k8s client-go原始碼分析 informer原始碼分析(6)-Indexer原始碼分析
client-go之Indexer原始碼分析
1.Indexer概述
Indexer中有informer維護的指定資源物件的相對於etcd資料的一份本地記憶體快取,可通過該快取獲取資源物件,以減少對apiserver、對etcd的請求壓力。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
items map[string]interface{}
indexers Indexers
indices Indices
...
}
informer所維護的快取依賴於threadSafeMap結構體中的items屬性,其本質上是一個用map構建的鍵值對,資源物件都存在items這個map中,key為資源物件的namespace/name組成,value為資源物件本身,這些構成了informer的本地快取。
Indexer除了維護了一份本地記憶體快取外,還有一個很重要的功能,便是索引功能了。索引的目的就是為了快速查詢,比如我們需要查詢某個node節點上的所有pod、查詢某個名稱空間下的所有pod等,利用到索引,可以實現快速查詢。關於索引功能,則依賴於threadSafeMap結構體中的indexers與indices屬性。
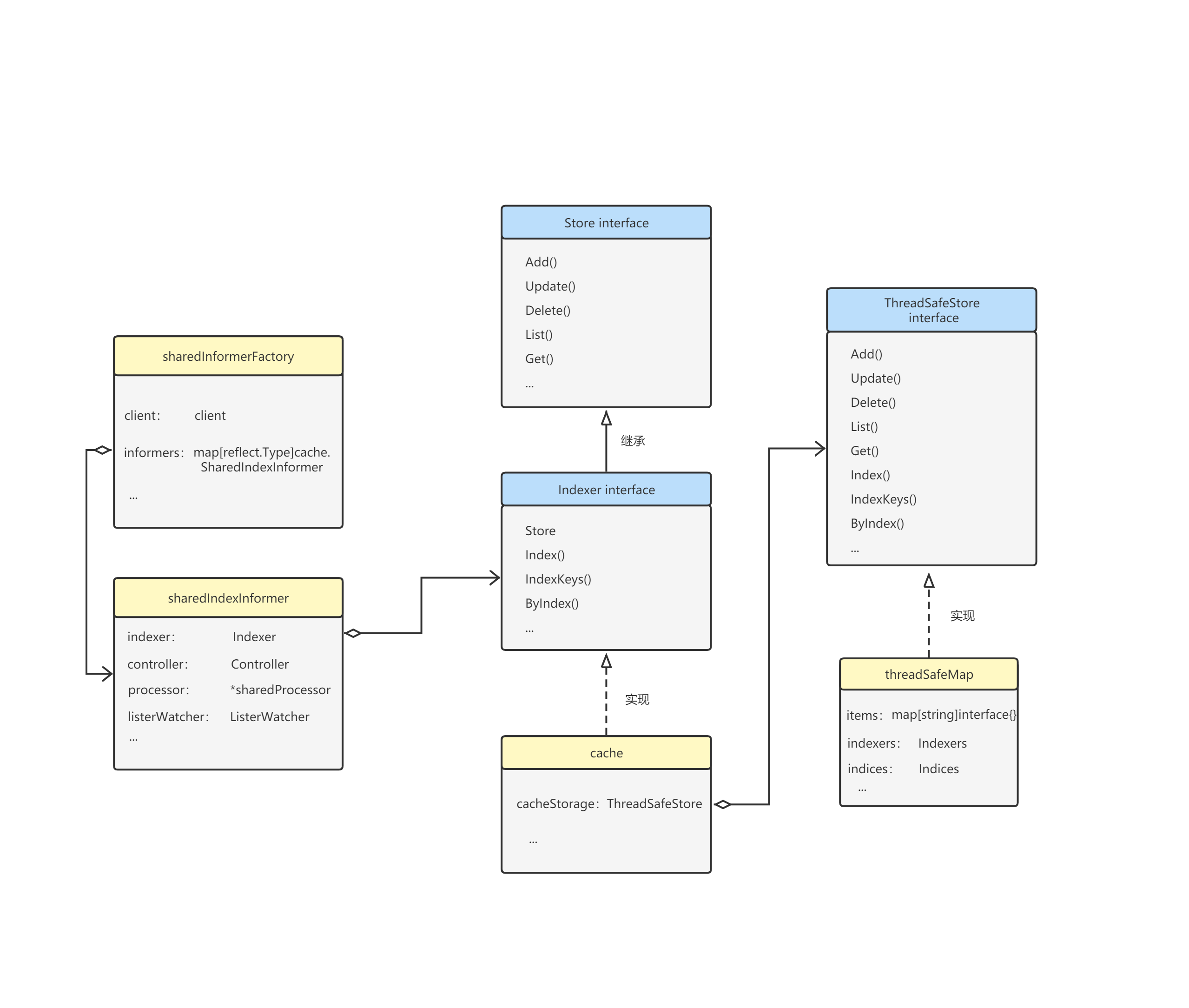
先通過一張informer概要架構圖看一下Indexer所處位置與其概要功能。

2.Indexer的結構定義分析
2.1 Indexer interface
Indexer介面繼承了一個Store介面(實現本地快取),以及包含幾個index索引相關的方法宣告(實現索引功能)。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
type Indexer interface {
Store
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
2.2 Store interface
Store介面本身,定義了Add、Update、Delete、List、Get等一些物件增刪改查的方法宣告,用於操作informer的本地快取。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
type Store interface {
Add(obj interface{}) error
Update(obj interface{}) error
Delete(obj interface{}) error
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
Replace([]interface{}, string) error
Resync() error
}
2.3 cache struct
結合程式碼,可以看到cache struct是Indexer介面的一個實現,所以自然也是Store介面的一個實現,cache struct包含一個ThreadSafeStore介面的實現,以及一個計算object key的函數KeyFunc。
cache struct會根據keyFunc生成某個obj物件對應的一個唯一key, 然後呼叫ThreadSafeStore介面中的方法來操作本地快取中的物件。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
type cache struct {
cacheStorage ThreadSafeStore
keyFunc KeyFunc
}
2.4 ThreadSafeStore interface
ThreadSafeStore介面包含了操作本地快取的增刪改查方法以及索引功能的相關方法,其方法名稱與Indexer介面的類似,最大區別是ThreadSafeStore介面的增刪改查方法入參基本都有key,由cache struct中的KeyFunc函數計算得出object key。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type ThreadSafeStore interface {
Add(key string, obj interface{})
Update(key string, obj interface{})
Delete(key string)
Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Replace(map[string]interface{}, string)
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
Resync() error
}
2.5 threadSafeMap struct
threadSafeMap struct是ThreadSafeStore介面的一個實現,其最重要的一個屬性便是items了,items是用map構建的鍵值對,資源物件都存在items這個map中,key根據資源物件來算出,value為資源物件本身,這裡的items即為informer的本地快取了,而indexers與indices屬性則與索引功能有關。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
