【RocketMQ】訊息的刷盤機制
刷盤策略
CommitLog的asyncPutMessage方法中可以看到在寫入訊息之後,呼叫了submitFlushRequest方法執行刷盤策略:
public class CommitLog {
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
// ...
try {
// 獲取上一次寫入的檔案
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile();
// ...
// 寫入訊息
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback, putMessageContext);
// ...
} finally {
beginTimeInLock = 0;
putMessageLock.unlock();
}
// ...
// 執行刷盤
CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> flushResultFuture = submitFlushRequest(result, msg);
// ...
}
}
刷盤有兩種策略:
-
同步刷盤,表示訊息寫入到記憶體之後需要立刻刷到磁碟檔案中。
同步刷盤會構建
GroupCommitRequest組提交請求並設定本次刷盤後的位置偏移量的值(寫入位置偏移量+寫入資料位元組數),然後將請求新增到flushDiskWatcher和GroupCommitService中進行刷盤。 -
非同步刷盤,表示訊息寫入記憶體成功之後就返回,由MQ定時將資料刷入到磁碟中,會有一定的資料丟失風險。
public class CommitLog {
// 監控刷盤
private final FlushDiskWatcher flushDiskWatcher;
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> submitFlushRequest(AppendMessageResult result, MessageExt messageExt) {
// 是否是同步刷盤
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
// 獲取GroupCommitService
final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
// 是否等待
if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
// 構建組提交請求,傳入本次刷盤後位置的偏移量:寫入位置偏移量+寫入資料位元組數
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes(),
this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
// 新增到wather中
flushDiskWatcher.add(request);
// 新增到service
service.putRequest(request);
// 返回
return request.future();
} else {
service.wakeup();
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);
}
}
// 如果是非同步刷盤
else {
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);
}
}
}
同步刷盤
如果使用的是同步刷盤,首先獲取了GroupCommitService,然後構建GroupCommitRequest組提交請求,將請求新增到flushDiskWatcher和GroupCommitService中,其中flushDiskWatcher用於監控刷盤是否超時,GroupCommitService用於提交刷盤資料。
構建GroupCommitRequest提交請求
GroupCommitRequest是CommitLog的內部類:
- nextOffset:寫入位置偏移量+寫入資料位元組數,也就是本次刷盤成功後應該對應的flush偏移量
- flushOKFuture:刷盤結果
- deadLine:刷盤的限定時間,值為當前時間 + 傳入的超時時間,超過限定時間還未刷盤完畢會被認為超時
public class CommitLog {
public static class GroupCommitRequest {
private final long nextOffset;
// 刷盤狀態
private CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> flushOKFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
private final long deadLine;// 刷盤的限定時間,超過限定時間還未刷盤完畢會被認為超時
public GroupCommitRequest(long nextOffset, long timeoutMillis) {
this.nextOffset = nextOffset;
// 設定限定時間:當前時間 + 超時時間
this.deadLine = System.nanoTime() + (timeoutMillis * 1_000_000);
}
public void wakeupCustomer(final PutMessageStatus putMessageStatus) {
// 結束刷盤,設定刷盤狀態
this.flushOKFuture.complete(putMessageStatus);
}
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> future() {
// 返回刷盤狀態
return flushOKFuture;
}
}
}
GroupCommitService處理刷盤
GroupCommitService是CommitLog的內部類,從繼承關係中可知它實現了Runnable介面,在run方法呼叫waitForRunning等待刷盤請求的提交,然後處理刷盤,不過這個執行緒是在什麼時候啟動的呢?
public class CommitLog {
/**
* GroupCommit Service
*/
class GroupCommitService extends FlushCommitLogService {
// ...
// run方法
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
// 等待刷盤請求的到來
this.waitForRunning(10);
// 處理刷盤
this.doCommit();
} catch (Exception e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
// ...
}
}
}
刷盤執行緒的啟動
在BrokerController的啟動方法中,可以看到呼叫了messageStore的start方法,前面可知使用的是DefaultMessageStore,進入到DefaultMessageStore的start方法,它又呼叫了commitLog的start方法,在CommitLog的start方法中,啟動了刷盤的執行緒和監控刷盤的執行緒:
public class BrokerController {
public void start() throws Exception {
if (this.messageStore != null) {
// 啟動
this.messageStore.start();
}
// ...
