基於Python的滲透測試資訊收集系統的設計和實現
資訊收集系統的設計和實現
滲透測試是保衛網路安全的一種有效且必要的技術手段,而滲透測試的本質就是資訊收集,資訊蒐集整理可為後續的情報跟進提供強大的保證,目標資產資訊蒐集的廣度,決定滲透過程的複雜程度,目標主機資訊蒐集的深度,決定後滲透許可權的持續把控。
實現功能
系統主要基於Python實現了Web指紋探測、埠掃描和服務探測、真實IP資訊探測、WAF防火牆探測、子域名掃描、目錄掃描和敏感資訊探測的功能。
設計思路
Web指紋探測
CMS識別功能主要通過呼叫本地識別介面識別,或者呼叫網路識別介面識別兩種方式,其中本地介面識別主要是通過比對常見CMS的特徵來完成識別。系統收集了1400+的國內常見指紋,並且以josn檔案型別的方式儲存,便於以後的補充和擴充套件。
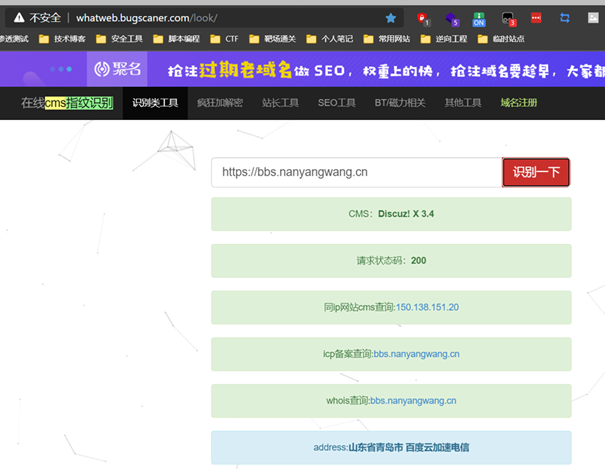
而網路介面識別則是通過線上指紋識別網站whatweb的api來實現,whatweb線上識別演示如圖所示。
CDN檢測
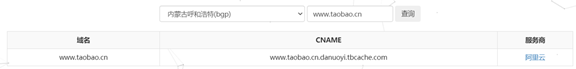
CDN判斷功能主要是通過兩種本地判斷方式和三種網路介面線上判斷方式共同執行,最後結合五種判斷方式得到的結果得出最終結論的方法實現。本地判斷主要是藉助Socket模組中的getaddrinfo方法來解析域名,以及nslookup查詢域名資訊的方法來判斷是否存在CDN防護。

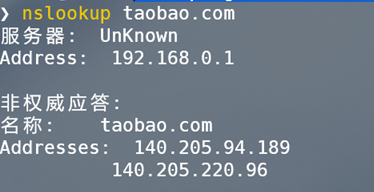
三種網路介面線上判斷CDN服務的演示如圖所示。
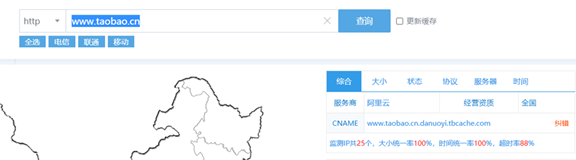

子域名掃描
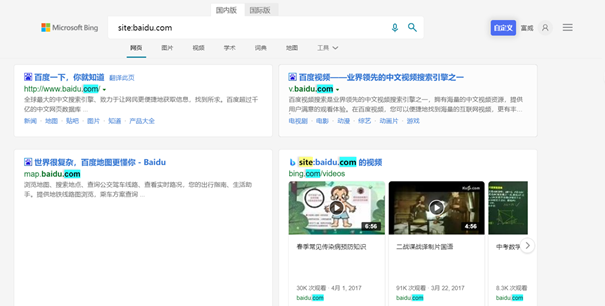
子域名掃描功能一方面是通過本地字典爆破,另外一方面主要是通過Bing搜尋引擎,對要查詢的域名進行谷歌語法搜尋子域名。
敏感目錄檔案掃描
敏感目錄檔案掃描功能主要是通過讀取本地字典檔案,然後拼接URL,並且把拼接後的URL通過Python中的HackRequests模組進行request請求,如果拼接後的URL返回狀態碼200,那麼我們可以判斷拼接後的URL可以正常存取,也就說明我們從本地字典中讀取到的目錄或者檔案是存在的。如果拼接後的URL返回狀態碼不是200,那麼我們從本地字典中讀取到的目錄或檔案可能是不存在的。
埠掃描服務探測
埠掃描功能主要是通過Python中的Socket模組建立TCP三次握手連線,並通過返回值是否為0來判斷埠是否存活。以及使用Python中的Nmap模組,來呼叫埠掃描神器Nmap進行埠掃描功能。
服務探測主要是通過Socket模組中的sendall方法來傳送請求,然後接收響應包並對響應包中的內容與本地儲存的服務特徵資訊進行關鍵字匹配,以此來判斷開放埠對應的服務型別,同時輸出返回資訊,可以在本地無法匹配到相關特徵時進行人工判斷服務型別。
關鍵程式碼實現
系統以webinfo.py為主程式檔案,通過與使用者互動,獲取使用者指令,然後根據使用者輸入的指令來呼叫不同的模組程式碼檔案,進而實現對應的功能。
系統主函數功能實現
系統主函數的主要功能是通過與使用者互動,提示使用者輸入正確的選項,並根據使用者的輸入來呼叫其他對應的功能函數,完成使用者想要完成的不同功能。同時應做好程式的例外處理機制,防止因使用者的不正確輸入,而導致的程式崩潰的情況發生,提高程式的健壯性。
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
demo=input("請選擇功能模組a.cms識別,b.cdn判斷,c.子域名掃描,d.敏感目錄檔案掃描,e.埠掃描服務探測(輸入序號即可):")
if(demo=="a"):
try:
test = int(input("輸入數位1進行單個url解析cms,輸入數位2進行檔案批次解析cms:"))
if(test==1):
try:
domain = input("輸入要檢測web指紋的url(注意不帶路徑如https://www.baidu.com):")
try:
urllib.request.urlopen(domain)
print("開始呼叫本地介面檢測"+domain+"的cms!")
webcms=webcms(domain)
webcms.run()
print("開始呼叫網路介面檢測"+domain+"的cms!")
info=str(cmso2(domain))
print(domain+"解析到的其他資訊為:"+info)
except urllib.error.HTTPError:
print("域名有誤,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
except urllib.error.URLError:
print("域名有誤,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
except Exception as e:
print("程式執行出錯!請檢查並再次嘗試!")
time.sleep(2)
if(test==2):
threads = [20]
filename = input("請輸入要解析的url檔案路徑:")
try:
t=threading.Thread(target=cmsfile(filename),args=filename)
for ti in threads:
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
for ti in threads:
t.join()
except Exception as e:
print("輸入有誤,或檔案路徑找不到,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
except Exception as e:
print("輸入有誤,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
elif(demo=="b"):
cdn.run()
elif(demo=="c"):
