通用樹形結構的迭代與組合模式實現方案
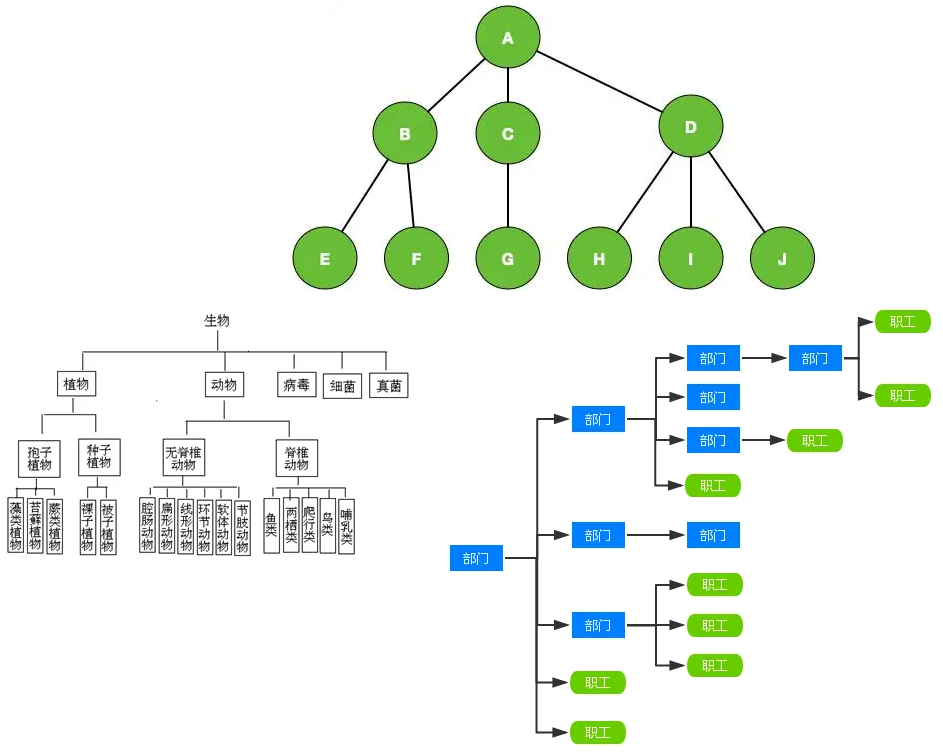
日常開發過程過程中。樹形結構運用的非常頻繁。
例如:公司組織結構、各種分類結構、分組結構等等。
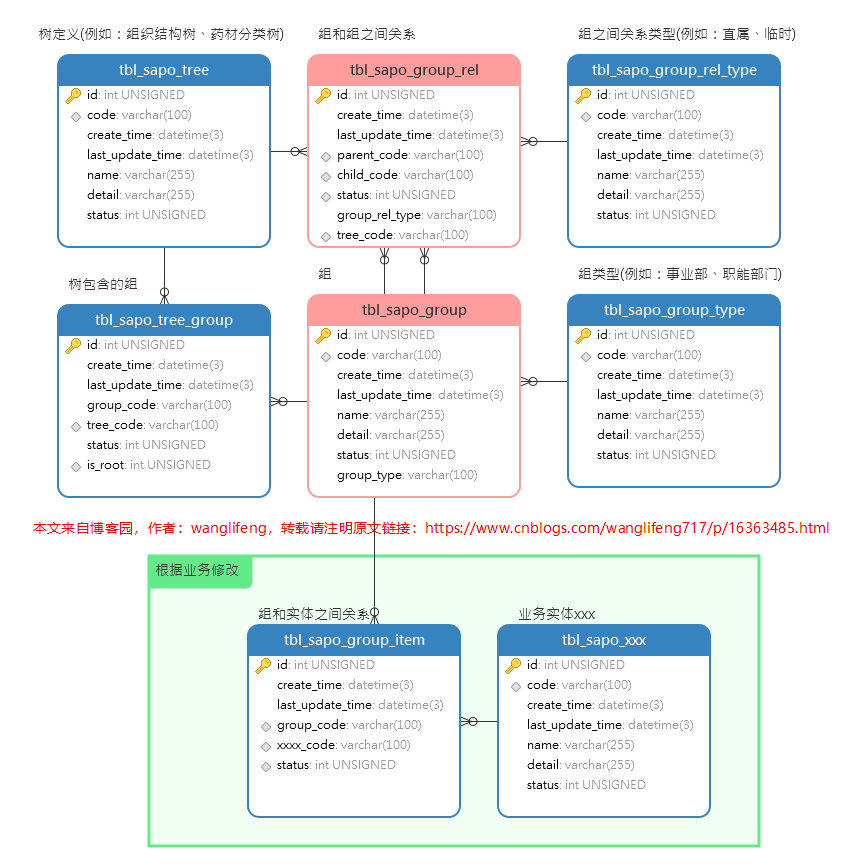

SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_sapo_group` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵', `code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '唯一編碼', `create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL COMMENT '建立時間', `last_update_time` datetime(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最後更新時間', `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '名稱', `detail` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '詳情', `status` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 2 COMMENT '狀態:0-無效,1-有效,2-編輯', `group_type` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '組型別', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `uni_idx_group_code` (`code`), KEY `idx_group_group_type` (`group_type`), CONSTRAINT `fk_group_group_type` FOREIGN KEY (`group_type`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_group_type` (`code`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='組'; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_sapo_group_rel` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵', `create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL COMMENT '建立時間', `last_update_time` datetime(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最後更新時間', `parent_code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '父節點程式碼,tbl_sapo_group表code', `child_code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '子節點程式碼,tbl_sapo_group表code', `status` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 2 COMMENT '狀態:0-無效,1-有效,2-編輯', `group_rel_type` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '組關係型別程式碼,來自tbl_sapo_group_rel_type表code', `tree_code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '樹節點程式碼,tbl_sapo_tree表code', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_group_rel_child_code` (`child_code`), KEY `idx_group_rel_parent_code` (`parent_code`), KEY `idx_group_rel_group_rel_type` (`group_rel_type`), KEY `idx_group_rel_tree_code_status_parent_code_child_code` (`tree_code`,`status`,`parent_code`,`child_code`), CONSTRAINT `fk_group_rel_child_code` FOREIGN KEY (`child_code`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_group` (`code`), CONSTRAINT `fk_group_rel_group_rel_type` FOREIGN KEY (`group_rel_type`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_group_rel_type` (`code`), CONSTRAINT `fk_group_rel_parent_code` FOREIGN KEY (`parent_code`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_group` (`code`), CONSTRAINT `fk_group_rel_tree_code` FOREIGN KEY (`tree_code`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_tree` (`code`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='組關係'; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_sapo_group_rel_type` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵', `code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '唯一編碼', `create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL COMMENT '建立時間', `last_update_time` datetime(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最後更新時間', `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '名稱', `detail` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '詳情', `status` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 2 COMMENT '狀態:0-無效,1-有效,2-編輯', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `uni_idx_group_rel_type_code` (`code`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='組關係型別'; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_sapo_group_type` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵', `code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '唯一編碼', `create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL COMMENT '建立時間', `last_update_time` datetime(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最後更新時間', `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '名稱', `detail` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '詳情', `status` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 2 COMMENT '狀態:0-無效,1-有效,2-編輯', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `uni_idx_group_type_code` (`code`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='組型別'; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_sapo_tree` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵', `code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '唯一編碼', `create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL COMMENT '建立時間', `last_update_time` datetime(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最後更新時間', `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '名稱', `detail` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '詳情', `status` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 2 COMMENT '狀態:0-無效,1-有效,2-編輯', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `uni_idx_tree_code` (`code`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='樹定義'; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_sapo_tree_group` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵', `create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL COMMENT '建立時間', `last_update_time` datetime(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最後更新時間', `group_code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '組程式碼,tbl_sapo_group表code', `tree_code` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '樹程式碼,tbl_sapo_tree表code', `status` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 2 COMMENT '狀態:0-無效,1-有效,2-編輯', `is_root` int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '是否根節點:1-根節點,null非根節點', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `uni_idx_tree_group_tree_code_is_root` (`tree_code`,`is_root`), KEY `idx_tree_group_group_code` (`group_code`), CONSTRAINT `fk_tree_group_group_code` FOREIGN KEY (`group_code`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_group` (`code`), CONSTRAINT `fk_tree_group_tree_code` FOREIGN KEY (`tree_code`) REFERENCES `tbl_sapo_tree` (`code`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='樹包含的組'; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
如圖所示關係型資料庫模型,基本滿足一個系統多顆樹、組可以複用的目的。
樹的節點可能是一個單獨的節點,也可能是一個子樹的根。我們需要遍歷的時候需要不同節點不同處理,使用【多型】。
但是處理的時候不要區分是何種節點,提供一種【透明化】處理方式,要實現需要參照兩個模式:迭代模式、組合模式
老規矩,先引入概念,之後實現。
| 迭代器模式 | 提供一個方式來遍歷集合而無需暴露集合的實現 |
| 組合模式 | 客戶可以將物件的集合以及個別物件一視同仁 |