}
}
public class DefaultMessageStore implements MessageStore {
/**
* @throws Exception
*/
public void start() throws Exception {
// ...
this.flushConsumeQueueService.start();
// 呼叫CommitLog的啟動方法
this.commitLog.start();
this.storeStatsService.start();
// ...
}
}
public class CommitLog {
private final FlushCommitLogService flushCommitLogService; // 刷盤
private final FlushDiskWatcher flushDiskWatcher; // 監控刷盤
private final FlushCommitLogService commitLogService; // commitLogService
public void start() {
// 啟動刷盤的執行緒
this.flushCommitLogService.start();
flushDiskWatcher.setDaemon(true);
// 啟動監控刷盤的執行緒
flushDiskWatcher.start();
if (defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
this.commitLogService.start();
}
}
}
刷盤請求的處理
既然知道了執行緒在何時啟動的,接下來詳細看一下GroupCommitService是如何處理刷盤提交請求的。
前面知道在GroupCommitService的run方法中,呼叫了waitForRunning方法等待刷盤請求,waitForRunning在GroupCommitService父類別ServiceThread中實現。ServiceThread是一個抽象類,實現了Runnable介面,裡面使用了CountDownLatch進行執行緒間的通訊,大小設為1。
waitForRunning方法在進入的時候先判斷hasNotified是否為true(已通知),並嘗試將其更新為false(未通知),由於hasNotified的初始化值為false,所以首次進入的時候條件不成立,不會進入到這個處理邏輯,會繼續執行後面的程式碼。
接著呼叫 waitPoint的reset方法將其重置為1,並呼叫waitPoint的await方法進行等待:
// ServiceThread
public abstract class ServiceThread implements Runnable {
// 是否通知,初始化為false
protected volatile AtomicBoolean hasNotified = new AtomicBoolean(false);
// CountDownLatch用於執行緒間的通訊
protected final CountDownLatch2 waitPoint = new CountDownLatch2(1);
// 等待執行
protected void waitForRunning(long interval) {
// 判斷hasNotified是否為true,並嘗試將其更新為false
if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
// 呼叫onWaitEnd
this.onWaitEnd();
return;
}
// 重置waitPoint的值,也就是值為1
waitPoint.reset();
try {
// 會一直等待waitPoint值降為0
waitPoint.await(interval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("Interrupted", e);
} finally {
// 是否被通知設定為false
hasNotified.set(false);
this.onWaitEnd();
}
}
}
一、新增刷盤請求,喚醒刷盤執行緒
上面可知需要刷盤的時候呼叫了GroupCommitService的putRequest方法新增刷盤請求,在putRequest方法中,將刷盤請求GroupCommitRequest新增到了requestsWrite組提交寫請求連結串列中,然後呼叫wakeup方法喚醒刷盤執行緒,wakeup方法在它的父類別ServiceThread中實現。
在wakeup方法中可以看到,首先將hasNotified更改為了true表示處於已通知狀態,然後呼叫了countDown方法,此時waitPoint值變成0,就會喚醒之前waitForRunning方法中一直在等待的執行緒。
public class CommitLog {
/**
* 組提交Service
*/
class GroupCommitService extends FlushCommitLogService {
// 組提交寫請求連結串列
private volatile LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite = new LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest>();
// ...
// 新增提交請求
public synchronized void putRequest(final GroupCommitRequest request) {
// 加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
// 加入到寫請求連結串列
this.requestsWrite.add(request);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
// 喚醒執行緒執行提交任務
this.wakeup();
}
// ...
}
}
// ServiceThread
public abstract class ServiceThread implements Runnable {
// CountDownLatch用於執行緒間的通訊
protected final CountDownLatch2 waitPoint = new CountDownLatch2(1);
// 喚醒刷盤執行緒
public void wakeup() {
// 更改狀態為已通知狀態
if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// waitPoint的值減1,由於大小設定為1,減1之後變為0,會喚醒等待的執行緒
waitPoint.countDown();
}
}
// ...
