爬蟲(6)
2022-07-04 18:01:44
什麼是Beautiful Soup庫
- Beautiful Soup提供一些簡單的、python式的函數用來處理導航、搜尋、修改分析樹等功能
- 它是一個工具箱,通過解析檔案為使用者提供需要抓取的資料,因為簡單,所以不需要多少程式碼就可以寫出一個完整的應用程式
- Beautiful Soup就是python的一個庫,最主要的功能是從網頁獲取資料
- BeautifulSoup4==4.7.1第四版本,簡稱bs4
學習Beautiful Soup庫的目的
增加一種獲取資料的方法
- 正規表示式:https://www.cnblogs.com/gltou/p/15783716.html
- Xpath:https://www.cnblogs.com/gltou/p/16327688.html
- bs4
安裝Beautiful Soup庫
cmd輸入以下命令:
pip install beautifulsoup4
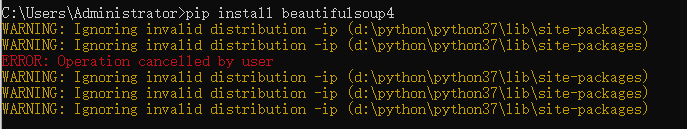
結果報錯了,解決方案:在d:\python\python37\lib\site-packages目錄下刪除~ip開頭的目錄資料夾
重新執行命令

Beautiful Soup支援的解析器
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 優勢 | 劣勢 |
| python標準庫 | BeautifulSoup(markup,"html.parser") | python的內建標準庫,執行速度適中、檔案容錯能力強 | python 2.7.3及Python 3.2.2之前的版本檔案容錯能力差 |
| lxml HTML解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup,"lxml") | 速度快、檔案容錯能力強 | 需要安裝C語言庫 |
| lxml XML解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup,"xml") | 速度快,唯一支援XML的解析器 | 需要安裝C語言庫 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup,"html5lib") | 最好的容錯性、以瀏覽器的方式解析檔案、生成HTML5的格式的檔案 | 速度慢、不依賴外部擴充套件 |
實際工作中前兩個用的最多,前兩個中重點掌握第二個;後面的筆記以lxml為主
安裝lxml解析器
pip install lxml
我之前已經安裝過了,所以沒有安裝過程截圖。
解析節點及屬性值
範例
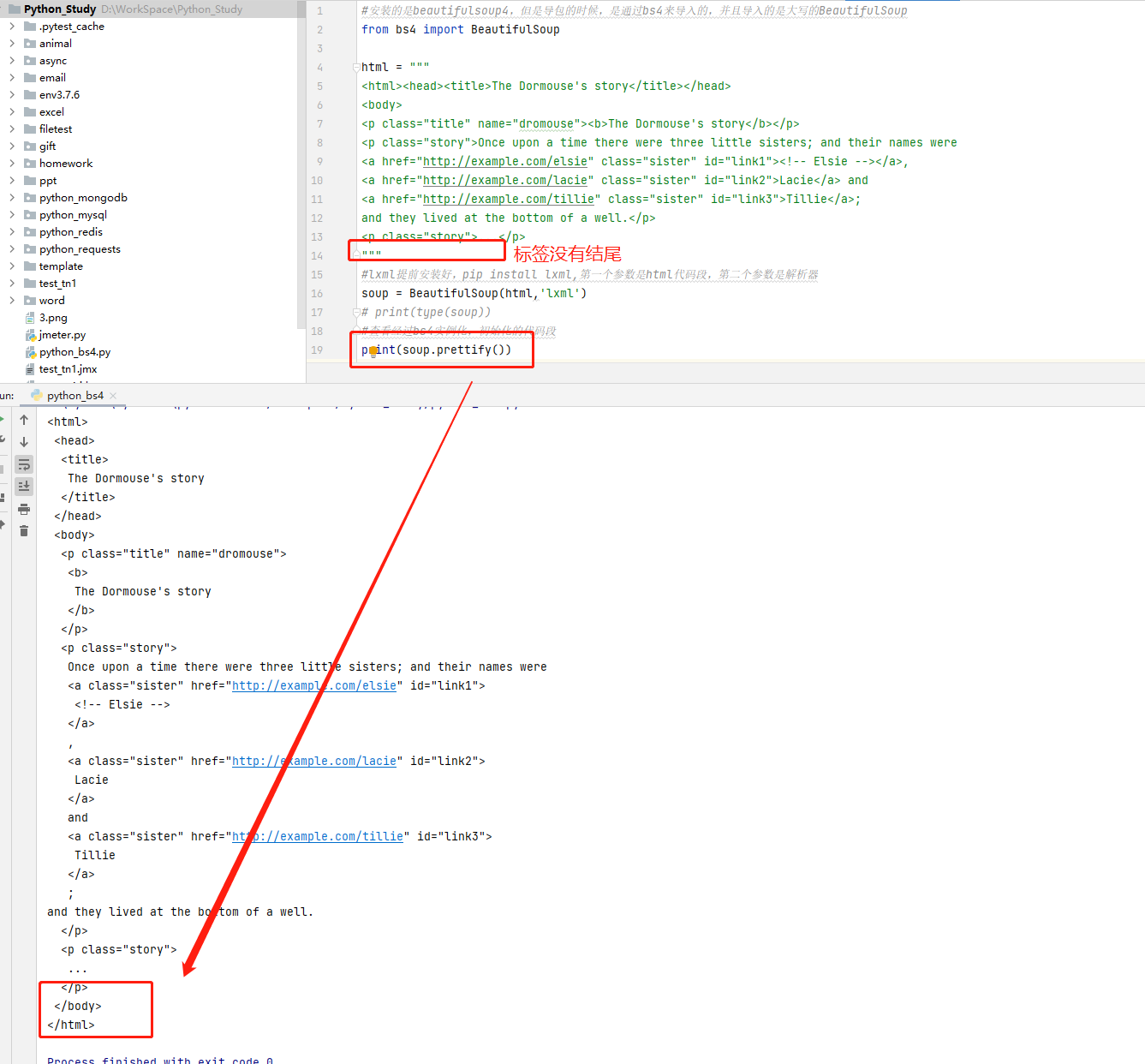
1 #安裝的是beautifulsoup4,但是導包的時候,是通過bs4來匯入的,並且匯入的是大寫的BeautifulSoup 2 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 3 4 html = """ 5 <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> 6 <body> 7 <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> 8 <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 9 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, 10 <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and 11 <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; 12 and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> 13 <p class="story">...</p> 14 """ 15 #lxml提前安裝好,pip install lxml,第一個引數是html程式碼段,第二個引數是解析器 16 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 17 #檢視經過bs4範例化,初始化的程式碼段 18 # print(soup.prettify()) 19 #獲取到的是資料結構,tag,tag有很多方法,如string 20 # print(type(soup.title)) 21 #來檢視檔案中title的屬性值 22 # print(soup.title.string) 23 # print(soup.head) 24 #當有多個節點的時候,我們當前的這種選擇模式,只能匹配到第一個節點,其他節點會被忽略 25 # print(soup.p) 26 #獲取節點的名稱 27 # print(soup.title.name) 28 #attrs會返回標籤的所有屬性值,返回的是一個字典 29 # print(soup.p.attrs) 30 # print(soup.p.attrs['name']) 31 #返回的節點屬性,可能是列表,也可能是字串,需要進行實際的判斷 32 # print(soup.p['name']) 33 # print(soup.p['class'])