2.6 Indexer結構定義小結
下面對上面介紹的Indexer的相關struct與interface做個小結:
(1)Store interface: 定義了Add、Update、Delete、List、Get等一些物件增刪改查的方法宣告,用於操作informer的本地快取;
(2)Indexer interface: 繼承了一個Store介面(實現本地快取),以及包含幾個index索引相關的方法宣告(實現索引功能);
(3)cache struct: Indexer介面的一個實現,所以自然也是Store介面的一個實現,cache struct包含一個ThreadSafeStore介面的實現,以及一個計算object key的函數KeyFunc;
(4)ThreadSafeStore interface: 包含了操作本地快取的增刪改查方法以及索引功能的相關方法,其方法名稱與Indexer介面的類似,最大區別是ThreadSafeStore介面的增刪改查方法入參基本都有key,由cache struct中的KeyFunc函數計算得出object key;
(5)threadSafeMap struct: ThreadSafeStore介面的一個實現,其最重要的一個屬性便是items了,items是用map構建的鍵值對,資源物件都存在items這個map中,key根據資源物件來算出,value為資源物件本身,這裡的items即為informer的本地快取了,而indexers與indices屬性則與索引功能有關;
3.Indexer的索引功能
在threadSafeMap struct中,與索引功能有關的是indexers與indices屬性;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
type Indices map[string]Index
type Index map[string]sets.String
3.1 type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc / type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
Indexers包含了所有索引器(索引分類)及其索引器函數IndexFunc,IndexFunc為計算某個索引鍵下的所有物件鍵列表的方法;
Indexers: {
"索引器1": 索引函數1,
"索引器2": 索引函數2,
}
資料範例:
Indexers: {
"namespace": MetaNamespaceIndexFunc,
"nodeName": NodeNameIndexFunc,
}
func MetaNamespaceIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
return []string{meta.GetNamespace()}, nil
}
func NodeNameIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
pod, ok := obj.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object is not a pod)
}
return []string{pod.Spec.NodeName}, nil
}
3.2 type Indices map[string]Index / type Index map[string]sets.String
Indices包含了所有索引器(索引分類)及其所有的索引資料Index;而Index則包含了索引鍵以及索引鍵下的所有物件鍵的列表;
Indices: {
"索引器1": {
"索引鍵1": ["物件鍵1", "物件鍵2"],
"索引鍵2": ["物件鍵3"],
},
"索引器2": {
"索引鍵3": ["物件鍵1"],
"索引鍵4": ["物件鍵2", "物件鍵3"],
}
}
資料範例:
pod1 := &v1.Pod {
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta {
Name: "pod-1",
Namespace: "default",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeName: "node1",
}
}
pod2 := &v1.Pod {
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta {
Name: "pod-2",
Namespace: "default",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeName: "node2",
}
}
pod3 := &v1.Pod {
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta {
Name: "pod-3",
Namespace: "kube-system",
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeName: "node2",
}
}
Indices: {
"namespace": {