}
二、執行緒被喚醒,執行刷盤前的操作
waitForRunning方法中的await方法一直在等待countdown的值變為0,當上一步呼叫了wakeup後,就會喚醒該執行緒,然後開始往下執行,在finally中可以看到將是否被通知hasNotified又設定為了false,然後呼叫了onWaitEnd方法,GroupCommitService方法中重寫了該方法,裡面又呼叫了swapRequests方法將讀寫請求列表的資料進行了交換,putRequest方法中將提交的刷盤請求放在了寫連結串列中,經過交換,資料會被放在讀連結串列中,後續進行刷盤時會從讀連結串列中獲取請求進行處理:
// ServiceThread
public abstract class ServiceThread implements Runnable {
// CountDownLatch
protected final CountDownLatch2 waitPoint = new CountDownLatch2(1);
// 等待執行
protected void waitForRunning(long interval) {
if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
// 交換
this.onWaitEnd();
return;
}
// 重置
waitPoint.reset();
try {
// 會一直等待countdown為0
waitPoint.await(interval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("Interrupted", e);
} finally {
// 是否被通知設定為false
hasNotified.set(false);
this.onWaitEnd();
}
}
}
public class CommitLog {
/**
* 組提交Service
*/
class GroupCommitService extends FlushCommitLogService {
// 組提交寫請求連結串列
private volatile LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite = new LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest>();
// 組提交讀請求連結串列
private volatile LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> requestsRead = new LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest>();
@Override
protected void onWaitEnd() {
// 交換讀寫請求列表的資料請求
this.swapRequests();
}
private void swapRequests() {
// 加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
// 將讀寫請求連結串列的資料進行交換
LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> tmp = this.requestsWrite;
this.requestsWrite = this.requestsRead;
this.requestsRead = tmp;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// ...
}
}
這裡使用讀寫連結串列進行交換應該是為了提升效能,如果只使用一個連結串列,在提交請求的時候需要往連結串列中新增請求,此時需要加鎖,而刷盤執行緒在處理完請求之後是需要從連結串列中移除請求的,假設新增請求時加的鎖還未釋放,刷盤執行緒就要一直等待,而新增和處理完全可以同時進行,所以使用了兩個連結串列,在新增請求的時候使用寫連結串列,處理請求的時候對讀寫連結串列的資料進行交換使用讀連結串列,這樣只需在交換資料的時候加鎖,以此來提升效能。
三、執行刷盤
waitForRunning執行完畢後,會回到GroupCommitService中的run方法開始繼續往後執行程式碼,從程式碼中可以看到接下來會呼叫doCommit方法執行刷盤。
doCommit方法中對讀連結串列中的資料進行了判空,如果不為空,進行遍歷處理每一個提交請求,處理邏輯如下:
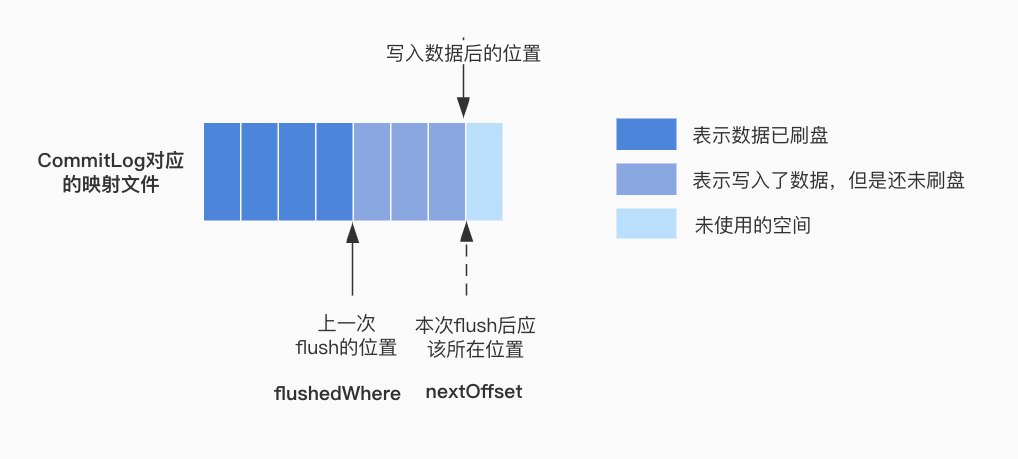
- 獲取CommitLog對映檔案記錄的刷盤位置偏移量
flushedWhere,判斷是否大於請求設定的刷盤位置偏移量nextOffset,正常情況下flush的位置應該小於本次刷入資料後的偏移量,所以如果flush位置大於等於本次請求設定的flush偏移量,本次將不能進行刷盤
-
開啟一個迴圈,呼叫
mappedFileQueue的flush方法執行刷盤(具體的實現在非同步刷盤的時候再看),由於CommitLog大小為1G,所以本次刷完之後,如果當前已經刷入的偏移量小於請求設定的位置,表示資料未刷完,需要繼續刷,反之表示資料已經刷完,flushOK為true,for迴圈條件不滿足結束執行。 -
請求處理之後會清空讀連結串列。
public class CommitLog {
/**
* 組提交Service
*/
class GroupCommitService extends FlushCommitLogService {
// 執行
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
// 如果沒有停止
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
// 等待喚醒刷盤執行緒
this.waitForRunning(10);
// 進行提交
this.doCommit();
} catch (Exception e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
// 睡眠10毫秒
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " Exception, ", e);
}
synchronized (this) {
this.swapRequests();
