Spring XmlBeanFactory 容器的基本實現
容器的基本用法
熟悉 Spring 的朋友應該都很瞭解下段程式碼:
public void testBeanFactory() {
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml"));
TestBean testBean = bf.getBean("testBean");
}
一段簡單的通過容器獲取 Bean 的程式碼,它所完成的功能無非就是以下幾點:
- 讀取組態檔 beanFactoryTest.xml
- 根據 beanFactoryTest.xml 中的設定找到對應類的設定,並範例化
- 獲取範例化後的範例
接下來我們來分析這段程式碼的實現原理
Spring 核心類介紹
在開始正式的原始碼分析之前,有必要先了解 Spring 核心的兩個類
1. DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory 繼承自 DefaultListableBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory 是整個 bean 載入的核心部分,是 Spring 註冊及載入 bean 的預設實現。XmlBeanFactory 與 DefaultListableBeanFactory 的不同之處就在於 XmlBeanFactory 使用了自定義的 XML 讀取器 XmlBeanDefinitionReader
2. XmlBeanDefinitionReader
在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 中主要包含以下幾步處理:
- 通過繼承自 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的方法,使用 ResourceLoader 將資原始檔路徑轉換為對應的 Resoure 檔案
- 通過 DocumentLoader 對 Resource 檔案進行轉換,將 Resource 檔案轉換為 Document 檔案
- 通過實現 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 的 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 類對 Document 進行解析,並使用 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate 對 Element 進行解析
容器基礎 XmlBeanFactory
接下來我們將深入分析以下程式碼的功能實現
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml"));
通過 XmlBeanFactory 初始化時序圖,我們來看一看上面程式碼的執行邏輯
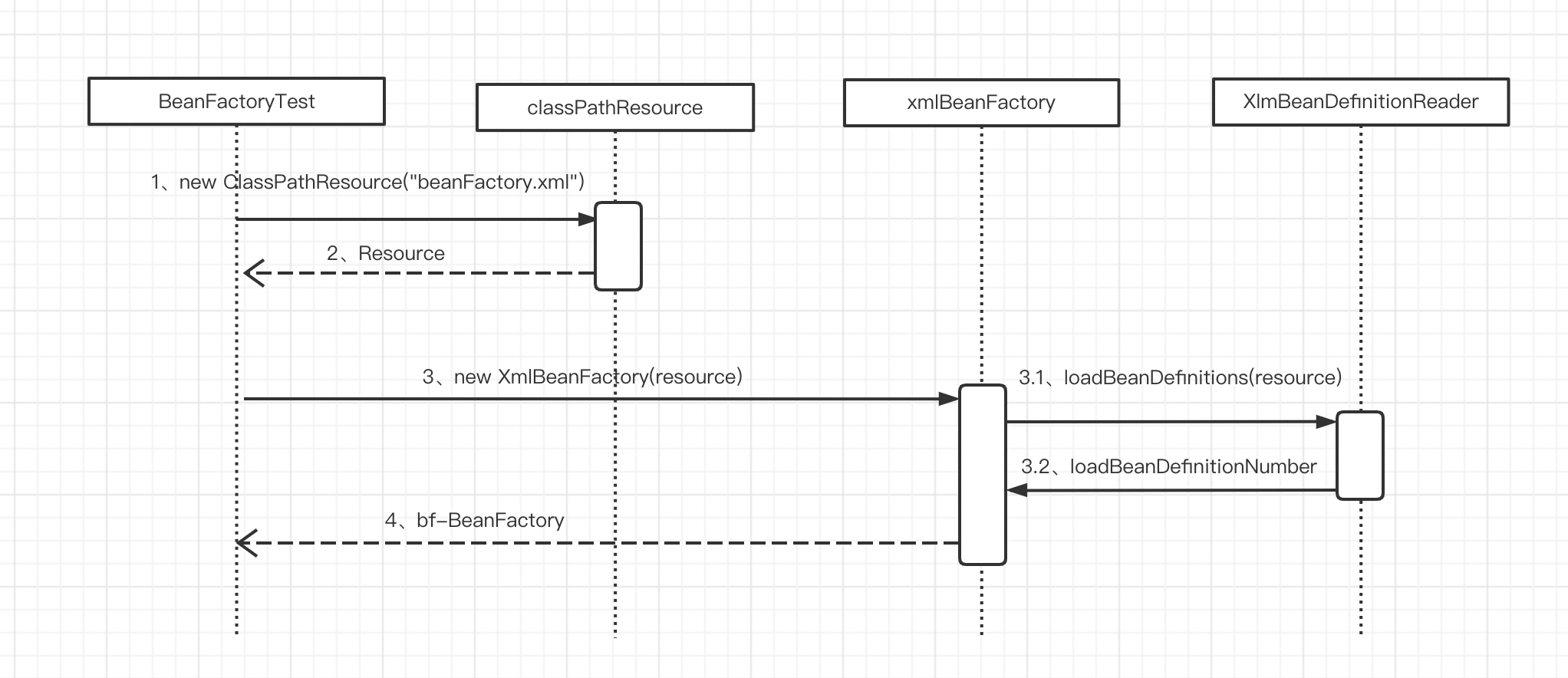
1. 封裝組態檔
Spring 的組態檔讀取是通過 ClassPathResource 封裝成 Resource,Resource 的結構如下:
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
default boolean isReadable() {
return this.exists();
}
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(this.getInputStream());
}
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String var1) throws IOException;
@Nullable
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
Resource 介面抽象了所有 Spring 內部使用的底層資源:File、URL、Classpath 等等,並定義了有關資源操作的方法。對於不同來源的資原始檔,都有對應的 Resource 實現:檔案(FileSystemResource)、Classpath(ClasspathResource)、URL(UrlResource )、InputStream(InputStreamResource)、Byte(ByteResource)等等,有了 Resource 介面就可以對所有資原始檔進行統一處理,至於處理的實現其實很簡單,以 ClasspathResource 為例,實現方式就是通過 class 或者 classLoader 提供的底層方式進行呼叫
2. 資料準備階段
通過 Resource 完成組態檔的封裝以後,就將 Resource 作為 XmlBeanFactory 的建構函式引數傳入,程式碼如下:
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, (BeanFactory)null);
}
建構函式內部再次呼叫內部建構函式:
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 是整個資源載入的切入點,這個方法的處理過程如下:
- 對引數 Resource 使用 EncodedResource 類進行封裝
- 從 Resource 獲取對應的 InputStream 並構造 InputSource
- 通過構造的 InputSource 範例和 Resource 範例繼續呼叫函數 doLoadBeanDefinitions
我們來看一下 loadBeanDefinitions 函數具體的實現過程:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return this.loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
EncodedResource 的作用是對資原始檔的編碼進行處理,可以通過設定編碼屬性指定 Spring 使用響應的編碼進行處理
當構造好 EncodedResource 物件後,再次轉入到 loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
// 獲取已經載入的資源
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = (Set)this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
} else {
int var6;
try {
// 從已經封裝的 Resource 物件獲取 InputStream
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
Throwable var4 = null;
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 進入真正的邏輯核心部分
var6 = this.doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
} catch (Throwable var24) {
var4 = var24;
throw var24;
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
if (var4 != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (Throwable var23) {
var4.addSuppressed(var23);
}
} else {
inputStream.close();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException var26) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), var26);
} finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
return var6;
}
}
再次整理資料準備階段的邏輯,首先對傳入的 Resource 引數進行編碼處理,將準備的資料傳入到真正的核心處理部分 doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法
3. 獲取 Document
doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法的程式碼如下:
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = this.doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