"default": ["pod-1", "pod-2"],
"kube-system": ["pod-3"],
},
"nodeName": {
"node1": ["pod-1"],
"node2": ["pod-2", "pod-3"],
}
}
3.3 索引結構小結
Indexers: {
"索引器1": 索引函數1,
"索引器2": 索引函數2,
}
Indices: {
"索引器1": {
"索引鍵1": ["物件鍵1", "物件鍵2"],
"索引鍵2": ["物件鍵3"],
},
"索引器2": {
"索引鍵3": ["物件鍵1"],
"索引鍵4": ["物件鍵2", "物件鍵3"],
}
}
3.4 索引功能方法分析
看到Indexer interface,除了繼承的Store外,其他的幾個方法宣告均與索引功能相關,下面對幾個常用方法進行介紹。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
type Indexer interface {
Store
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
下面的方法介紹基於以下資料:
Indexers: {
"namespace": MetaNamespaceIndexFunc,
"nodeName": NodeNameIndexFunc,
}
Indices: {
"namespace": {
"default": ["pod-1", "pod-2"],
"kube-system": ["pod-3"],
},
"nodeName": {
"node1": ["pod-1"],
"node2": ["pod-2", "pod-3"],
}
}
3.4.1 ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
呼叫ByIndex方法,傳入索引器名稱indexName,以及索引鍵名稱indexedValue,方法尋找該索引器下,索引鍵對應的物件鍵列表,然後根據物件鍵列表,到Indexer快取(即threadSafeMap中的items屬性)中獲取出相應的物件列表。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
func (c *cache) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {
return c.cacheStorage.ByIndex(indexName, indexKey)
}
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
index := c.indices[indexName]
set := index[indexKey]
list := make([]interface{}, 0, set.Len())
for key := range set {
list = append(list, c.items[key])
}
return list, nil
}
使用範例:
pods, err := index.ByIndex("namespace", "default")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for _, pod := range pods {
fmt.Println(pod.(*v1.Pod).Name)
}
fmt.Println("=====")
pods, err := index.ByIndex("nodename", "node1")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
for _, pod := range pods {
fmt.Println(pod.(*v1.Pod).Name)
}
輸出:
pod-1
pod-2
=====
pod-1
3.4.2 IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
IndexKeys方法與ByIndex方法類似,只不過只返回物件鍵列表,不會根據物件鍵列表,到Indexer快取(即threadSafeMap中的items屬性)中獲取出相應的物件列表。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
func (c *cache) IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error) {
return c.cacheStorage.IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey)
}
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
index := c.indices[indexName]
set := index[indexKey]
return set.List(), nil
}
4.Indexer本地快取
從前面的分析可以知道,informer中的本地快取實際上指的是Indexer中的threadSafeMap,具體到屬性,則是threadSafeMap中的items屬性;
threadSafeMap struct