}
// 停止之前提交一次
this.doCommit();
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
// 提交刷盤
private void doCommit() {
// 如果不為空
if (!this.requestsRead.isEmpty()) {
// 遍歷刷盤請求
for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) {
// 獲取對映檔案的flush位置,判斷是否大於請求設定的刷盤位置
boolean flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
for (int i = 0; i < 2 && !flushOK; i++) {
// 進行刷盤
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
// 由於CommitLog大小為1G,所以本次刷完之後,如果當前已經刷入的偏移量小於請求設定的位置,表示資料未刷完,需要繼續刷,反之表示資料已經刷完,flushOK為true,for迴圈條件不滿足結束執行
flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
}
// 設定刷盤結果
req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK ? PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK : PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
// 請求處理完之後清空連結串列
this.requestsRead = new LinkedList<>();
} else {
// Because of individual messages is set to not sync flush, it
// will come to this process
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
}
}
}
}
刷盤超時監控
FlushDiskWatcher用於監控刷盤請求的耗時,它也繼承了ServiceThread,在Broker啟動時開啟了該執行緒,在run方法中,使用while迴圈,只要服務未停止,會一直從阻塞佇列中獲取提交的刷盤請求,開啟while迴圈隔一段時間判斷一下刷盤是否完成,如果未完成,會做如下判斷:
- 使用當前時間減去請求設定的刷盤截止時間,如果已經超過截止時間,說明刷盤時間已經超時,呼叫
wakeupCustomer方法設定刷盤結果為已超時 - 如果未超時,為了避免當前執行緒頻繁的進行判斷,將當前執行緒睡眠一會兒,睡眠的計算方式是使用刷盤請求設定的截止時間 - 當前時間,表示剩餘的時間,然後除以1000000化為毫秒,得到距離刷盤截止時間的毫秒數sleepTime:
sleepTime如果為0,只能是當前時間等於截止時間,也就是到了截止時間,此時同樣呼叫wakeupCustomer方法設定刷盤結果為已超時sleepTime不為0,在10毫秒和sleepTime的值之間取較小的那個作為睡眠的毫秒數將當前執行緒睡眠,等待刷盤任務執行
public class FlushDiskWatcher extends ServiceThread {
private static final InternalLogger log = InternalLoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggerName.STORE_LOGGER_NAME);
// 阻塞佇列,存放提交請求
private final LinkedBlockingQueue<GroupCommitRequest> commitRequests = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
@Override
public String getServiceName() {
return FlushDiskWatcher.class.getSimpleName();
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 如果未停止
while (!isStopped()) {
GroupCommitRequest request = null;
try {
// 從阻塞佇列中獲取提交請求
request = commitRequests.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("take flush disk commit request, but interrupted, this may caused by shutdown");
continue;
}
// 如果還未完成
while (!request.future().isDone()) {
long now = System.nanoTime();
// 如果已經超時
if (now - request.getDeadLine() >= 0) {
// 設定刷盤結果為超時
request.wakeupCustomer(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
break;
}
// 避免頻繁的判斷,使用(截止時間 - 當前時間)/1000000 計算一個毫秒數
long sleepTime = (request.getDeadLine() - now) / 1_000_000;
// 在計算的毫秒數與10之間取最小的
sleepTime = Math.min(10, sleepTime);
// 如果sleepTime為0表示已經到了截止時間
if (sleepTime == 0) {
// 設定刷盤結果為超時
request.wakeupCustomer(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
break;
}
try {
// 睡眠等待刷盤任務的執行
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn(