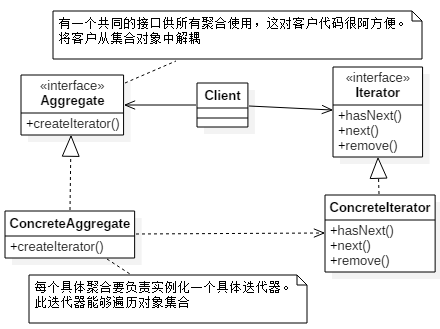
迭代器模式:
|
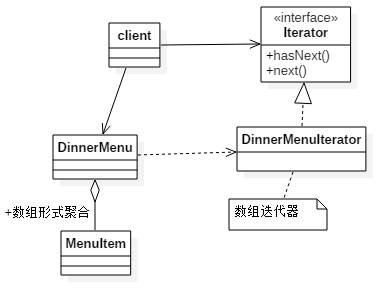
迭代器範例:陣列實現迭代器

// 迭代器介面 interface Iterator { boolean hasNext(); Object next(); } // 選單項 class MenuItem { String name; String description; boolean vegetarian; double price; public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) { this.name = name; this.description = description; this.vegetarian = vegetarian; this.price = price; } // getter,setter方法 public String getName() { return name; } } // 選單 class DinerMenu { static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6; int numberOfItems = 0; MenuItem[] menuItems; public DinerMenu() { menuItems = new MenuItem[MAX_ITEMS]; addItem("紅燒獅子頭", "江南名菜", true, 50d); addItem("夫妻肺片", "和夫妻沒啥關係", true, 70d); } public void addItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) { MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price); if (numberOfItems >= MAX_ITEMS) { System.out.println("sorry,menu is full"); } else { menuItems[numberOfItems] = menuItem; numberOfItems += 1; } } public MenuItem[] getMenuItems() { return menuItems; } public Iterator createIteator() { return new DinerMenuIterator(menuItems); } } class DinerMenuIterator implements Iterator { MenuItem[] items; int position = 0; public DinerMenuIterator(MenuItem[] items) { this.items = items; } public Object next() { MenuItem menuItem = items[position]; position = position + 1; return menuItem; } public boolean hasNext() { // 陣列可能沒裝滿 if (position >= items.length || items[position] == null) { return false; } else { return true; } } public void remove() { if (position <= 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("you can't an item unitl you've done at least on next()"); } if (items[position - 1] != null) { for (int i = position - 1; i < (items.length - 1); i++) { items[i] = items[i + 1]; } items[items.length - 1] = null; } } } // 測試 class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Iterator iterator = (new DinerMenu()).createIteator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ MenuItem menuItem = (MenuItem) iterator.next(); System.out.println(menuItem.getName()); } } } 迭代器模式範例 1.當然remove可以不實現,因為可能並行remove,迭代器不安全。 我們簡單處理丟擲java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 2.java5之後,集合可以使用for/in形式代替了顯示的建立迭代器。 for( Object obj: collection){ } |
對於不同的集合,我們有不同的遍歷方式。有沒有一種通用的遍歷集合的模式,遮蔽這種差異,該模式就是迭代器。
迭代器模式提供一種方法順序存取一個聚合物件中的各個元素,而不暴露其內部的表示。
其實說白了,迭代器模式就是通過定義統一操作介面,來遮蔽不同底層的操作邏輯。
如果你能有一個統一的方法存取聚合中的每一個物件,你就可以編寫多型的程式碼和這些聚合搭配。
把遊走的任務放在迭代器上,而不是聚合上。這樣簡化了聚合的介面和實現。責任分配明晰。
符合【單一職責】,如果不使用迭代器模式,集合改變的話,例如由集合變陣列,這個類必須改變,遍歷方式也跟著改變。
組合模式:
允許你將物件組合成樹形結構來表現「整體/部分」層次結構。
組合能讓客戶以一致的方式處理個別物件以及物件組合。即我們可以忽略物件組合和個別物件之間的差別,而使用相同操作。
組合模式犧牲【單一責任】獲取【透明性】,透明性即客戶處理組合和葉節點一視同仁。一個節點是組合還是葉節點,對客戶是透明的。
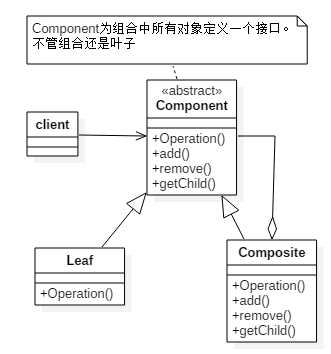
|
組合模式範例:

public abstract class MenuComponent { // 操作節點需要方法 public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public MenuComponent getChild(int i) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } // 選單本身方法 public String getName() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public String getDescription() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public double getPrice() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public boolean isVegetarian() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public void print() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } } 