threadSafeMap struct中的items屬性即為informer的本地快取;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
接下來分析下threadSafeMap的幾個核心方法,主要都是操作items屬性的;
前面對informer-Controller的分析中(程式碼如下),提到的s.indexer.Add、s.indexer.Update、s.indexer.Delete、s.indexer.Get等方法其實最終就是呼叫的threadSafeMap.Add、threadSafeMap.Update、threadSafeMap.Delete、threadSafeMap.Get等;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/shared_informer.go
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Added, Updated:
isSync := d.Type == Sync
s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
}
case Deleted:
if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}
4.1 threadSafeMap.Add
呼叫鏈:s.indexer.Add --> cache.Add --> threadSafeMap.Add
threadSafeMap.Add方法將key:object存入items中,並呼叫updateIndices方法更新索引(updateIndices方法這裡不展開分析,可以自行檢視原始碼);
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj
c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}
也可以看到對threadSafeMap進行操作的方法,基本都會先獲取鎖,然後方法執行完畢釋放鎖,所以是並行安全的。
4.2 threadSafeMap.Update
呼叫鏈:s.indexer.Update --> cache.Update --> threadSafeMap.Update
threadSafeMap.Update方法邏輯與threadSafeMap.Add方法相同;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Update(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj
c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}
4.3 threadSafeMap.Delete
呼叫鏈:s.indexer.Delete --> cache.Delete --> threadSafeMap.Delete
threadSafeMap.Delete方法中,先判斷本地快取items中是否存在該key,存在則呼叫deleteFromIndices刪除相關索引,然後刪除items中的key及其對應object;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Delete(key string) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
if obj, exists := c.items[key]; exists {
c.deleteFromIndices(obj, key)
delete(c.items, key)
}
}
4.4 threadSafeMap.Get
呼叫鏈:s.indexer.Get --> cache.Get --> threadSafeMap.Get
threadSafeMap.Get方法邏輯相對簡單,沒有索引的相關操作,而是直接從items中通過key獲取對應的object並返回;
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
item, exists = c.items[key]
return item, exists
}
總結
Indexer中有informer維護的指定資源物件的相對於etcd資料的一份本地記憶體快取,可通過該快取獲取資源物件,以減少對apiserver、對etcd的請求壓力。
informer所維護的快取依賴於threadSafeMap結構體中的items屬性,其本質上是一個用map構建的鍵值對,資源物件都存在items這個map中,key為資源物件的namespace/name組成,value為資源物件本身,這些構成了informer的本地快取。
Indexer除了維護了一份本地記憶體快取外,還有一個很重要的功能,便是索引功能了。索引的目的就是為了快速查詢,比如我們需要查詢某個node節點上的所有pod、查詢某個名稱空間下的所有pod等,利用到索引,可以實現快速查詢。關於索引功能,則依賴於threadSafeMap結構體中的indexers與indices屬性。
最後以一張圖來回顧總結一下Indexer在informer中所處位置與其概要功能。
