react生命週期的三個過程是什麼
2022-06-28 18:01:04
react生命週期的三個過程:1、掛載期,也叫範例化期,是一個元件範例初次被建立的過程;2、更新期,也被稱為存在期,是元件在建立之後再次渲染的過程;3、解除安裝期,也被稱為銷燬期,是元件在使用完後被銷燬的過程。

本教學操作環境:Windows10系統、react17.0.1版、Dell G3電腦。
react生命週期的三個過程是什麼
React的生命週期從廣義上分為三個階段:掛載、渲染、解除安裝
從出生到成長,最後到死亡,這個過程的時間可以理解為生命週期。React的生命週期同理也是這麼一個過程。
React的生命週期分為三個階段:掛載期(也叫範例化期)、更新期(也叫存在期)、解除安裝期(也叫銷燬期)。在每個週期中React都提供了一些勾點函數。
生命週期的描述如下:
掛載期:一個元件範例初次北建立的過程。
更新期:元件在建立後再次渲染的過程。
解除安裝期:元件在使用完後被銷燬的過程。
元件的掛載:
元件在首次建立後,進行第一次的渲染為掛載期。掛載期有的一些方法會被依次觸發,列舉如下:
- constructor(建構函式,初始化狀態值)
- getInitialState(設定狀態機)
- getDefaultProps(獲取預設的props)
- UNSAFE_componentWillMount(首次渲染前執行)
- render(渲染元件)
- componentDidMount(render渲染之後執行的操作)
//元件掛載import React from 'react';import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';class HelloWorld extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log("1,建構函式");
this.state={};
console.log("2,設定狀態機");
}
static defaultProps={
name:"React",
}
UNSAFE_componentWillMount(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log("3,完成首次渲染前呼叫");
}
render() {
console.log("4,元件進行渲染");
return (
<p>
<p>{this.props.name}</p>
</p>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log("5,componentDidMount render渲染後的操作")