int count = this.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var5) {
throw var5;
} catch (SAXParseException var6) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + var6.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", var6);
} catch (SAXException var7) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", var7);
} catch (ParserConfigurationException var8) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, var8);
} catch (IOException var9) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, var9);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, var10);
}
}
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, this.getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, this.getValidationModeForResource(resource), this.isNamespaceAware());
}
不考慮處理異常的程式碼,其實只做了三件事:
- 獲取對 XML 檔案的驗證模式
- 載入 XML 檔案,並得到對應的 Document
- 根據返回的 Document 註冊 Bean 資訊
獲取 XML 驗證模式是為了保證 XML 檔案的正確性,常用的驗證模式有 DTD 和 XSD 兩種。Spring 通過 getValidationModeForResource 方法獲取對應資源的驗證模式,這裡不再贅述
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) {
int validationModeToUse = this.getValidationMode();
// 如果手動指定了驗證模式就使用指定的驗證模式
if (validationModeToUse != 1) {
return validationModeToUse;
} else {
// 如果未指定就使用自動檢測
int detectedMode = this.detectValidationMode(resource);
return detectedMode != 1 ? detectedMode : 3;
}
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader 將檔案讀取交由 DocumentLoader 去處理,DocumentLoader 是個介面,真正呼叫的是 DefaultDocumentLoader,解析程式碼如下:
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver, ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = this.createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = this.createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
對於這部分程式碼沒有太多可以描述的,因為通過 SAX 解析 XML 檔案的套路大都相同,解析完成返回一個 Document 物件
4. 解析及註冊 BeanDefinitions
當程式擁有 Document 物件後,就會被引入下面這個方法:
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 使用 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 範例化 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = this.createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
// 記錄統計前 BeanDefinition 的載入個數
int countBefore = this.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 載入及註冊 bean
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, this.createReaderContext(resource));
// 記錄本次載入的 BeanDefinition 個數
return this.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 是一個介面,通過 createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 方法完成範例化,實際型別是 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader,registerBeanDefinitions 方法程式碼如下:
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
this.doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
getDocumentElement 方法的重要目的之一是提取 root,以便於再次將 root 作為引數繼續 BeanDefinition 的註冊
再次進入 doRegisterBeanDefinitions 方法:
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// 專門處理解析
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = this.createDelegate(this.getReaderContext(), root, parent);
// 處理 profile 屬性
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute("profile");
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, ",; ");
if (!this.getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + this.getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
// 解析前處理,留給子類實現
this.preProcessXml(root);
this.parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
// 解析後處理,留給子類實現
this.postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
這裡使用了模板方法設計模式,如果繼承自 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 的子類需要在 Bean 解析前後做一些處理的話,可以重寫 preProcessXml 和 postProcessXml 方法
在註冊 Bean 的最開始是先對 profile 屬性解析,profile 屬性可用於在組態檔中部署兩套設定分別適用生產環境和開發環境,做到方便的的切換環境
處理完 profile 屬性以後就可以進行 XML 的讀取,跟蹤程式碼進入 parseBeanDefinitions 方法
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element)node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
this.parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
根節點或者子節點是預設名稱空間的話採用 parseDefaultElement 方法解析,否則使用 delegate.parseCustomElement 方法解析,而對於標籤的解析,我們放到下一篇文章作講解