【Java集合】ArrayDeque原始碼解讀
簡介
雙端佇列是一種特殊的佇列,它的兩端都可以進出元素,故而得名雙端佇列。
ArrayDeque是一種以迴圈陣列方式實現的雙端佇列,它是非執行緒安全的。
它既可以作為佇列也可以作為棧。
繼承體系
ArrayDeque實現了 Deque介面,Deque介面繼承自 Queue介面,它是對 Queue的一種增強。
同時實現了 Serializable和 Cloneable介面,可以進行序列化和克隆。
原始碼解讀
主要屬性
// 儲存元素的陣列
transient Object[] elements; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// 佇列頭位置
transient int head;
// 佇列尾位置
transient int tail;
// 最小初始容量
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
// 序列號
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2340985798034038923L;
head指向頭元素
tail指向尾元素的下一個位置
這裡注意到,head,tail,elements屬性都被 transient修飾,不會參與序列化。
可能會有疑問,**elements**要是不參與序列化,集合內的資料不就無法持久化嗎。
這個問題先放在這裡,講完 ArrayList擴容原理之後再進行回答。
構造方法
// 預設構造方法,初始容量為16
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
}
// 指定元素個數初始化
public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
allocateElements(numElements);
}
// 將集合c中的元素初始化到陣列中
public ArrayDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
allocateElements(c.size());
addAll(c);
}
// 初始化陣列
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
elements = new Object[calculateSize(numElements)];
}
// 計算容量,這段程式碼的邏輯是算出大於numElements的最接近的2的n次方且不小於8
// 比如,3算出來是8,9算出來是16,33算出來是64
private static int calculateSize(int numElements) {
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// Find the best power of two to hold elements.
// Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
return initialCapacity;
}
通過構造方法,我們知道預設初始容量是16,最小容量是8。
這裡比較有意思的是 calculateSize容量計算方法,本質是為了獲取大於當前數值的最小的2的冪,比如 3 算出來是 8,9 算出來是 16,33 算出來是 64。
由於 2 的冪用二進位制表示的特點就是隻有一個二進位位是 1 ,其餘數位都是 0,所以從二進位制的角度,分為兩步操作
- 第一步:將該數二進位制的最高位 1 之後的所有數位設定為 1(如果 numElements < 8 則直接返回 8)
// 第一步
0000 0001 0101 1110 1000 1111 0001 1010 // 原數
0000 0001 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 // 第一步完成
- 第二步:原數加一(如果小於 0,說明超過最大容量,整體右移一位)
// 第二步
0000 0001 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 // 第一步完成
0000 0010 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 // 第二部完成,成為 2 的冪
對於calculateSize 一種直接的想法是使用迴圈加位運算,找到最高位的二進位制 1(形成獨立的一個 2 的冪),然後將該數位左移一位返回,時間複雜度 O(n),最壞情況下需要進行 31 次。
int tmp = 1 << 31;
int count = 31;
while ((numElements & tmp) == 0 && count > 0) {
tmp >>>= 1;
count--;
}
