Mybatis原始碼分析
一、Mybatis的使用
-
建立maven工程。
-
新增maven依賴
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.20</version>
</dependency>
- 新增組態檔mybatis.xml,內容如下:
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/aoptest"/>
<property name="username" value="xxx"/>
<property name="password" value="xxx"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- 把上面的Mapper.xml 註冊進來,路徑寫在resources目錄下的路徑-->
<mapper resource="com/ybe/mapper/BookMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 新增實體類,程式碼如下:
package com.ybe.entity;
public class Book {
int id;
double price;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
- 新增BookMapper介面,程式碼如下:
package com.ybe.mapper;
import com.ybe.entity.Book;
public interface BookMapper {
Book getBook();
}
- 新增BookMapper.xml組態檔,內容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ybe.mapper.BookMapper">
<select id="getBook" resultType="com.ybe.entity.Book">
select * from book where id = 1
</select>
</mapper>
- 替換pom檔案的 build節點,把resources路徑下的xml檔案包括在打包目錄中,內容如下:
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
- App主類新增程式碼,使用mybaits:
//載入mybatis的組態檔
InputStream input = Book.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
// 用建造者模式,創造 生產SqlSession的工廠(這個工廠的型別由組態檔決定)
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(input);
// 工廠生產Sqlsession
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
Book book = sqlSession.selectOne("getBook");
System.out.println(book);
//關閉IO資源(工廠物件會自動回收)
input.close();
sqlSession.close();
二、Mybatis的初始化
- Mybatis的初始化就是建立一個SqlSessionFactory範例物件。
步驟一、先根據組態檔建立資源流,
步驟二、根據檔案流解析生成SqlSessionFactory物件
-
時序圖如下:

-
初始化程式碼如下,
InputStream input = Book.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
// 用建造者模式,創造 生產SqlSession的工廠(這個工廠的型別由組態檔決定)
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(input);
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(input)方法的程式碼如下,
// 建立XMLConfigBuilder物件,該物件解析組態檔,並給configuration物件賦值。
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// parser.parse()進行具體的解析,返回configuration範例
// build構建 SqlSessionFactory物件
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
-
其中邏輯主要是建立了一個XMLConfigBuilder範例,並進行了parse()呼叫,該方法返回的是Configuration範例,Configuration儲存了主組態檔的所有資訊,比如,資料庫事務工廠、資料來源物件、型別別名註冊器、型別處理註冊器等。Configuration範例用於物件查詢中整個過程,非常重要。
-
parser.parse()方法進行具體解析,parseConfiguration()核心程式碼如下:
// issue #117 read properties first
// 解析 properties 內容
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析 settings 內容
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
//新增vfs的自定義實現,這個功能不怎麼用
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
//設定類的別名,設定後就可以用別名來替代全限定名
//mybatis預設設定了很多別名,參考附錄部分
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//解析攔截器和攔截器的屬性,set到 Configration的interceptorChain中
//MyBatis 允許你在已對映語句執行過程中的某一點進行攔截呼叫。預設情況下,MyBatis 允許使用外掛來攔截的方法呼叫
//包括:
//Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
//ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
//ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
//StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//Mybatis建立物件是會使用objectFactory來建立物件,一般情況下不會自己設定這個objectFactory,
// 使用系統預設的objectFactory就好了
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
//設定在setting標籤中設定的設定
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//解析環境資訊,包括事物管理器和資料來源,SqlSessionFactoryBuilder在解析時需要指定環境id
// ,如果不指定的話,會選擇預設的環境;
//最後將這些資訊set到 Configration的 Environment屬性裡面
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
//無論是 MyBatis 在預處理語句(PreparedStatement)中設定一個引數時,還是從結果集中取出一個值時,
// 都會用型別處理器將獲取的值以合適的方式轉換成 Java 型別。解析typeHandler。
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//解析mapper檔案
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
- build(Configuration config)返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory物件,程式碼如下,
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
- Configuration類主要屬性說明:
variables:用來存放 properties 節點中解析出來的 Properties 資料。
typeAliasRegistry:用來存放 typeAliases 節點中解析出來的資料。