subdomain.jkxz()
elif(demo=="d"):
dirfilesm.bprun()
elif(demo=="e"):
portscan.port()
else:
print("輸入出錯,請重試!")
time.sleep(2)
except Exception as e:
print("程式執行出錯!請檢查並再次嘗試!")
time.sleep(2)
CMS識別功能的實現
CMS識別時先通過與使用者互動,判斷使用者是進行單個URL識別還是進行批次檔案識別,這一過程實現方式和主函數模組類似,主要是通過if判斷變數test的值。如果test的值為1,則代表使用者選擇單個URL識別功能,如果test的值為2,則代表使用者選擇批次檔案識別的功能。批次檔案識別時,主要涉及到Python中檔案的操作。
具體識別時主要分為本地介面識別和網路介面api識別兩種方式。本地識別先通過爬蟲獲取目標網站的特徵資訊,這一過程通過類Downloader來完成。Downloader類主要定義了三個函數方法:get,post和download,通過這三個函數可以對目標網站進行爬蟲,獲取到目標網站的基本特徵資訊。
獲取到的網站特徵資訊再和原生的josn檔案進行比對,從而識別出目標網站的CMS資訊。這個過程主要是通過類webcms來實現,類webcms一方面將本地josn檔案中的內容讀取到佇列中,另外一方面將爬取到的資訊與佇列中的資訊進行正則匹配,根據匹配結果得出識別結論。為了提高程式執行效率,需要同時對提取本地josn檔案內容的過程和比對資訊的過程進行多執行緒的操作。
網路api識別介面的實現,主要是對通過api請求得到的資料進行二次處理,得到相應的CMS資訊,同時也可藉助該介面得到目標網站的其他相關資訊。
class webcms(object):
workQueue = queue.Queue()
URL = ""
threadNum = 0
NotFound = True
Downloader = Downloader()
result = ""
def __init__(self,url,threadNum = 20):
self.URL = url
self.threadNum = threadNum
filename = os.path.join(sys.path[0], "data", "data.json")
fp = open(filename,encoding="utf-8")
webdata = json.load(fp,encoding="utf-8")
for i in webdata:
self.workQueue.put(i)
fp.close()
def getmd5(self, body):
m2 = hashlib.md5()
m2.update(body.encode())
return m2.hexdigest()
def th_whatweb(self):
if(self.workQueue.empty()):
self.NotFound = False
return False
if(self.NotFound is False):
return False
cms = self.workQueue.get()
_url = self.URL + cms["url"]
html = self.Downloader.get(_url)
print ("[whatweb log]:checking %s"%_url)
if(html is None):
return False
if cms["re"]:
if(html.find(cms["re"])!=-1):
self.result = cms["name"]
self.NotFound = False
return True
else:
md5 = self.getmd5(html)
if(md5==cms["md5"]):
self.result = cms["name"]
self.NotFound = False
return True
def run(self):
while(self.NotFound):
th = []
for i in range(self.threadNum):
t = threading.Thread(target=self.th_whatweb)
t.start()
th.append(t)
for t in th:
t.join()
if(self.result):
print ("[cmsscan]:%s cms is %s"%(self.URL,self.result))
else:
print ("[cmsscan]:%s cms NOTFound!"%self.URL)
def cmso2(domain):
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings()
response = requests.get(domain,verify=False)
whatweb_dict = {"url":response.url,"text":response.text,"headers":dict(response.headers)}
whatweb_dict = json.dumps(whatweb_dict)
whatweb_dict = whatweb_dict.encode()
whatweb_dict = zlib.compress(whatweb_dict)
data = {"info":whatweb_dict}
res=requests.post("http://whatweb.bugscaner.com/api.go",files=data)
dic=json.loads(res.text)
if('CMS' in dic.keys()):
info=str(dic['CMS'])
info=info.replace("[","")
info=info.replace("]","")
info=info.replace("'","")
print(domain+"的cms為:"+info)
else:
print(domain+"的cms未能識別!")
return dic