| 方法 | 作用 | 範例結果 |
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') |
範例化物件,解析器用的是lxml |
>> print(type(soup)) <class 'bs4.BeautifulSoup'> |
soup.prettify() |
初始化程式碼段,即將範例不規則程式碼, |
 |
soup.title |
獲取到的是資料結構tag,tag有很多 |
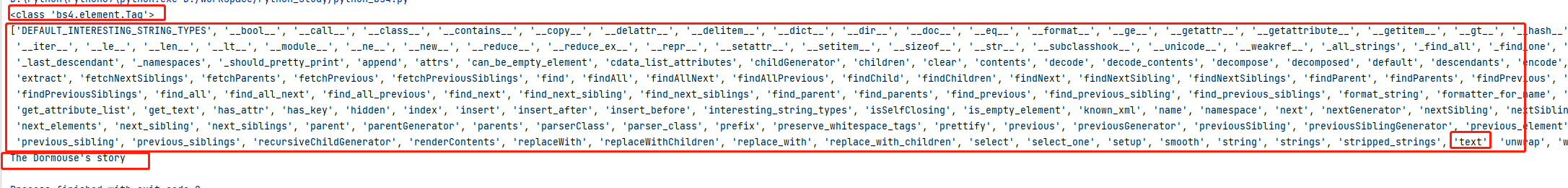
>>> print(type(soup.title)) >>> print(dir(soup.title)) >>> print(soup.title.text)
|
soup.title.string |
檢視檔案中title的屬性值 |
>>>print(soup.title) <title>The Dormouse's story</title> >>>print(soup.title.string) The Dormouse's story |
soup.p |
當有多個節點的時候,我們當前的這種 |
>>> print(soup.p) <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> |
soup.title.name |
獲取節點的名稱 |
>>> print(soup.title.name) title |
soup.p.attrs |
attrs會返回標籤的所有屬性值,返回的 |
>>> print(soup.p.attrs) {'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'} >>> print(soup.p.attrs['name']) dromouse |
soup.p['name'] soup.p['class'] |
返回的節點屬性,可能是列表,也可能是 |
>>> print(soup.p['name']) dromouse >>> print(soup.p['class']) ['title'] |
BeautifulSoup解析節點,只能匹配第一個節點!!!
獲取子節點和孫節點
範例-1:巢狀呼叫
1 #巢狀呼叫 2 3 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 4 5 html = """ 6 <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> 7 <body> 8 <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> 9 <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 10 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, 11 <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and 12 <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; 13 and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> 14 <p class="story">...</p> 15 """ 16 17 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 18 #巢狀呼叫,查詢head節點下面的title節點 19 print(soup.head.title) 20 21 #兩個都是bs4.element.Tag 22 print(type(soup.head)) 23 print(type(soup.head.title)) 24 25 #查詢head節點下面的title節點的內容 26 print(soup.head.title.string)
| 方法 | 作用 | 範例結果 |