}}ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorld />, document.getElementById('root'));
元件的更新:
元件更新,指的是在元件初次渲染後,進行了元件狀態的改變。React在生命週期中的更新過程包括以下幾個方法:
- UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps :當父元件更新子元件state時,該方法會被呼叫。
- shouldComponentUpdate : 該方法決定元件state或props的改變是否需要重新渲染元件。
- UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate : 在元件接受新的state或者props時,即將進行重新渲染前呼叫該方法,和UNSAFE_componentWillMount方法類似。
- componentDidUpdate : 在元件重新渲染後呼叫該方法,和componentDidMount方法類似。
//元件更新class HelloWorldFather extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.updateChildProps=this.updateChildProps.bind(this);
this.state={ //初始化父元件
name:"React"
}
}
updateChildProps(){ //更新父元件state
this.setState({
name:"Vue"
})
}
render() {
return (
<p>
<HelloWorld name={this.state.name} /> {/*父元件的state傳遞給子元件*/}
<button onClick={this.updateChildProps}>更新子元件props</button>
</p>
)
}}class HelloWorld extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log("1,建構函式");
console.log("2,設定狀態機")
}
UNSAFE_componentWillMount() {
console.log("3,完成首次渲染前呼叫");
}
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, nextContext) {
console.log("6,父元件更新子元件時呼叫該方法");