CDN判斷功能的實現
CDN判斷功能的實現主要是通過系統中的五個功能函數,分別對目標域名進行CDN檢測,最後再統計各個功能函數的檢測結果。當五個功能函數的檢測結果中有三個或者三個以上是存在CDN防護的情況下,可以認為目標域名存在CDN防護,反之則可以認為目標域名不存在CDN防護。這一過程的實現主要是通過設定flag,並根據函數返回結果對flag進行加權賦值,最後再根據flag的值得出最終的結果。
五個功能函數中的前兩個函數主要是通過Socket模組中的getaddrinfo方法解析域名,以及nslookup查詢域名資訊的方法來得到域名對應的IP列表。如果以此得到的目標域名的IP數量在兩個或者兩個以上,則說明目標域名可能存在CDN防護,這兩個函數返回結果為True,反之則說明目標域名可能不存在CDN防護,函數返回結果為False。
另外三個函數主要藉助第三方查詢網站查詢目標域名的cname域名資訊,並以此判斷目標域名是否存在CDN防護。具體實現則主要藉助爬蟲來完成,同時對返回的資料資訊進行篩選處理,得到我們想要的結果。
def getipo1(domain):
ip_list=[]
flag1 = 0
ipaddr = socket.getaddrinfo(domain,None)
for item in ipaddr:
if item[4][0] not in ip_list:
ip_list.append(item[4][0])
flag1 = flag1+1
return flag1,ip_list
def getipo2(domain):
flag2 = 0
pi = subprocess.Popen('nslookup {}'.format(domain), shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
out = pi.stdout.read().decode('gbk') # 編碼根據實際結果調整
# 判斷返回值中是否有 Addresses 欄位,且該欄位下 ip 地址要大於等於 2 個,即說明使用了 CDN
strs = re.findall(r'Addresses:(\s*(((25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|1\d{2}|[1-9]?\d)\.){3}(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|1\d{2}|[1-9]?\d)\s*)*)', out, re.S)
if strs == []:
return flag2
else:
l = strs[0][0].split('\r\n\t')
for address in l:
flag2 = flag2+1
return flag2
def getipo3(domain):
flag3 = 0
url = 'http://cdn.chinaz.com/search/?host='+domain
strhtml = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(strhtml.text,'lxml')
#a = soup.find_all(text=(re.compile("可能使用CDN雲加速")))
b = soup.find_all(text=(re.compile("不屬於CDN雲加速")))
if(b==[]):
flag3=flag3+1
return flag3
if(b!=[]):
return flag3
def getipo4(domain):
flag4 = 0
info = "未知"
url = 'http://tools.bugscaner.com/api/whichcdn/'
payload = {'url':domain}
res = requests.post(url,data=payload)
content = json.loads(res.text)
if(str(content['secess'])=="True"):
flag4 = flag4+1
info=content['info']
return flag4,info
if(str(content['secess'])=="False"):
return flag4,info
def getipo5(domain):
flag5 = 0
info="未知"
#browser=webdriver.PhantomJS(executable_path=r'D:\GeckoDriver\phantomjs-2.1.1-windows\bin\phantomjs.exe')
url = 'https://tools.ipip.net/cdn.php'
#browser.get(url)
#Cookie = browser.get_cookies()
#browser.close()
#strr = ''
#for c in Cookie:
#strr += c['name']
#strr += '='
#strr += c['value']
#strr += ';'
cookie="LOVEAPP_SESSID=19676de35da2f3d730a92ceac59888c2d9f44f1b; __jsluid_s=7312e36ccdfd6c67bd2d54a59f5ef9f2; _ga=GA1.2.671769493.1617350155; _gid=GA1.2.268809088.1617350155; Hm_lvt_6b4a9140aed51e46402f36e099e37baf=1617350155; login_r=https%253A%252F%252Ftools.ipip.net%252F;"
payload = {'node':663,'host':domain}
user_agent=UserAgent().random
headers={"User-Agent":user_agent,"Cookie":cookie}
res = requests.post(url,data=payload,headers=headers)