soup.head.title |
巢狀呼叫,查詢head節點下面的title節點 |
>>> print(soup.head.title) <title>The Dormouse's story</title> |
soup.head
soup.head.title
|
檢視兩個節點的型別,都是bs4.element.Tag |
>>> print(type(soup.head)) >>> print(type(soup.head.title)) <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> |
soup.head.title.string |
查詢head節點下面的title節點的內容 |
>>> print(soup.head.title.string) The Dormouse's story |
範例-2:子節點和子孫節點呼叫
1 #子節點和子孫節點 2 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 3 4 html = """ 5 <html> 6 <head> 7 <title>The Dormouse's story</title> 8 </head> 9 <body> 10 <p class="story"> 11 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 12 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"> 13 <span>Elsie</span> 14 </a> 15 <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> 16 and 17 <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a> 18 and they lived at the bottom of a well. 19 </p> 20 <p class="story">...</p> 21 """ 22 23 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 24 25 #獲取p標籤的子節點,注意是子節點,返回的是一個列表 26 #列表中的元素是p節點的直接子節點 27 #返回結果沒有單獨的吧a標籤中的span標籤選出來 28 #contents方法獲取直接子節點的列表 29 print(soup.p.contents) 30 print(soup.p.contents[0]) 31 print(len(soup.p.contents)) 32 33 #contents和children返回的結果是一樣的,都是直接子節點 34 #只不過children方法返回的是一個迭代器,需要使用for迴圈來進行遍歷 35 print(soup.p.children) 36 for i,j in enumerate(soup.p.children): 37 print(i,j) 38 print("==============================") 39 40 #獲取子節點和孫節點 41 #會把中間的孫節點也單獨的取出來 42 print(soup.p.descendants) 43 for i,j in enumerate(soup.p.descendants): 44 print(i,j)
| 方法 | 作用 | 範例結果 |
soup.p.contents |
獲取p標籤的子節點,注意是子節點,返回的是一個列表;
列表中的元素是p節點的直接子節點;
返回結果沒有單獨的吧a標籤中的span標籤選出來;
contents方法獲取直接子節點,返回資料型別是列表;
|
>>> print(soup.p.contents) 
>>> print(soup.p.contents[0]) |
soup.p.children |
contents和children返回的結果是一樣的,都是直 |
>>> print(soup.p.children) 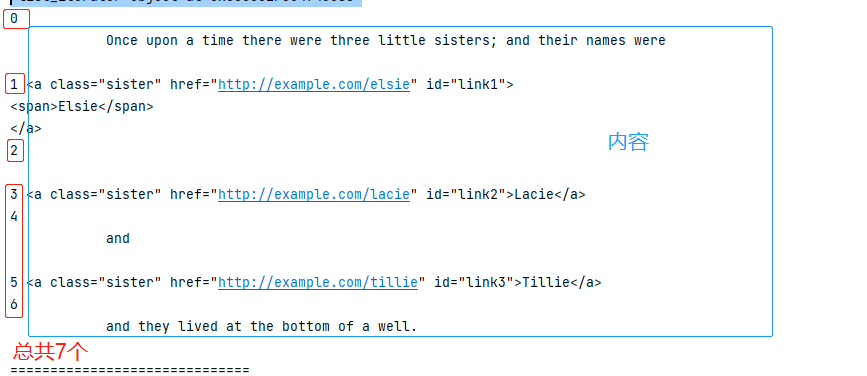 |
soup.p.descendants |
獲取p標籤子節點和孫節點; |
>>> print(soup.p.descendants)  |
這個裡面直接子節點和子節點是有區別的,可能不太容易理解,簡單講解一下:
直接子節點:
-
contents;children
- 所有兒子節點,至於你兒子節點裡面有沒有孫子節點,都跟你兒子節點算一個
- 人家跟你說:明天來吃席,一家都來哈。第二天你們家都去了,不分大人小孩坐在了一桌
子節點
-
descendants