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log("7,決定元件props或者state的改變是否需要重新進行渲染");
return true;
}
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log("8,當接收到新的props或state時,呼叫該方法");
}
render() {
console.log("4,元件進行渲染");
return (
<p>
<p>{this.props.name}</p>
</p>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log("5,componentDidMount render後的操作");
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log("9,元件被重新選然後呼叫該方法");
}}ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorldFather />,document.getElementById("root"));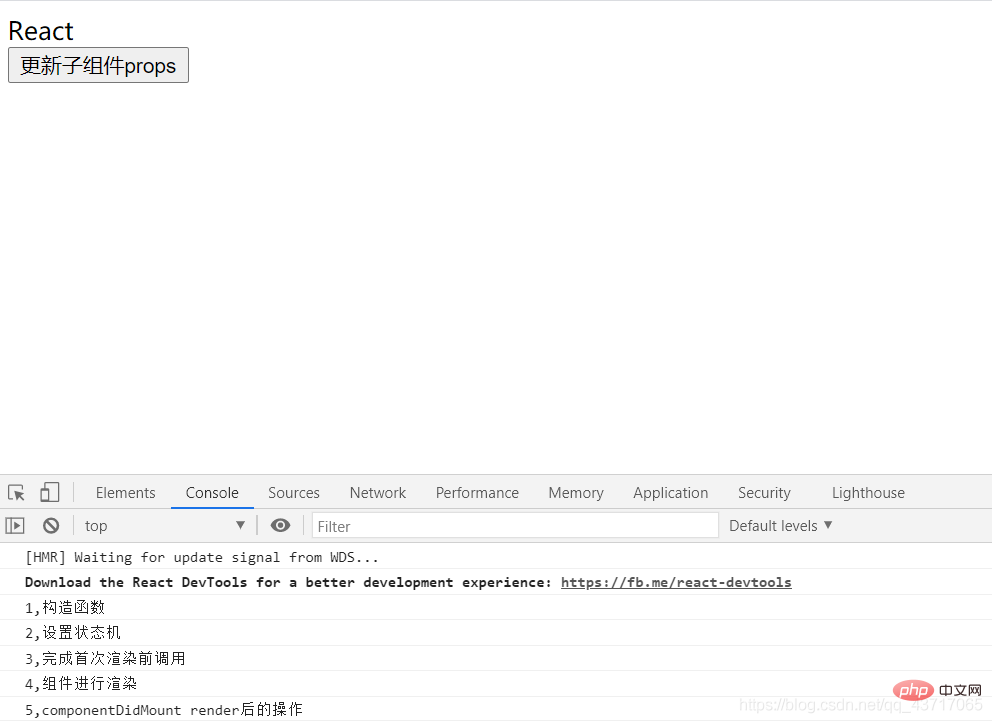
點選「更新子元件props」後: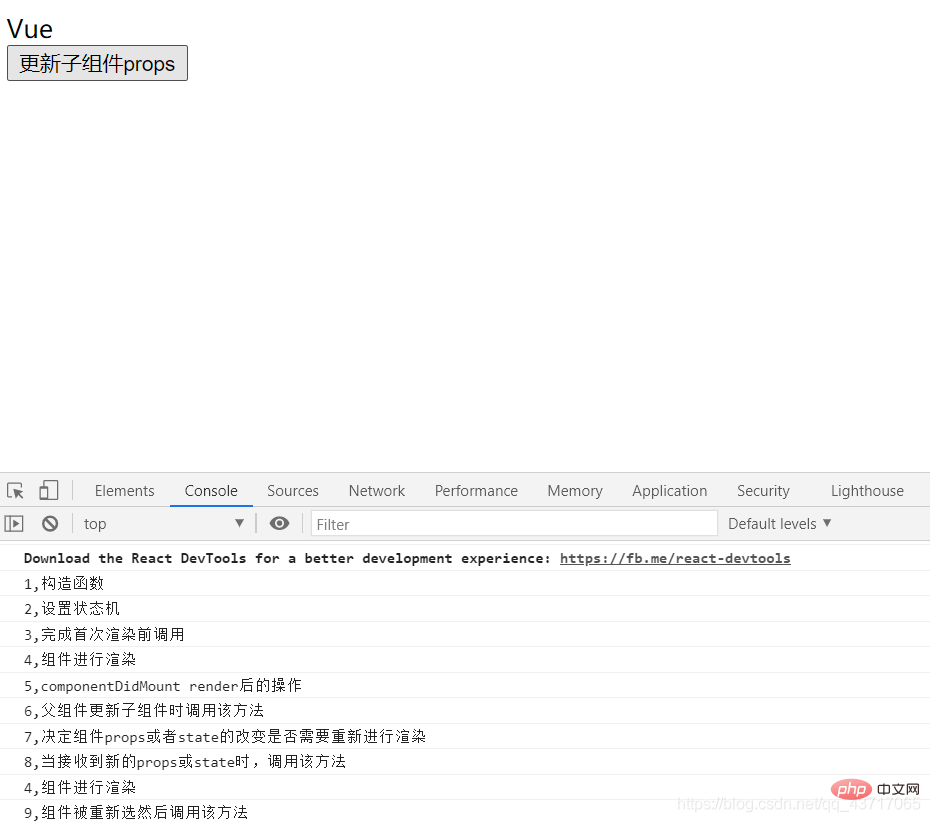
元件的解除安裝:
生命週期的最後一個過程為元件解除安裝期,也稱為元件銷燬期。該過程主要涉及一個 方法,即componentWillUnmount,當元件從DOM樹刪除的時候呼叫該方法。
//元件解除安裝class HelloWorldFather extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.updateChildProps=this.updateChildProps.bind(this);
this.state={ //初始化父元件
name:"React"
}
}
updateChildProps(){ //更新父元件state
this.setState({
name:"Vue"
})
}
render() {
return (
<p>
<HelloWorld name={this.state.name} /> {/*父元件的state傳遞給子元件*/}
<button onClick={this.updateChildProps}>更新子元件props</button>
</p>
)
}}class HelloWorld extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log("1,建構函式");