"An exception occurred while waiting for flushing disk to complete. this may caused by shutdown");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
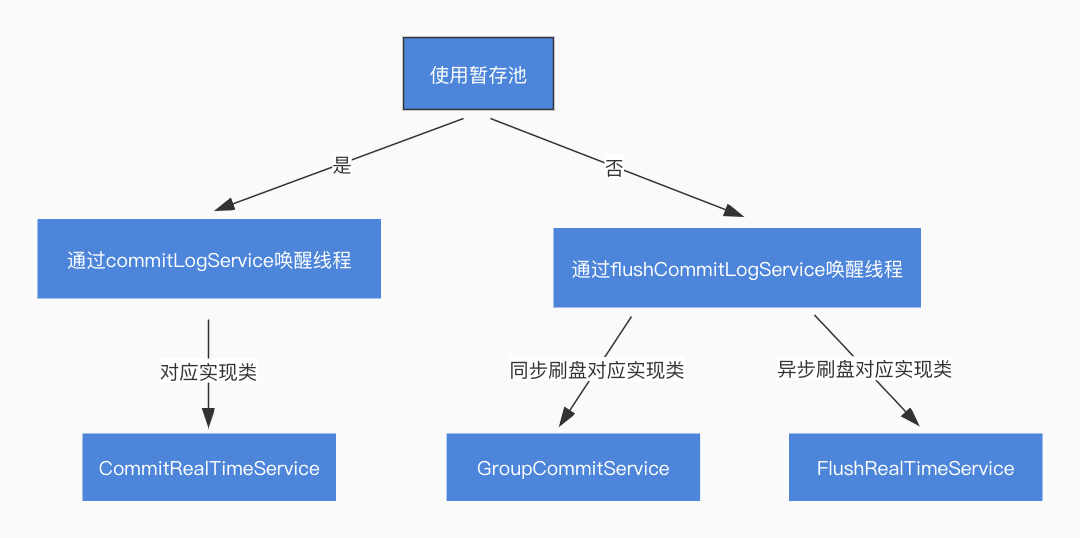
非同步刷盤
上面講解了同步刷盤,接下來去看下非同步刷盤,首先會判斷是否使用了暫存池,如果未開啟呼叫flushCommitLogService的wakeup喚醒刷盤執行緒,否則使用commitLogService先將資料寫入到FileChannel,然後統一進行刷盤:
public class CommitLog {
private final FlushDiskWatcher flushDiskWatcher;
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> submitFlushRequest(AppendMessageResult result, MessageExt messageExt) {
// 是否是同步刷盤
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
// ...
}
// 如果是非同步刷盤
else {
// 如果未使用暫存池
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
// 喚醒刷盤執行緒進行刷盤
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
// 如果使用暫存池,使用commitLogService,先將資料寫入到FILECHANNEL,然後統一進行刷盤
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
// 返回結果
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);
}
}
}
在CommitLog的建構函式中可以看到,commitLogService使用的是CommitRealTimeService進行範例化的,flushCommitLogService需要根據設定決定使用哪種型別進行範例化:
- 如果是同步刷盤,使用
GroupCommitService,由前面的同步刷盤可知,使用的就是GroupCommitService進行刷盤的。 - 如果是非同步刷盤,使用
FlushRealTimeService。
所以接下來需要關注CommitRealTimeService和FlushRealTimeService:
public class CommitLog {
private final FlushCommitLogService flushCommitLogService;
// 刷盤Service
private final FlushCommitLogService commitLogService;
public CommitLog(final DefaultMessageStore defaultMessageStore) {
// 如果設定的同步刷盤
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
// 使用GroupCommitService
this.flushCommitLogService = new GroupCommitService();
} else {
// 使用FlushRealTimeService
this.flushCommitLogService = new FlushRealTimeService();
}
// commitLogService
this.commitLogService = new CommitRealTimeService();
}
}
CommitRealTimeService

在開啟暫存池時,會使用CommitRealTimeService,它繼承了FlushCommitLogService,所以會實現run方法,處理邏輯如下:
- 從設定資訊中獲取提交間隔、每次提交的最少頁數和兩次提交的最大間隔時間
- 如果當前時間大於上次提交時間+兩次提交的最大間隔時間,意味著已經有比較長的一段時間沒有進行提交了,需要儘快刷盤,此時將每次提交的最少頁數設定為0不限制提交頁數
- 呼叫
mappedFileQueue的commit方法進行提交,並返回提交的結果:- 如果結果為true表示未提交任何資料
- 如果結果為false表示進行了資料提交,需要等待刷盤
- 判斷提交返回結果是否返回false,如果是呼叫
flushCommitLogService的wakeup方法喚醒刷盤執行緒,進行刷盤 - 呼叫
waitForRunning等待下一次提交處理
class CommitRealTimeService extends FlushCommitLogService {
// 上次提交時間戳
private long lastCommitTimestamp = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
// 如果未停止
while (!this.isStopped()) {
// 獲取提交間隔
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitIntervalCommitLog();
// 一次提交的最少頁數
int commitDataLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogLeastPages();
// 兩次提交的最大間隔時間
int commitDataThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogThoroughInterval();
// 開始時間
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果當前時間大於上次提交時間+提交的最大間隔時間
if (begin >= (this.lastCommitTimestamp + commitDataThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = begin; // 提交時間
commitDataLeastPages = 0;// 最少提交頁數設為0,表示不限制提交頁數
}
try {