- 所有兒子節點輸出的同時,如果節點裡面有孫子、重孫子...節點的依次輸出
- 人家跟你說:明天來吃席,一家都來哈。第二天你們家都去了,先看你家人都到了沒有,先做一桌子,輸出一下;以家為單位輸出結束後,再依次輸出你孫子一大家、然後重孫子一大家
獲取父節點、祖先節點、兄弟節點
範例-1:獲取父節點、祖先節點
1 #獲取父節點和獲取祖先節點 2 3 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 4 5 html = """ 6 <html> 7 <head> 8 <title>The Dormouse's story</title> 9 </head> 10 <body> 11 <p class="story"> 12 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 13 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"> 14 <span>Elsie</span> 15 </a> 16 </p> 17 <p class="story">...</p> 18 """ 19 20 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 21 #獲取a節點的父節點 22 print(soup.a.parent) 23 24 #獲取所有的祖先節點,返回的是迭代器 25 print(soup.a.parents) 26 for i,j in enumerate(soup.a.parents): 27 print(i,j)
| 方法 | 作用 | 範例結果 |
soup.a.parent |
獲取a節點的父節點; |
>>> print(soup.a.parent)  |
soup.a.parents |
依次往上找,獲取所有的祖先節點, |
>>> print(soup.a.parents) 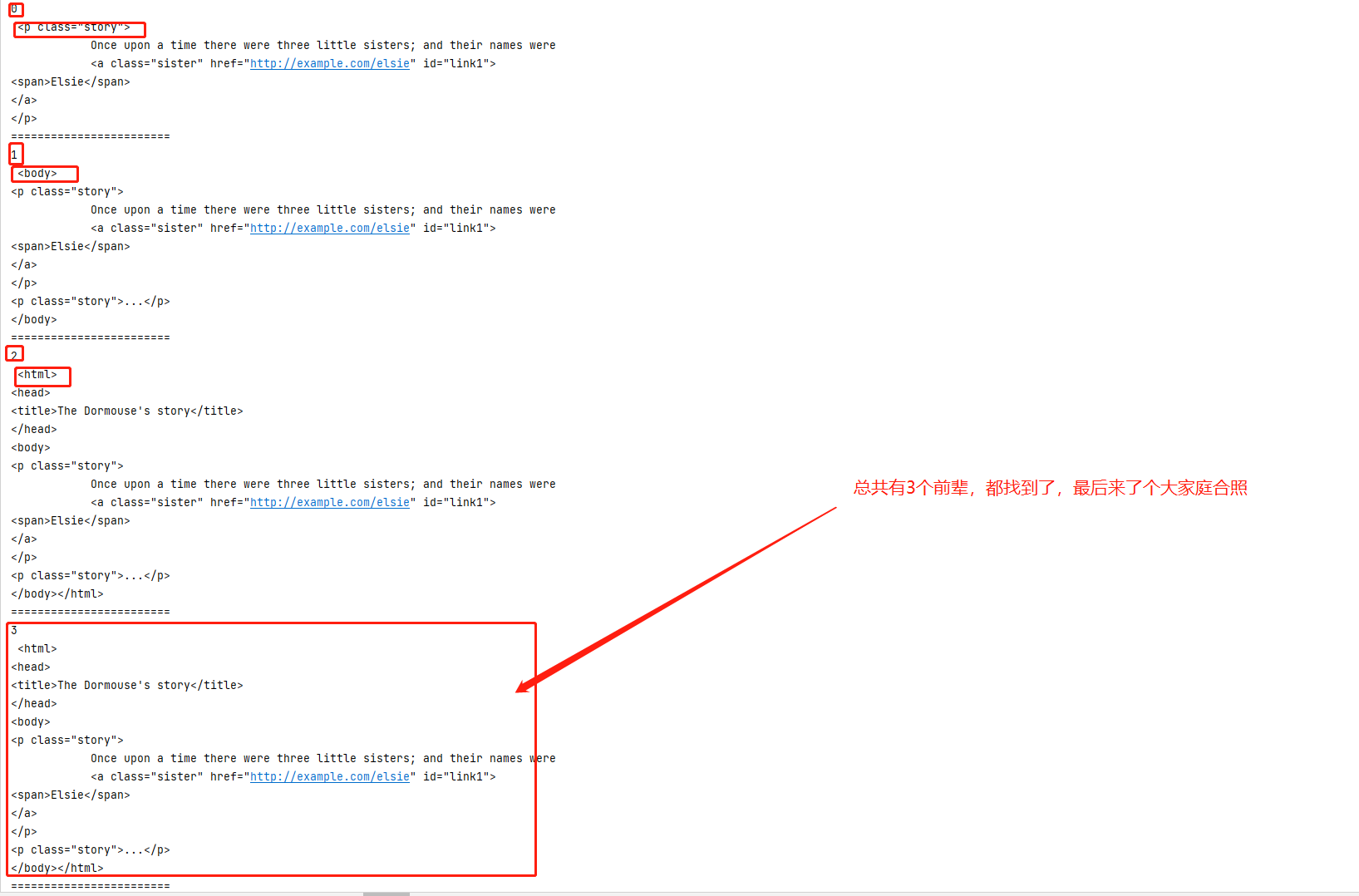 |
範例-2:獲取兄弟節點
1 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 2 3 html = """ 4 <html> 5 <body> 6 <p class="story"> 7 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 8 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"> 9 <span>Elsie</span> 10 </a> 11 Hello 12 <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> 13 and 14 <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a> 15 and they lived at the bottom of a well. 16 </p> 17 """ 18 19 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 20 #獲取a標籤的下一個兄弟節點 21 # print(soup.a.next_sibling) 22 23 #獲取上一個兄弟節點 24 # print(soup.a.previous_sibling) 25 26 #獲取當前節點後面的所有兄弟節點 27 # print(soup.a.next_siblings) 28 # for i,j in enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings): 29 # print(i,j) 30 31 #獲取當前節點前面所有的兄弟節點 32 print(soup.a.previous_siblings) 33 for i,j in enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings): 34 print(i,j)
| 方法 | 作用 | 範例結果 |
soup.a.next_sibling |
獲取a標籤的下一個兄弟節點 |
>>> print(soup.a.next_sibling)Hello |
soup.a.previous_sibling |
獲取上一個兄弟節點 |
>>> print(soup.a.previous_sibling) |
soup.a.next_siblings |
獲取當前節點後面的所有兄弟節點 |
>>> print(soup.a.next_siblings) <generator object PageElement.next_siblings at 0x0000018C60652648>  |