public class Menu extends MenuComponent { ArrayList<MenuComponent> menuComponents = new ArrayList<MenuComponent>(); String name; String description; public Menu(String name, String description) { this.name = name; this.description = description; } public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) { menuComponents.add(menuComponent); } public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) { menuComponents.remove(menuComponent); } public MenuComponent getChild(int i) { return (MenuComponent) menuComponents.get(i); } public String getName() { return name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void print() { System.out.print("\n" + getName()); System.out.println(", " + getDescription()); System.out.println("---------------------"); Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = menuComponents.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { MenuComponent menuComponent = (MenuComponent) iterator.next(); menuComponent.print(); } } } 
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent { String name; String description; boolean vegetarian; double price; public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian, double price) { this.name = name; this.description = description; this.vegetarian = vegetarian; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public boolean isVegetarian() { return vegetarian; } public void print() { System.out.print(" " + getName()); if (isVegetarian()) { System.out.print("(v)"); } System.out.println(", " + getPrice()); System.out.println(" -- " + getDescription()); } } 
public class Waitress { MenuComponent allMenus; public Waitress(MenuComponent allMenus) { this.allMenus = allMenus; } public void printMenu() { allMenus.print(); } }
|
範例:
使用迭代和組合模式實現一種通用的樹形結構:
1.核心及組和組的關係。
2.該方案實現了,內部迭代器和外部迭代器。根據實際情況使用。
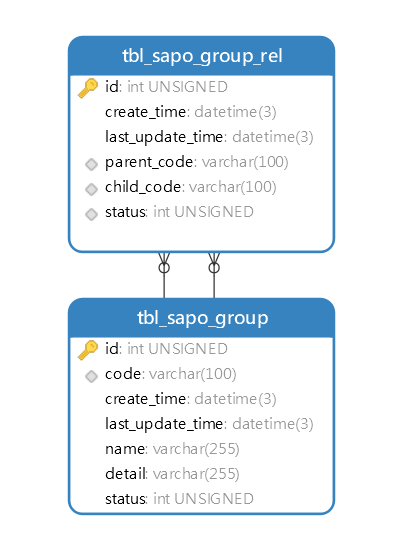
|
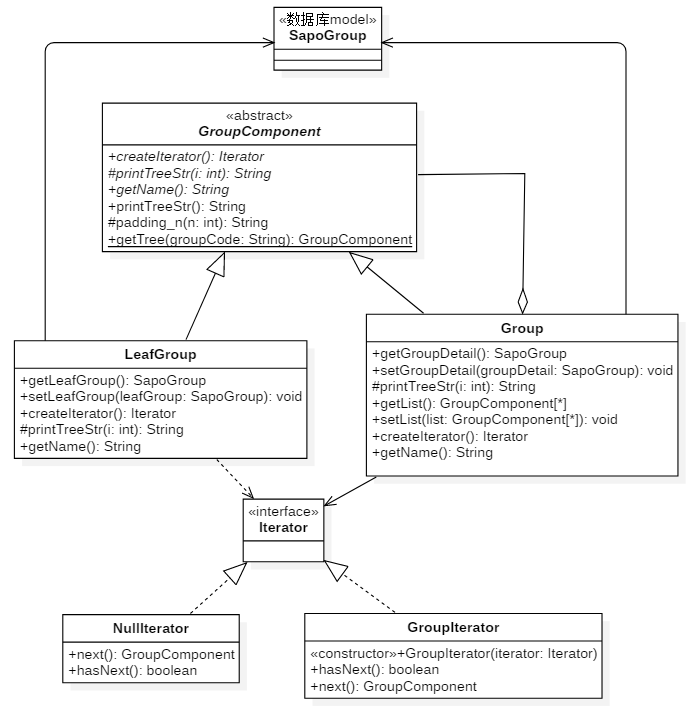
|

public abstract class GroupComponent { public abstract Iterator<GroupComponent> createIterator(); // 首行字元空幾格 protected abstract String printTreeStr(int i); public abstract String getName(); public String printTreeStr() { return printTreeStr(0); }; // 列印樹形解結構 protected String padding_n(int n) { StringBuffer space = new StringBuffer(""); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { space.append("-"); } space.append("|"); return space.toString(); } // 遞迴獲取樹形結構 public static GroupComponent getTree(String groupCode) { // 獲取通用dao CommonDao dao = SpringUtil.getBean(CommonDao.class); // 資料庫中組詳細資訊model類 SapoGroup sapoGroup = dao.getObj(SapoGroup.getInstance().setCode(groupCode)); // 查詢該節點所有兒子 List<SapoGroupRel> childList = dao.getObjListWithEmpty(SapoGroupRel.getInstance().setParentCode(groupCode)); // 如果沒有子節點,直接新建葉子節點返回 if (childList == null || childList.size() == 0) { LeafGroup leafGroup = new LeafGroup(); leafGroup.setLeafGroup(sapoGroup); return leafGroup; } else { // 如果有子節點 Group group = new Group(); group.setGroupDetail(sapoGroup); for (SapoGroupRel rel : childList) { // 遞迴拿到上一個節點 GroupComponent child = getTree(rel.getChildCode()); group.getList().add(child); } return group; } } }