interceptorChain: 用來存放 plugins 節點解析出來的攔截器鏈。
environment: 用來存放 environments 節點解析出來的資料,比如資料庫事務管理器和資料來源。
typeHandlerRegistry:用來存放 typeHandlers 節點解析出來的資料。
mapperRegistry:用來註冊Mapper介面 。
mappedStatements:用來儲存 MappedStatement 物件,MappedStatement用來表示XXXMapper.XML檔案中具體的 select|insert|update|delete節點資料 。
三、組態檔解析
Mybaits組態檔解析讀取的過程是通過建立不同的XML構建器來完成的,把解析出來的資料賦值給Configuration範例的屬性。
3.1 XML構造解析類
Mybatis主要構造解析類有XMLConfigBuilder、XMLMapperBuilder、XMLStatementBuilder、MapperBuilderAssistant。他們有一個共同的基礎類別BaseBuilder。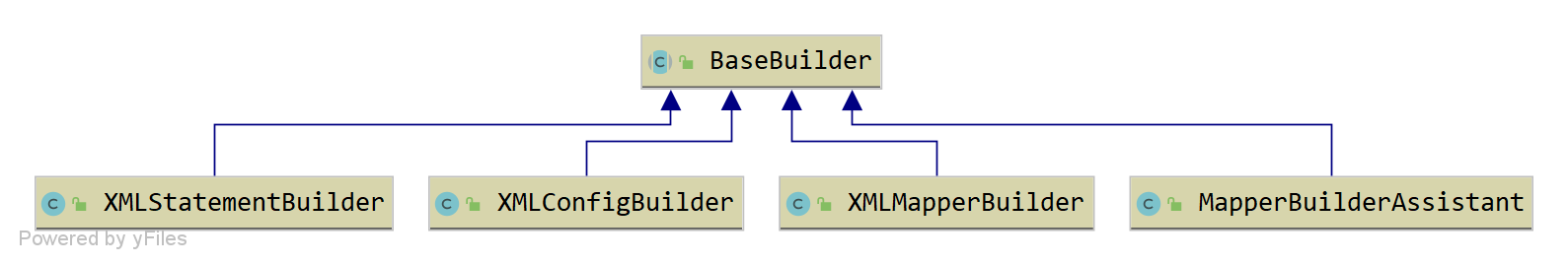
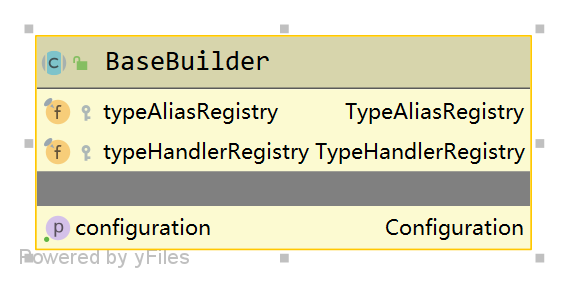
**BaseBuilder **類中有3個欄位,用來儲存別名註冊器、型別處理器註冊器、設定類。其中型別別名註冊器和型別處理註冊器是從configuration物件中獲取的。BaseBuilder提供了根據別名獲取具體的物件範例的方法以及根據java型別獲取型別處理器物件的方法等。
XMLConfigBuilder 主要用來構建解析主組態檔,構造方法中會建立XPathParser類,通過XPathParser 來解析和讀取XML檔案,XMLConfigBuilder的構造方法如下:
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
在構造方法中會建立了一個 Configuration的範例。在Configuration的構造方法中會進行一些別名的註冊和屬性的初始化,部分程式碼如下:
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry(this);
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<>("Caches collection");
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<>("Result Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<>("Parameter Maps collection");
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<>("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
public Configuration() {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}
其中的 TypeAliasRegistry 類的構造方法中也進行了一些資料型別別名的註冊,部分程式碼如下:
registerAlias("string", String.class);
registerAlias("byte", Byte.class);
registerAlias("long", Long.class);
registerAlias("short", Short.class);
registerAlias("int", Integer.class);
registerAlias("integer", Integer.class);
registerAlias("double", Double.class);
registerAlias("float", Float.class);
registerAlias("boolean", Boolean.class);
registerAlias("byte[]", Byte[].class);
registerAlias("long[]", Long[].class);
registerAlias("short[]", Short[].class);
registerAlias("int[]", Integer[].class);
registerAlias("integer[]", Integer[].class);
registerAlias("double[]", Double[].class);
registerAlias("float[]", Float[].class);
registerAlias("boolean[]", Boolean[].class);
XMLMapperBuilder: 主要用來解析 Mapper.XML檔案的。
XMLStatementBuilder :主要用來解析 Mapper.xml 檔案中 select|insert|update|delete 等語句的。
MapperBuilderAssistant :Mapper解析過程中的助手類,可以用來建立Mapper的二級快取,新增MappedStatement等。
MappedStatement:用來存放解析 Mapper.xml 檔案中的 select|insert|update|delete 節點資料。
3.2 解析過程
3.2.1environments節點解析
過程比較簡單,根據environments的預設值建立environments的子節點,其中主要是建立資料庫事務工廠和資料來源物件,並構建Environment類,賦值給configuration範例,程式碼如下,
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
// 解析 default 屬性值
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
// 獲取子節點
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
// 獲取 id 屬性值
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
// 判斷 子節點的id 是否 等於 default 值
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
// 獲取事務工廠
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
// 獲取資料來源工廠
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
// 獲取資料來源
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
// 構建 Environment 範例,賦值給configuration
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
break;
}
}
}
}
3.2.2mappers節點解析
整個解析過程中比較複雜,主要邏輯是要解析具體的mapper檔案或者mapper介面。關鍵業務實現在XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法中。根據mappers的子節點的name值和屬性來執行不同的方法。
一、如果為mappers子節點是以 package 開頭則呼叫
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName);
}
MapperRegistry類中方法如下:
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
//建立解析類
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
// 找到 package 路徑下所有繼承 superType的類, 並且放入 matches 屬性當中
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
// 獲取所有 matches 的值
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
// 新增 具體的 對映類
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 必須是介面型別才能新增成功
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 如果該型別以及新增,則拋異常
