ssim_map = ((2 * mu1_mu2 + C1) * v1) / ((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1) * v2) if size_average: ret = ssim_map.mean() else: ret = ssim_map.mean(1).mean(1).mean(1) if full: return ret, cs return ret class SSIM(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, window_size=11, size_average=True, val_range=None): super(SSIM, self).__init__() self.window_size = window_size self.size_average = size_average self.val_range = val_range # Assume 1 channel for SSIM self.channel = 1 self.window = create_window(window_size) def forward(self, img1, img2): (_, channel, _, _) = img1.size() if channel == self.channel and self.window.dtype == img1.dtype: window = self.window else: window = create_window(self.window_size, channel).to( img1.device).type(img1.dtype) self.window = window self.channel = channel return ssim(img1, img2, window=window, window_size=self.window_size, size_average=self.size_average)
6.模型訓練/測試
設定 epoch 為 500 次,儲存驗證集上 PSNR 最高的模型。兩個模型在測試集上的表現如下表所示:

從結果可以發現,FSRCNN 的 PSNR 比 SRCNN 低,但 FSRCNN 的 SSIM 比 SRCNN 高,說明 PSNR 和 SSIM 並不存在完全正相關的關係。
訓練/驗證程式碼:
model = FSRCNN(1).to(device) criterion = nn.MSELoss() optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2) scheduler = MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[50, 75, 100], gamma=0.1) best_psnr = 0.0 for epoch in range(nb_epochs): # Train epoch_loss = 0 for iteration, batch in enumerate(trainloader): input, target = batch[0].to(device), batch[1].to(device) optimizer.zero_grad() out = model(input) loss = criterion(out, target) loss.backward() optimizer.step() epoch_loss += loss.item() print(f"Epoch {epoch}. Training loss: {epoch_loss / len(trainloader)}") # Val sum_psnr = 0.0 sum_ssim = 0.0 with torch.no_grad(): for batch in valloader: input, target = batch[0].to(device), batch[1].to(device) out = model(input) loss = criterion(out, target) pr = psnr(loss) sm = ssim(input, out) sum_psnr += pr sum_ssim += sm print(f"Average PSNR: {sum_psnr / len(valloader)} dB.") print(f"Average SSIM: {sum_ssim / len(valloader)} ") avg_psnr = sum_psnr / len(valloader) if avg_psnr >= best_psnr: best_psnr = avg_psnr torch.save(model, r"best_model_FSRCNN.pth") scheduler.step()
測試程式碼:
BATCH_SIZE = 4 model_path = "best_model_FSRCNN.pth" testset = DatasetFromFolder(r"./data/images/test", zoom_factor) testloader = DataLoader(dataset=testset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=NUM_WORKERS) sum_psnr = 0.0 sum_ssim = 0.0 model = torch.load(model_path).to(device) criterion = nn.MSELoss() with torch.no_grad(): for batch in testloader: input, target = batch[0].to(device), batch[1].to(device) out = model(input) loss = criterion(out, target) pr = psnr(loss) sm = ssim(input, out) sum_psnr += pr sum_ssim += sm print(f"Test Average PSNR: {sum_psnr / len(testloader)} dB") print(f"Test Average SSIM: {sum_ssim / len(testloader)} ")
7.實圖測試
為了直觀感受兩個模型的效果,我用自己拍攝的圖進行實圖測試,效果如下:
s=1(放大倍數=1)
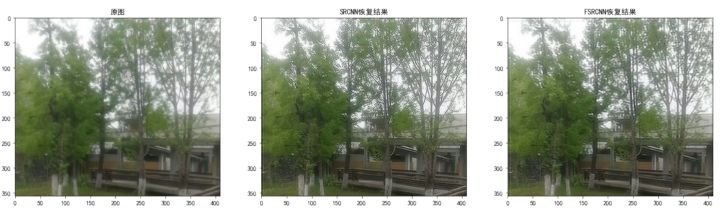
當放大倍數=1時,SRCNN的超分結果比FSRCNN的超分效果要更好一些,這和兩個模型平均 PSNR 的數值相吻合。
s=2(放大倍數=2)
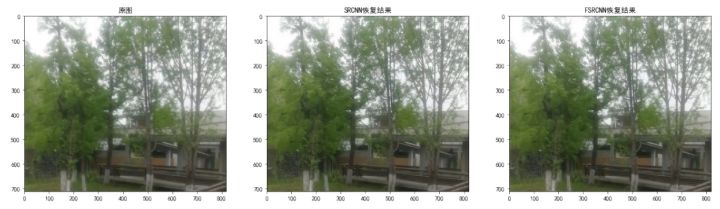
當放大倍數=2時,SRCNN 的超分結果和 FSRCNN 的超分效果相差不大。
相關程式碼:
# 引數設定 zoom_factor = 1 model = "best_model_SRCNN.pth" model2 = "best_model_FSRCNN.pth" image = "tree.png" cuda = 'store_true' device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 讀取圖片 img = Image.open(image).convert('YCbCr') img = img.resize((int(img.size[0] * zoom_factor), int(img.size[1] * zoom_factor)), Image.BICUBIC) y, cb, cr = img.split() img_to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor() input = img_to_tensor(y).view(1, -1, y.size[1], y.size[0]).to(device) # 輸出圖片 model = torch.load(model).to(device) out = model(input).cpu() out_img_y = out[0].detach().numpy() out_img_y *= 255.0 out_img_y = out_img_y.clip(0, 255) out_img_y = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(out_img_y[0]), mode='L') out_img = Image.merge('YCbCr', [out_img_y, cb, cr]).convert('RGB') model2 = torch.load(model2).to(device) out2 = model2(input).cpu() out_img_y2 = out2[0].detach().numpy() out_img_y2 *= 255.0 out_img_y2 = out_img_y2.clip(0, 255) out_img_y2 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(out_img_y2[0]), mode='L') out_img2 = Image.merge('YCbCr', [out_img_y2, cb, cr]).convert('RGB') # 繪圖顯示 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(20, 20)) ax[0].imshow(img) ax[0].set_title("原圖") ax[1].imshow(out_img) ax[1].set_title("SRCNN恢復結果") ax[2].imshow(out_img2) ax[2].set_title("FSRCNN恢復結果") plt.show() fig.savefig(r"tree2.png")