tmp <<= 1;
return tmp;
原始碼利用的是二分的思想,總共 32 位也就是 2 的 5 次方,只需要 5 次位運算即可,時間複雜度 O(logn)
0000 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 >>> 1
0000 0001 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 |=
0000 0000 0110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 >>> 2
0000 0001 1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 |=
0000 0000 0001 1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 >>> 4
0000 0001 1111 1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 |=
0000 0000 0000 0001 1111 1110 0000 0000 >>> 8
0000 0001 1111 1111 1111 1111 0000 0000 |=
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 1111 1111 >>> 16
0000 0001 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 |=
擴容
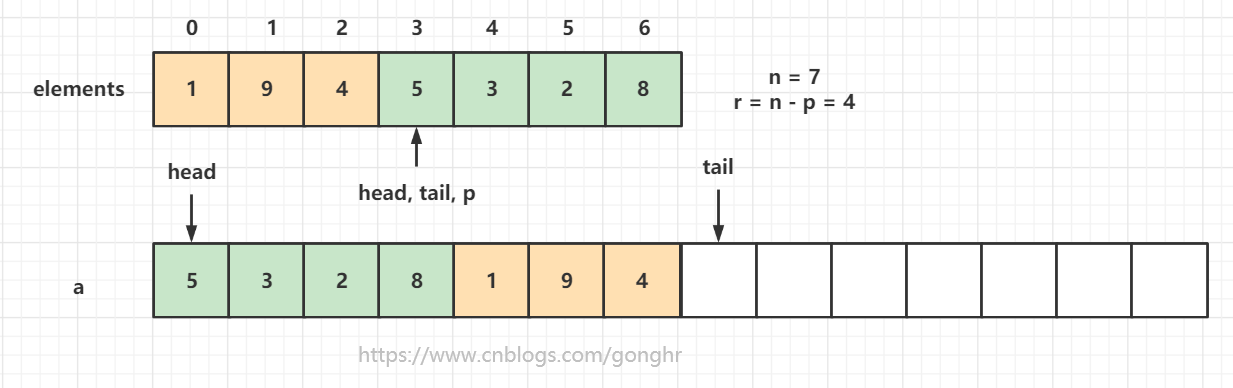
private void doubleCapacity() {
// 斷言集合已滿
assert head == tail;
// 頭指標的位置
int p = head;
// 舊陣列長度
int n = elements.length;
// 頭指標離陣列尾的距離
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
// 新長度為舊長度的兩倍
int newCapacity = n << 1;
// 判斷是否溢位
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
// 新建新陣列
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
// 將舊陣列head之後的元素拷貝到新陣列中
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
// 將舊陣列下標0到head之間的元素拷貝到新陣列中
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
// 賦值為新陣列
elements = a;
// head指向0,tail指向舊陣列長度表示的位置
head = 0;
tail = n;
}
擴容原理:集合滿了之後,建立一個原陣列容量 2 倍的集陣列,然後把元素拷貝到新陣列中。
陣列拷貝使用的是 System.arraycopy函數
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
// src – the source array.
// srcPos – starting position in the source array.
// dest – the destination array.
// destPos – starting position in the destination data.
// length – the number of array elements to be copied.
ok,講完擴容之後補一下坑,elements不參與序列化是從空間的角度考慮的,ArrayDeque的容量始終為 2 的冪,始終不是滿的,有位置沒有存放元素,如果是剛剛擴容完,可能有接近一半的空間未使用,如果參與序列化,會造成大量空間的浪費,消耗網路傳輸或者資料庫傳輸,降低吞吐量。
解決方案是把集合拆分成幾部分進行傳輸,而不是作為一個整體,來節約空間和減少序列化的時間
// 將 ArrayDeque 範例的狀態儲存到流(即序列化它)
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// 寫出當前類的所有非靜態欄位(non-static)和非瞬態欄位(non-transient)到ObjectOutputStream
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
// 將size寫出到ObjectOutputStream
s.writeInt(size());
// Write out elements in order.