soup.a.previous_siblings |
獲取當前節點前面所有的兄弟節點 |
>>> print(soup.a.previous_siblings) <generator object PageElement.previous_siblings at 0x000001246F202648> 
|
方法選擇器
find和find_all方法
- find_parents 和 find_parent:前者返回所有祖先節點,後者返回直接父節點。
- find_next_siblings 和 find_next_sibling:前者返回後面所有的兄弟節點,後者返回後面第一個兄弟節點。
- find_previous_siblings 和 find_previous_sibling:前者返回前面所有的兄弟節點,後者返回前面第一個兄弟節點。
- find_all_next 和 find_next:前者返回節點後所有符合條件的節點,後者返回第一個符合條件的節點。
- find_all_previous 和 find_previous:前者返回節點前所有符合條件的節點,後者返回第一個符合條件的節點。
| 方法 | 表示式 | 範例 |
soup.find_all() |
find_all:返回的是列表 find:返回的是單個元素,即第一個符合條件的 **kwargs說明: name="data" 獲取到當前文字中data標籤的資料 attrs={"key":"value"} attrs,傳入的是屬性引數和值,型別是字典,attrs={"id":"list-1"} id="data" 查詢id屬性值為data的資料 class_="data" 查詢class屬性值為data的資料,用class的時候,後面加上一個下劃線 text=re.compile("正規表示式") 通過text引數來獲取文字的值,可以傳遞正規表示式,返回是一個列表 |
#attrs,傳入的是屬性引數,型別是字典,attrs={"id":"list-1"} print(soup.find_all(attrs={"id":"list-1"})) print(soup.find_all(attrs={"name":"elements"})) #也可以直接傳入ID這個引數 print(soup.find_all(id="list-1")) #class在Python中是一個關鍵字,find_all方法裡面要用class的時候,後面加上一個下劃線 print(soup.find_all(class_="list")) #可以通過text引數來獲取文字的值,可以傳遞正規表示式,返回是一個列表 print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Foo\d")))
|
soup.find() |
#find方法,返回的是一個單個的元素,第一個匹配的元素,而find_all返回的是所有值的列表 print(soup.find(name="ul")) |
|
find_parents 和 find_parent:前者返回所有祖先節點,後者返回直接父節點 |
||
find_next_siblings 和 find_next_sibling:前者返回後面所有的兄弟節點,後者返回後面第一個兄弟節點 |
||
find_previous_siblings 和 find_previous_sibling:前者返回前面所有的兄弟節點,後者返回前面第一個兄弟節點 |
||
find_all_next 和 find_next:前者返回節點後所有符合條件的節點,後者返回第一個符合條件的節點 |
||
find_all_previous 和 find_previous:前者返回節點前所有符合條件的節點,後者返回第一個符合條件的節點 |
||
範例-1:find_all通過節點名進行查詢
1 #方法選擇器,find_all,通過節點名來進行查詢的 2 3 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 4 5 html=''' 6 <div class="panel"> 7 <div class="panel-heading"> 8 <h4>Hello</h4> 9 </div> 10 <div class="panel-body"> 11 <ul class="list" id="list-1"> 12 <li class="element">Foo</li> 13 <li class="element">Bar</li> 14 <li class="element">Jay</li> 15 </ul> 16 <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"> 17 <li