// 提交
boolean result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(commitDataLeastPages);
// 提交結束時間
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果返回false表示提交了一部分資料但是還未進行刷盤
if (!result) {
// 再次更新提交時間戳
this.lastCommitTimestamp = end;
// 喚醒flush執行緒進行刷盤
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
}
if (end - begin > 500) {
log.info("Commit data to file costs {} ms", end - begin);
}
// 等待下一次提交
this.waitForRunning(interval);
} catch (Throwable e) {
CommitLog.log.error(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {
result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(0);
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));
}
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
}
提交
提交的方法在MappedFileQueue的commit方法中實現,處理邏輯如下:
- 根據記錄的CommitLog檔案提交位置的偏移量獲取對映檔案,如果獲取不為空,呼叫MappedFile的commit方法進行提交,然後返回本次提交資料的偏移量
- 記錄本次提交的偏移量:檔案的偏移量 + 提交資料的偏移量
- 判斷本次提交的偏移量是否等於上一次的提交偏移量,如果等於表示本次未提交任何資料,返回結果置為true,否則表示提交了資料,等待刷盤,返回結果為false
- 更新上一次提交偏移量
committedWhere的值為本次的提交偏移量的值
public class MappedFileQueue {
protected long flushedWhere = 0; // flush的位置偏移量
private long committedWhere = 0; // 提交的位置偏移量
public boolean commit(final int commitLeastPages) {
boolean result = true;
// 根據提交位置的偏移量獲取對映檔案
MappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.committedWhere, this.committedWhere == 0);
if (mappedFile != null) {
// 呼叫mappedFile的commit方法進行提交,返回提交資料的偏移量
int offset = mappedFile.commit(commitLeastPages);
// 記錄本次提交的偏移量:檔案的偏移量 + 提交資料的偏移量
long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;
// 設定返回結果,如果本次提交偏移量等於上一次的提交偏移量為true,表示什麼也沒幹,否則表示提交了資料,等待刷盤
result = where == this.committedWhere;
// 更新上一次提交偏移量的值為本次的
this.committedWhere = where;
}
return result;
}
}
MappedFile
MappedFile中記錄CommitLog的寫入位置wrotePosition、提交位置committedPosition以及flush位置flushedPosition,在commit方法中,呼叫了isAbleToCommit判斷是否可以提交資料,判斷的流程如下:
-
獲取提交資料的位置偏移量和寫入資料的位置偏移量
-
如果最少提交頁數大於0,計算本次寫入的頁數是否大於或等於最少提交頁數
本次寫入資料的頁數計算方法:寫入位置/頁大小 - flush位置/頁大小
-
如果以上條件都滿足,判斷寫入位置是否大於flush位置,如果大於表示有一部資料未flush可以進行提交
滿足提交條件後,就會呼叫commit0方法提交資料,將資料寫入到fileChannel中:
public class MappedFile extends ReferenceResource {
// 資料寫入位置
protected final AtomicInteger wrotePosition = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 資料提交位置
protected final AtomicInteger committedPosition = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 資料flush位置
private final AtomicInteger flushedPosition = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 提交資料
public int commit(final int commitLeastPages) {
// 如果writeBuffer為空
if (writeBuffer == null) {
// 不需要提交任何資料到,返回之前記錄的寫入位置
return this.wrotePosition.get();
}
// 如果可以提交資料
if (this.isAbleToCommit(commitLeastPages)) {
if (this.hold()) {
// 提交資料
commit0();
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in commit, hold failed, commit offset = " + this.committedPosition.get());
}
}
// All dirty data has been committed to FileChannel.