public class Group extends GroupComponent { Iterator<GroupComponent> iterator = null; public List<GroupComponent> list = new ArrayList<GroupComponent>(); public SapoGroup groupDetail; public SapoGroup getGroupDetail() { return groupDetail; } public void setGroupDetail(SapoGroup groupDetail) { this.groupDetail = groupDetail; } /* * 列印樹形層級結構 */ protected String printTreeStr(int i) { // 需要列印的欄位 String waitPrintStr = this.groupDetail.getName(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(padding_n(i)); sb.append(waitPrintStr); sb.append("\r\n"); Iterator<GroupComponent> iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { GroupComponent next = iterator.next(); // 遞迴進行遍歷 String printTree = next.printTreeStr(i + 2); sb.append(printTree); } return sb.toString(); } public List<GroupComponent> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<GroupComponent> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public Iterator<GroupComponent> createIterator() { if (iterator == null) { iterator = new GroupIterator(list.iterator()); } return iterator; } @Override public String getName() { return "list: " + groupDetail.getName(); } }

public class LeafGroup extends GroupComponent { private SapoGroup leafGroup; public SapoGroup getLeafGroup() { return leafGroup; } public void setLeafGroup(SapoGroup leafGroup) { this.leafGroup = leafGroup; } public Iterator<GroupComponent> createIterator() { return new NullIterator(); } protected String printTreeStr(int i) { // 關鍵欄位 String waitPrintStr = this.getLeafGroup().getName(); return padding_n(i) + waitPrintStr + "\r\n"; } /* (non-Javadoc) * @see cn.com.fmsh.nfcos.sapo.biz.testGroup.GroupComponent#getName() */ @Override public String getName() { return "leaf: "+leafGroup.getName(); } }

public class GroupIterator implements Iterator<GroupComponent> { Stack<Iterator<GroupComponent>> stack = new Stack<Iterator<GroupComponent>>(); public GroupIterator(Iterator<GroupComponent> iterator) { stack.push(iterator); } public boolean hasNext() { if (stack.isEmpty()) { return false; } else { Iterator<GroupComponent> iterator = stack.peek(); if (!iterator.hasNext()) { stack.pop(); return hasNext(); } else { return true; } } } public GroupComponent next() { if(hasNext()) { Iterator<GroupComponent> iterator = stack.peek(); GroupComponent next = iterator.next(); stack.push(next.createIterator()); return next; }else { return null; } } }

public class NullIterator implements Iterator<GroupComponent> { public GroupComponent next() { return null; } public boolean hasNext() { return false; } }
測試程式,遍歷樹形結構、列印樹形結構。
@Test public void Test() { // 使用外部迭代器遍歷 GroupComponent tree = Group.getTree("hotel"); Iterator<GroupComponent> iterator = tree.createIterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { GroupComponent next = iterator.next(); // TODO 遍歷操作內容 } System.out.println("----列印樹形結構-----"); // 列印樹形結構 System.err.println(GroupComponent.getTree("hotel").printTreeStr()); }
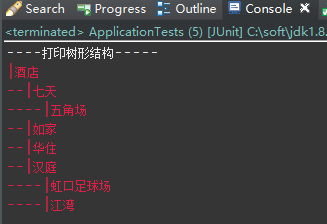
本文來自部落格園,作者:wanglifeng,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanglifeng717/p/16363485.html