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 新增type 型別的代理工程物件 到 knownMappers 物件中。
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
//建立 mapper 註解解析類
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
二、如果為mappers子節點是以 mapper 開頭並且屬性為 class 則呼叫
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
1. 這上面兩種方式,都會呼叫類MapperAnnotationBuilder的parse()方法進行Mapper檔案或者Mapper介面的解析,程式碼如下,
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
// 判斷資源是否已經新增過
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 載入 mapperxml 檔案
loadXmlResource();
//新增 已經載入的資源
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 解析二級快取
parseCache();
// 解析快取參照
parseCacheRef();
// 遍歷mapper 介面的 方法
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
// 解析 ResultMap
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
// 解析具體的sql語句
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
- loadXmlResource()方法是進行Mapper.Xml檔案解析,parseStatement()方法則是進行Mapper介面的解析。這裡主要講解mapper.xml檔案解析,loadXmlResource中主要邏輯為:找到資原始檔流,建立XMLMapperBuilder範例,呼叫其parse()方法進行MapperXML檔案的解析,主要程式碼如下,
// 通過檔案流建立 XMLMapper 解析物件,
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
// 進行具體解析
xmlParser.parse();
- XMLMapperBuilder.parse()解析Mapper檔案的mapper節點,程式碼如下:
// 判斷 資源 是否載入過
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析 具體的 mapper.xml 檔案
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 設定為已經載入過的 資源
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 繫結該資源的 Mapper介面到 configuration 中
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
- configurationElement()為具體解析 mapper節點的方法,其中會解析 mapper中的namespace、cache、parameterMap、resultMap、sql、select|insert|update|delete,程式碼如下:
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 獲取節點的 namespace 值
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 設定助手類的 CurrentNamespace,即 mapper.xml 檔案中的 namespace 值
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 解析 mapper 的 parameterMap
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析 mapper 的 resultMap
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析 sql 片段
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析 select|insert|update|delete
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- buildStatementFromContext()方法用來解析mapper檔案中 select|insert|update|delete 節點,程式碼如下,
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
// 建立 XMLStatementBuilder 類
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// 解析 具體的 select|insert|update|delete 節點
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
- XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode()方法為實際解析select|insert|update|delete 節點的方法,主要邏輯為從節點中獲取相關引數構建MapperStatement物件,呼叫builderAssistant.addMappedStatement方法把MapperStatement新增到configuration.mappedStatements集合中去。部分程式碼如下,
// 獲取節點名稱
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 節點名稱就是資料命令名稱
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// 判斷是否是 SELECT 命令
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 設定是否重新整理快取
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
// 設定是否用快取
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
// 獲取自定義sql指令碼語言驅動 預設 為 XMLLanguageDriver
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// 通過 XMLLanguageDriver 來解析我們的sql 指令碼物件,解析 SqlNode ,
// 注意,只是解析成一個個的SqlNode,並不會完全解析sql,因為這個
// 時候引數都沒確定,動態sql無法解析
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
// 獲取 StatementType 型別
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
// 構建 MappedStatement 物件,新增到configuration.mappedStatements集合中去
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
- langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass),具體的Sql語句被解解構造為了實現了SqlSource介面的類。這些實現類通過SqlNode節點來記錄具體的Sql語句、引數型別、configuration物件。此過程只是根據設定的Sql語句生成具體的SqlNode物件,以便後面在執行sql語句的時候進行解析。
- builderAssistant.addMappedStatement();構建MappedStatement類裡面主要存放了 statementLog紀錄檔物件、,新增到configuration範例的mappedStatements集合中去。集合key值為 mapper檔案的 namaspace值 + id 值。