int mask = elements.length - 1;
// i = (i + 1) & mask 表示迴圈陣列下標的移動
for (int i = head; i != tail; i = (i + 1) & mask)
s.writeObject(elements[i]); // 有序的將elementData中已使用的元素讀出到流中
}
// 從流中重構 ArrayDeque 範例(即,對其進行反序列化)
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 讀入size和非transient非static屬性
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size and allocate array
// 讀入容量
int size = s.readInt();
// 重新分配容量
int capacity = calculateSize(size);
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity);
allocateElements(size);
head = 0;
tail = size;
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
// // 按正確的順序讀入所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elements[i] = s.readObject();
}
入隊
// 從佇列頭入隊
public void addFirst(E e) {
// 不允許null元素
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 將head指標減1並與陣列長度減1取模
// 這是為了防止陣列到頭了邊界溢位
// 如果到頭了就從尾再向前
// 相當於迴圈利用陣列
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
// 如果頭尾挨在一起了,就擴容
// 擴容規則也很簡單,直接兩倍
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
// 從佇列尾入隊
public void addLast(E e) {
// 不允許null元素
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 在尾指標的位置放入元素
// 可以看到tail指標指向的是佇列最後一個元素的下一個位置
elements[tail] = e;
// tail指標加1,如果到陣列尾了就從頭開始
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
- 入隊有兩種方式,從佇列頭或者從佇列尾;
- 如果容量不夠了,直接擴大為兩倍;
- 通過取模的方式讓頭尾指標在陣列範圍內迴圈;
x & (len - 1) = x % len,使用&的方式更快;
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
- 剩下幾種入隊操作本質都是
addFirst和addLast,不過是多了返回值。
出隊
// 從佇列頭出隊
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 取佇列頭元素
E result = (E) elements[h];
// 如果佇列為空,就返回null
if (result == null)
return null;
// 將佇列頭置為空
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
// 佇列頭指標右移一位
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
// 返回取得的元素
return result;
}
// 從佇列尾出隊
public E pollLast() {
// 尾指標左移一位
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 取當前尾指標處元素
E result = (E) elements[t];
// 如果佇列為空返回null
if (result == null)
return null;
// 將當前尾指標處置為空
elements[t] = null;
// tail指向新的尾指標處
tail = t;
// 返回取得的元素
return result;
}
- 出隊有兩種方式,從佇列頭或者從佇列尾;
- 通過取模的方式讓頭尾指標在陣列範圍內迴圈;
- 出隊之後沒有縮容
// 移除隊頭元素
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
// 移除隊尾元素
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
// 移除隊頭元素
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
// 移除隊頭元素
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
剩下幾種出隊操作本質是 pollFirst 和 pollLast,區別就是 remove*操作可能丟擲 NoSuchElementException異常。
入棧
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
出棧
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
入棧和出棧操作本質都是操作佇列頭。
容量
public int size() {
return (tail - head) & (elements.length - 1);
}
用與運算取代取模運算,速度更快。
檢視兩端元素
public E peekFirst() {
// elements[head] is null if deque empty
return (E) elements[head];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekLast() {
return (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
}
如果元素不存在,返回 null
public E getFirst() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[head];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E getLast() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
如果元素不存在,丟擲 NoSuchElementException異常
是否為空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
head和 tail相同時表示為空
清空
public void clear() {
int h = head;
int t = tail;
// 如果 head == tail 則為空,直接返回,指向哪裡無所謂,是迴圈陣列
if (h != t) { // clear all cells
// 如果 head != tail 表示有元素,head 和 tail 都指向 0
head = tail = 0;
int i = h;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
// 從頭元素開始迴圈清空陣列
do {
elements[i] = null;
i = (i + 1) & mask;
} while (i != t);
}
}
效能測試
ArrayDeque 與 LinkedList
ArrayDeque 跟同樣實現了 Deque 介面的 LinkedList 對比。
- 二者都新增 200000 個資料。
long start = 0, end = 0;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
for (int i=0; i<2000000; i++) {
linkedList.addFirst(i);
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("LinkedList addFirst 2000000 cost time = " + (end-start) + "ms");
LinkedList addFirst 2000000 cost time = 351ms
long start = 0, end = 0;
ArrayDeque arrayDeque = new ArrayDeque();
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0; i < 2000000; i++){
arrayDeque.addFirst(i);
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("ArrayDeque addFirst 2000000 cost time = " + (end-start) + "ms");
ArrayDeque addFirst 2000000 cost time = 20ms
可以看到,ArrayDeque是 LinkedList速度的 15 倍
- 二者都移除 200000 個資料。
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (linkedList.size() != 0) {
linkedList.removeFirst();
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("LinkedList removeFirst cost time = " + (end-start) + "ms");
LinkedList removeFirst cost time = 21ms
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (arrayDeque.size() != 0) {
arrayDeque.removeFirst();
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("ArrayDeque removeFirst cost time = " + (end-start) + "ms");
ArrayDeque removeFirst cost time = 10ms
可以看到,ArrayDeque是 LinkedList速度的 2 倍