console.log("2,設定狀態機")
}
UNSAFE_componentWillMount() {
console.log("3,完成首次渲染前呼叫");
}
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, nextContext) {
console.log("6,父元件更新子元件時呼叫該方法");
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log("7,決定元件props或者state的改變是否需要重新進行渲染");
return true;
}
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log("8,當接收到新的props或state時,呼叫該方法");
}
delComponent(){ //新增解除安裝方法
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById("root"));
}
render() {
console.log("4,元件進行渲染");
return (
<p>
<p>{this.props.name}</p>
<button onClick={this.delComponent}>解除安裝元件</button> {/*宣告解除安裝按鈕*/}
</p>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log("5,componentDidMount render後的操作");
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log("9,元件被重新選然後呼叫該方法");
}
componentWillUnmount() { //元件解除安裝後執行
console.log("10,元件已被解除安裝");
}}ReactDOM.render(<HelloWorldFather />,document.getElementById("root"));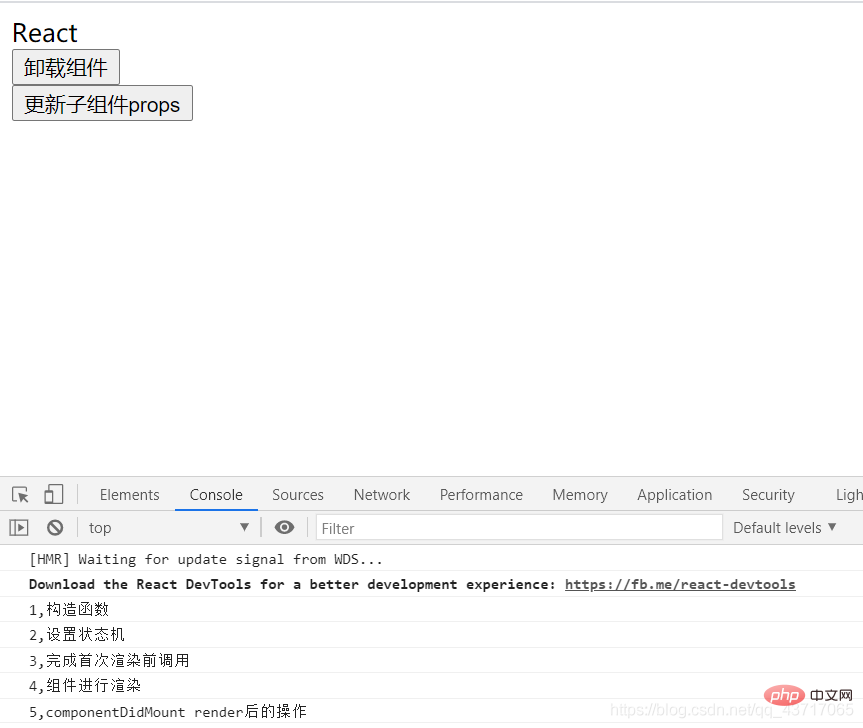
點選解除安裝按鈕後: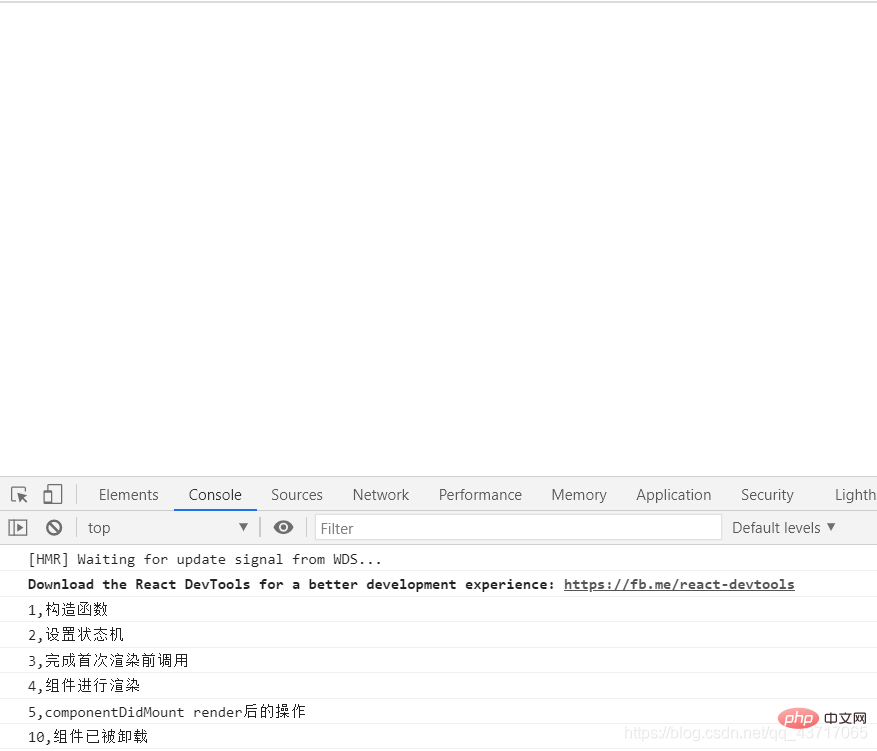
總覽元件生命週期: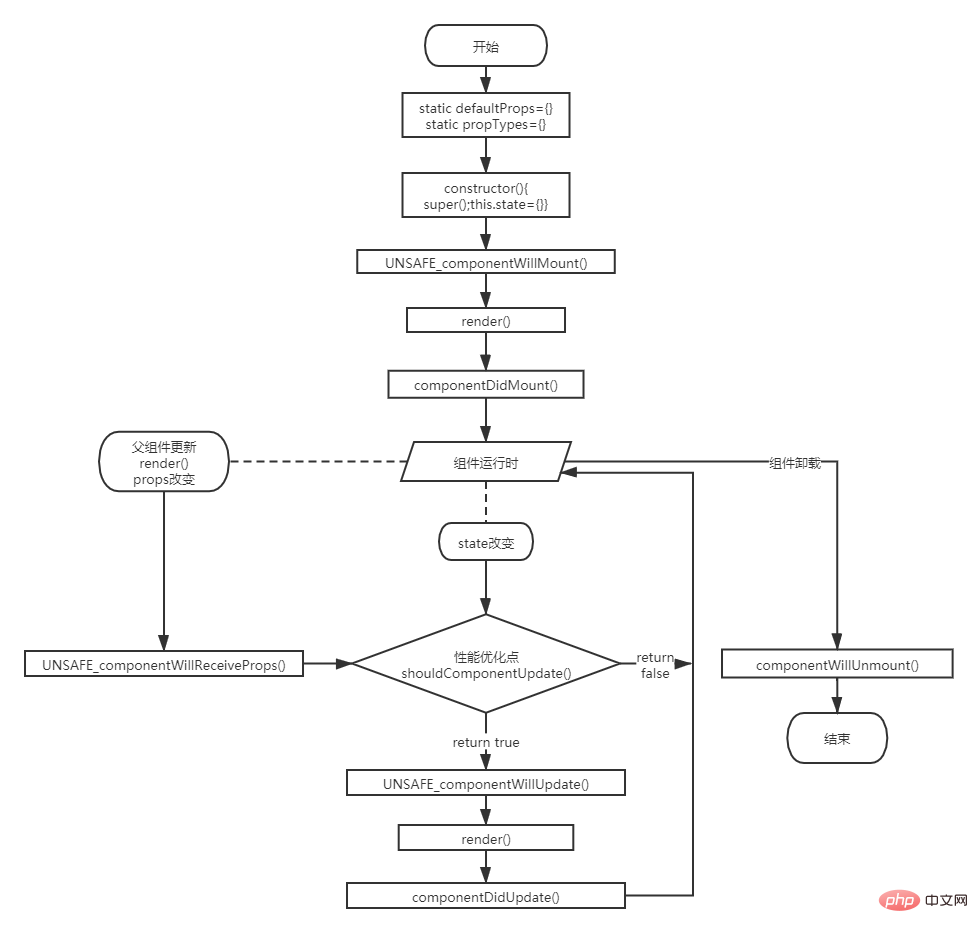
【相關推薦:、】
以上就是react生命週期的三個過程是什麼的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!