class="element">Foo</li> 18 <li class="element">Bar</li> 19 </ul> 20 </div> 21 </div> 22 ''' 23 24 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 25 #find_all,name=li,可以獲取到當前文字中所有li標籤的資料,返回的是一個列表 26 print(soup.find_all(name='li')) #[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>, <li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>] 27 print(soup.find_all(name='li')[0]) #<li class="element">Foo</li> 28 29 #tag型別 30 print(type(soup.find_all(name='li')[0])) #<class 'bs4.element.Tag'> 31 32 #可以進行巢狀查詢 33 for ul in soup.find_all(name="ul"): 34 for li in ul.find_all(name='li'): 35 #tag 36 print(li.string) #FooBar Jay Foo Bar
範例-2:find_all通屬性進行查詢
1 #通過屬性來進行查詢 2 #通過text文字來獲取匹配的文字 3 4 import re 5 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 6 7 html=''' 8 <div class="panel"> 9 <div class="panel-heading"> 10 <h4>Hello</h4> 11 </div> 12 <div class="panel-body"> 13 <ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements"> 14 <li class="element">Foo</li> 15 <li class="element">Bar</li> 16 <li class="element">Jay</li> 17 </ul> 18 <ul class="list" id="list-1"> 19 <li class="element">Foo2</li> 20 <li class="element">Bar2</li> 21 <li class="element">Jay2</li> 22 </ul> 23 <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"> 24 <li class="element">Foo</li> 25 <li class="element">Bar</li> 26 </ul> 27 </div> 28 </div> 29 ''' 30 31 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') 32 #attrs,傳入的是屬性引數,型別是字典,attrs={"id":"list-1"} 33 print(soup.find_all(attrs={"id":"list-1"})) 34 print(soup.find_all(attrs={"name":"elements"})) 35 36 #也可以直接傳入ID這個引數 37 print(soup.find_all(id="list-1")) 38 39 #class在Python中是一個關鍵字,find_all方法裡面要用class的時候,後面加上一個下劃線 40 print(soup.find_all(class_="list")) 41 42 #可以通過text引數來獲取文字的值,可以傳遞正規表示式,返回是一個列表 43 print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Foo\d"))) 44 45 #find方法,返回的是一個單個的元素,第一個匹配的元素,而find_all返回的是所有值的列表 46 print(soup.find(name="ul"))
使用css選擇器獲取元素
- 建議大家使用find find_all查詢匹配單個結果或多個結果
- css選擇器非常的熟悉,那麼就可以使用css選擇器