三、如果為mappers子節點是以 mapper 開頭並且屬性為 resouce 或者 url 則呼叫
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
#具體解析過程請看上面講解
mapperParser.parse();
四、Mybatis的使用
使用分為兩步,第一步獲取SqlSession物件,第二步呼叫SqlSession物件具體方法。
4.1 獲取SqlSession物件
通過factory.openSession()獲取DefaultSqlSession範例。主要邏輯為,先從configuration物件中獲取 environment環境變數、Executor執行器物件,然後從環境變數中建立事務物件,最後構建DefaultSqlSession物件範例。程式碼如下,
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 獲取 環境物件
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 獲取事務工廠
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 建立事務
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 獲取 executor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 構造 DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType),根據事務物件和執行器型別建立執行器,執行器有三種型別SIMPLE(簡單), REUSE(可複用), BATCH(批次)。預設為SIMPLE。如果開啟cacheEnabled(二級快取),則會建立CachingExecutor物件範例包裝SimpleExecutor範例。cacheEnabled預設是true。然後判斷是否有攔截器進行代理,如果有會建立CachingExecutor範例的代理類。程式碼如下,
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 是否開啟快取,預設開啟二級快取
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 獲取攔截器的代理
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
4.2 根據id呼叫SqlSession具體的方法
執行sqlSession.selectOne("getBook")語句來獲取 Book物件範例。selectOne其實內部呼叫的是SelectList。主要邏輯:先通過statment的id獲取configuration中的MappedStatement範例,再呼叫執行器的query方法進行查詢,並返回。程式碼如下,
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
// 根據 id 獲取 MappedStatement類
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 呼叫執行器執行查詢語句,並返回物件範例
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
executor.query 是執行的 CachingExecutor的query方法。主要邏輯:先通過 呼叫 範例獲取ms.getBoundSql()方法獲取 BondSql範例,BondSql中有具體的sql語句、傳入的引數物件。
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 解析獲取 SqlSource 實現類,獲取BoundSql, BoundSql裡面儲存了 解析之後的sql語句 ,引數物件
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 建立快取key (名稱空間id + sql語句 + 引數值 + 環境變數id)
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 進行查詢
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql),建立快取的key,key的規則為(名稱空間id + sql語句 + 引數值 + 環境變數id)。query()方法主體邏輯為:先獲取MappedStatement範例中的快取,如果快取存則獲取key的物件,程式碼如下,
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 獲取二級快取
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果有二級快取
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 如果是查詢,並且 resultHandler 為null
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 從 TransactionalCacheManager 中獲取 key的 快取物件
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 呼叫代理執行器(預設為 SimpleExecutor)
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql),呼叫代理執行器(預設為 SimpleExecutor)的query方法,具體執行的是BaseExecutor.query方法,此方法的主要邏輯為:先從本地快取中獲取key的物件,如果快取存在即返回該物件,如果快取不存在則呼叫queryFromDatabase()方法走資料庫查詢。程式碼如下,
queryStack++;
// 從一級快取中拿資料
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 如果沒有則走資料庫查詢
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
queryFromDatabase()的關鍵邏輯為,先執行sql語句拿到具體的物件範例,再把返回結果存入本地快取,最終返回執行結果。程式碼如下,
// 具體的查詢語句
doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 把資料存入一級快取
localCache.putObject(key, list);
return list;
doQuery()方法中執行資料庫sql,並且將資料庫結果集轉成具體的物件範例。主要邏輯為:通過 MappedStatement 獲取configuration物件,然後configuration建立 StatementHandler的範例,預設值為PreparedStatementHandler型別的範例。再通過prepareStatement方法對Statement物件進行初始化 。最後通過呼叫StatementHandler的query方法,返回物件範例。程式碼如下,
// 獲取 configuration 範例
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 建立 StatementHandler 範例
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 初始化 Statement 物件
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 執行 Statement,並且處理結果集
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
handler.query(stmt, resultHandler),會呼叫PreparedStatementHandler的query方法, 主體邏輯執行statement.execute拿到結果集,再通過結果處理器將資料庫結果集轉成物件範例,最終返回。
// 轉成 PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
// 執行sql,拿到結果
ps.execute();
// 結果處理器處理資料庫結果集
// 最終會返回實體物件
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps)方法主要是轉換查詢出的資料庫結果集為設定的物件範例,最終返回物件範例。程式碼如下,
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