if (writeBuffer != null && this.transientStorePool != null && this.fileSize == this.committedPosition.get()) {
this.transientStorePool.returnBuffer(writeBuffer);
this.writeBuffer = null;
}
// 返回提交位置
return this.committedPosition.get();
}
// 是否可以提交資料
protected boolean isAbleToCommit(final int commitLeastPages) {
// 獲取提交資料的位置偏移量
int flush = this.committedPosition.get();
// 獲取寫入資料的位置偏移量
int write = this.wrotePosition.get();
if (this.isFull()) {
return true;
}
// 如果最少提交頁數大於0
if (commitLeastPages > 0) {
// 寫入位置/頁大小 - flush位置/頁大小 是否大於至少提交的頁數
return ((write / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE)) >= commitLeastPages;
}
// 判斷是否需要flush資料
return write > flush;
}
protected void commit0() {
// 獲取寫入位置
int writePos = this.wrotePosition.get();
// 獲取上次提交的位置
int lastCommittedPosition = this.committedPosition.get();
if (writePos - lastCommittedPosition > 0) {
try {
// 建立共用緩衝區
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer.slice();
// 設定上一次提交位置
byteBuffer.position(lastCommittedPosition);
byteBuffer.limit(writePos);
this.fileChannel.position(lastCommittedPosition);
// 資料寫入fileChannel
this.fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
// 更新寫入的位置
this.committedPosition.set(writePos);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when commit data to FileChannel.", e);
}
}
}
}
FlushRealTimeService
如果未開啟暫存池,會直接使用FlushRealTimeService進行刷盤,當然如果開啟暫存池,寫入一批資料後,同樣會使用FlushRealTimeService進行刷盤,FlushRealTimeService同樣繼承了FlushCommitLogService,是用於執行刷盤的執行緒,處理邏輯與提交刷盤資料邏輯相似,只不過不是提交資料,而是呼叫flush方法將提交的資料刷入磁碟:
- 從設定資訊中獲取flush間隔、每次flush的最少頁數和兩次flush的最大間隔時間
- 如果當前時間大於上次flush時間+兩次flush的最大間隔時間,意味著已經有比較長的一段時間沒有進行flush,此時將每次flush的最少頁數設定為0不限制flush頁數
- 呼叫
waitForRunning等待被喚醒 - 如果被喚醒,呼叫
mappedFileQueue的flush方法進行刷盤
class FlushRealTimeService extends FlushCommitLogService {
private long lastFlushTimestamp = 0; // 上一次flush的時間
private long printTimes = 0;
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
// 如果未停止
while (!this.isStopped()) {
//
boolean flushCommitLogTimed = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isFlushCommitLogTimed();
// 獲取flush間隔
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushIntervalCommitLog();
// flush至少包含的頁數
int flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogLeastPages();
// 兩次flush的時間間隔
int flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogThoroughInterval();
boolean printFlushProgress = false;
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果當前毫秒數 大於上次flush時間 + 兩次flush之間的間隔
if (currentTimeMillis >= (this.lastFlushTimestamp + flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastFlushTimestamp = currentTimeMillis; // 更新flush時間
flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = 0; // flush至少包含的頁數置為0
printFlushProgress = (printTimes++ % 10) == 0;
}
try {
//
if (flushCommitLogTimed) {
// 睡眠
Thread.sleep(interval);
} else {
// 等待flush被喚醒
this.waitForRunning(interval);
}
if (printFlushProgress) {
// 列印刷盤程序
this.printFlushProgress();
}
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 進行刷盤
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages);
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
long past = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
if (past > 500) {
log.info("Flush data to disk costs {} ms", past);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