#使用css選擇器,只需要呢,呼叫select方法,傳入css選擇器即可 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html=''' <div class="panel"> <div class="panel-heading"> <h4>Hello</h4> </div> <div class="panel-body"> <ul class="list" id="list-1"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul> <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> </ul> </div> </div> ''' soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') #需要呼叫select方法,傳入css選擇器,class用.來表示;通過空格繼續書寫子節點 # print(soup.select(".panel .panel-heading")) #獲取ul標籤下所有Li標籤 # print(soup.select("ul li")) #獲取id為list-2,class為element兩個Li標籤;id屬性簡寫是# # print(type(soup.select("#list-2 .element")[0])) #支援巢狀選擇 #先獲取到ul標籤,tag型別,for 呼叫select方法在次傳入css選擇器 for ul in soup.select("ul"): for li in ul.select("li"): #呼叫tag型別裡面的方法,string方法來獲取文字內容 # print(li.string) print(li['class']) #支援使用屬性獲取元素 # for ul in soup.select("ul"): # print(ul['id']) #建議大家使用find find_all查詢匹配單個結果或多個結果 #css選擇器非常的熟悉,那麼就可以使用css選擇器
案例-BS4解析網站資料
1 import requests 2 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 3 4 5 def handle_detail_bs4(content): 6 """ 7 解析目標頁面返回資料的 8 :param content:response.text 9 :return: 10 """ 11 # 資料的範例化,傳入要解析的資料,和解析器,解析器使用的是lxml 12 soup = BeautifulSoup(content, "lxml") 13 # 獲取所有的圖書條目,使用find_all,查詢div標籤,通過class屬性查詢,class是一個關鍵字,class_ 14 all_book_items = soup.find_all("div", class_="row col-padding") 15 # 列印未格式化的資料,可以看到html標籤的 16 for item in all_book_items: 17 # print(item) 18 # 獲取圖書資訊,先查詢上層的div,發現裡面包含著三個span,find_all來查詢所有span 19 info = item.find("div", class_="col-md-7 flex-vertical description-font").find_all("span") 20 # 獲取作者,出版社,價格資訊 21 author_press_price = info[1].string.split("/") 22 if len(author_press_price) == 3: 23 print( 24 { 25 # 最終資訊 26 "title": info[0].string, 27 "author": author_press_price[0], 28 "press": author_press_price[1], 29 "price": author_press_price[2], 30 "summary": info[2].string 31 } 32 ) 33 34 35 def main(): 36 header = { 37 "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.72 Safari/537.36" 38 } 39 for i in range(1, 5): 40 url = "http://yushu.talelin.com/book/search?q=python&page={}".format(i) 41 response = requests.get(url=url, headers=header) 42 handle_detail_bs4(response.text) 43 44 45 if __name__ == '__main__': 46 main()