// 獲取 資料庫結果集的包裝類 ResultSetWrapper
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
// 獲取返回結果Map物件
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
// 判斷 rsw 結果集不為空 ,並且 mappedStatement的 resultMapCount 數量 小於 1
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
// 獲取結果 Map 物件
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
// 處理結果集,集體返回結果存在 multipleResults 中
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
// 獲取下一個結果集
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
//獲取返回結果Set物件
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
// 返回結果
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null)方法,封裝了處理資料庫結果集的具體邏輯,原始碼裡面邏輯比較複雜,大概邏輯:利用反射建立需要返回的物件範例,再根據資料庫結果集以及相關設定,把資料庫結果集的資料賦值給反射建立物件的屬性。並且把結果新增在multipleResults範例中。整個過程至此完結。
說明:通過SqlSession獲取Mapper介面,再呼叫Mapper介面的方法執行SQL。其實是先通過JKD生成代理類,底層也是用的根據id呼叫SqlSession方法的邏輯,和上面講解的一樣。這裡不做講解。
五、快取
1.一級快取
結論:一級快取可以理解為同一個SqlSession的快取。一級快取預設開啟。開啟後,在同一個SqlSession中用相同引數值多次呼叫同一方法,只會查詢一次資料庫,返回物件範例的記憶體地址相同,物件範例屬性也相同。
原始碼分析:在BaseExecutor類中localCache屬性表示一級快取,它型別為PerpetualCache,底層是一個HashMap物件,用來快取查詢結果物件。快取的 key 是在createCacheKey()方法中建立,key的規則為(名稱空間id + sql語句 + 引數值 + 環境變數id),在BaseExecutor類中query方法裡面有localCache.getObject(key),表示從快取中獲取物件。queryFromDatabase方法中的localCache.putObject(key, list),表示把查出來的物件範例放進key的快取中。
2.二級快取
結論:二級快取可以理解為Mapper檔案的快取,多個SqlSession之間的快取。二級快取預設不開啟。開啟後,在不同的SqlSession中用相同引數值按照同步順序多次呼叫同一個方法,(每次用完SqlSession需要呼叫SqlSession的close()關閉SqlSession),只會查詢一次資料庫,返回物件範例的記憶體地址不相同,物件範例屬性相同。開啟二級快取需要物件支援序列化。
原始碼分析:
2.1二級快取的建立
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement中呼叫cacheElement()方法,原始碼如下
private void cacheElement(XNode context) {
// 如果節點不為null,則建立二級快取
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 建立新快取
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
useNewCache()方法是建立快取的具體方法,其中建立了一個快取類,並且給currentCache賦值。程式碼如下
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
//
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
//給組態檔新增二級快取類
configuration.addCache(cache);
//給 currentCache 賦值
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
在 org.apache.ibatis.builder.MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement()方法中構建MapperStatement的時候,會把二級快取物件傳進去,程式碼如下:
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
//賦值二級快取
.cache(currentCache);
至此,二級快取物件被初始化在了MappedStatement 物件中。
2.2二級快取使用
在 org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor#query()方法中會先查詢快取,如果快取物件不為空,則判斷是否使用快取,再從TransactionalCacheManager物件中獲取快取資料。程式碼如下,
// 獲取二級快取
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果有二級快取
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 如果是查詢,並且 resultHandler 為null
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 從 TransactionalCacheManager 中獲取 key的 快取物件
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
// 繼續查詢快取物件
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 放入快取管理物件中,這裡只是放入tcm的 臨時集合物件中,二級快取具體的更新是在session關閉之後才會提交更新
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);放入快取管理物件中,這裡只是放入tcm的 臨時集合物件中,二級快取具體的更新是在session關閉之後才會提交更新,putObject的程式碼如下,
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
//放入臨時集合中,儲存快取的資料
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
session.close()方法程式碼會呼叫executor.close方法進行執行器的關閉,executor.close程式碼如下
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
// issues #499, #524 and #573
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
tcm.commit()方法中,會呼叫tcm快取管理器中所有快取物件的commit的方法,程式碼如下
public void commit() {
// 遍歷 transactionalCaches 物件的 values 進行提交
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.commit();
}
}
transactionalCaches的commit的方法程式碼如下,
public void commit() {
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
// 重新整理 快取中的待重新整理的快取資料
flushPendingEntries();
reset();
}
private void flushPendingEntries()
// 提交entriesToAddOnCommit集合的資料到二級快取代物件
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) {
delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}