this.printFlushProgress();
}
}
// 如果服務停止,確保資料被刷盤
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {
// 進行刷盤
result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));
}
this.printFlushProgress();
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
刷盤
刷盤的方法在MappedFileQueue的flush方法中實現,處理邏輯如下:
- 根據 flush的位置偏移量獲取對映檔案
- 呼叫
mappedFile的flush方法進行刷盤,並返回刷盤後的位置偏移量 - 計算最新的flush偏移量
- 更新flushedWhere的值為最新的flush偏移量
public class MappedFileQueue {
protected long flushedWhere = 0; // flush的位置偏移量
private long committedWhere = 0; // 提交的位置偏移量
// flush刷盤
public boolean flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
boolean result = true;
// 獲取flush的位置偏移量對映檔案
MappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.flushedWhere, this.flushedWhere == 0);
if (mappedFile != null) {
// 獲取時間戳
long tmpTimeStamp = mappedFile.getStoreTimestamp();
// 呼叫MappedFile的flush方法進行刷盤,返回刷盤後的偏移量
int offset = mappedFile.flush(flushLeastPages);
// 計算最新的flush偏移量
long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;
result = where == this.flushedWhere;
// 更新flush偏移量
this.flushedWhere = where;
if (0 == flushLeastPages) {
this.storeTimestamp = tmpTimeStamp;
}
}
// 返回flush的偏移量
return result;
}
}
flush的邏輯也與commit方法的邏輯類似:
-
呼叫
isAbleToFlush判斷是否滿足刷盤條件,獲取上次flush位置偏移量和當前寫入位置偏移量進行如下校驗:-
檔案是否已寫滿,即檔案大小是否與寫入資料位置相等,如果相等說明檔案已經寫滿需要執行刷盤,滿足刷盤條件
-
如果最少flush頁數大於0,計算本次flush的頁數是否大於或等於最少flush頁數,如果滿足可以進行刷盤
本次flush資料的頁數計算方法:寫入位置/頁大小 - flush位置/頁大小
-
如果寫入位置偏移量是否大於flush位置偏移量,如果大於表示有資料未進行刷盤,滿足刷盤條件
-
-
呼叫
fileChannel的force或者mappedByteBuffer的force方法進行刷盤 -
記錄本次flush的位置,並作為結果返回
public class MappedFile extends ReferenceResource {
protected final AtomicInteger wrotePosition = new AtomicInteger(0);
protected final AtomicInteger committedPosition = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final AtomicInteger flushedPosition = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 進行刷盤並返回flush後的偏移量
*/
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
// 是否可以刷盤
if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {
if (this.hold()) {
int value = getReadPosition();
try {
// 如果writeBuffer不為空
if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {
// 將資料刷到硬碟
this.fileChannel.force(false);
} else {
this.mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when force data to disk.", e);
}
// 記錄flush位置
this.flushedPosition.set(value);
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in flush, hold failed, flush offset = " + this.flushedPosition.get());
this.flushedPosition.set(getReadPosition());
}
}
// 返回flush位置
return this.getFlushedPosition();
}
// 是否可以刷盤
private boolean isAbleToFlush(final int flushLeastPages) {
// 獲取上次flush位置
int flush = this.flushedPosition.get();
// 寫入位置偏移量
int write = getReadPosition();
if (this.isFull()) {
return true;
}
// 如果flush的頁數大於0,校驗本次flush的頁數是否滿足條件
if (flushLeastPages > 0) {
// 本次flush的頁數:寫入位置偏移量/OS_PAGE_SIZE - 上次flush位置偏移量/OS_PAGE_SIZE,是否大於flushLeastPages
return ((write / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE)) >= flushLeastPages;
}
// 寫入位置偏移量是否大於flush位置偏移量
return write > flush;
}
// 檔案是否已寫滿
public boolean isFull() {
// 檔案大小是否與寫入資料位置相等
return this.fileSize == this.wrotePosition.get();
}
/**
* 返回當前有效資料的位置
*/
public int getReadPosition() {
// 如果writeBuffer為空使用寫入位置,否則使用提交位置
return this.writeBuffer == null ? this.wrotePosition.get() : this.committedPosition.get();
}
}