#print(res.text)
soup=BeautifulSoup(res.text,'lxml')
data = soup.find_all('td')
#print(data)
a=soup.find_all(text=(re.compile("未知")))
if(a!=[]):
return flag5,info
else:
for item in data:
info1 = item.find('a')
info=info1.text
#print(info)
flag5=flag5+1
return flag5,info
子域名掃描功能的實現
子域名掃描功能主要是通過本地字典爆破和搜尋引擎搜尋兩種方法來實現。其中字典爆破是通過載入本地字典來拼接URL,並對拼接後的URL進行request請求,然後根據返回的狀態碼來判斷子域名是否存在。
搜尋引擎搜尋則主要藉助特殊搜尋語法site的使用,同時藉助爬蟲技術,對搜尋到的資料進行篩選處理,進而得到目標域名的子域名資訊。
def bp(url):
user_agent=UserAgent().random
header={"User-Agent":user_agent}
try:
h = HackRequests.hackRequests()
res = h.http(url,headers=header)
if (res.status_code==200):
print("成功爆破出子域名:"+url)
except:
pass
def zymbp(filename,domain):
try:
f = open(filename,encoding='utf8')
lines = f.readlines()
i = -1
for key in lines:
i=i+1
key=lines[i].strip('\n')
url = "http://"+key+"."+domain
threads = [20]
t=threading.Thread(target=bp(url),args=url)
for ti in threads:
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
for ti in threads:
t.join()
except Exception as e:
print("輸入有誤,或檔案路徑找不到,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
def bprun():
filename=input("請輸入要爆破的子域名字典路徑:")
try:
domain=input("請輸入要爆破的域名(格式為:baidu.com):")
try:
threads = [20]
t=threading.Thread(target=zymbp(filename,domain),args=(filename,domain))
for ti in threads:
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
for ti in threads:
t.join()
except Exception as e:
print("程式執行出錯!請檢查並再次嘗試!")
time.sleep(2)
except Exception as e:
print("輸入有誤,或檔案路徑找不到,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
def bing_search(site,pages):
subdomain=[]
user_agent=UserAgent().random
headers={'User-Agent':user_agent,'Accept':'*/*','Accept_Language':'en-US,en;q=0.5','Accept-Encoding':'gzip,deflate','referer':"http://cn.bing.com/search?q=email+site%3abaidu.com&qs=n&sp=-1&pq=emailsite%3abaidu.com&first=2&FORM=PERE1"}
for i in range(1,int(pages)+1):
url="https://cn.bing.com/search?q=site%3a"+site+"&go=Search&qs=Search&qs=ds&first="+str((int(i)-1)*10)+"&FORM=PERE"
conn=requests.session()
conn.get('http://cn.bing.com',headers=headers)
html=conn.get(url,stream=True,headers=headers,timeout=8)
soup=BeautifulSoup(html.content,'html.parser')
job_bt=soup.findAll('h2')
for i in job_bt:
link=i.a.get('href')
domain=str(urlparse(link).scheme+"://"+urlparse(link).netloc)
if(domain in subdomain):
pass
else:
subdomain.append(domain)
print("成功搜尋出子域名:"+domain)
def runbing():
try:
site=input("請輸入要查詢的域名(格式為:baidu.com):")
page=int(input("請輸入查詢的頁數:"))
try:
bing_search(site,page)
except Exception as e:
print("程式執行出錯!請檢查並再次嘗試!")
time.sleep(2)
except Exception as e:
print("輸入有誤,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
敏感目錄檔案掃描功能的實現
敏感目錄檔案的掃描功能主要是通過載入本地字典檔案,對當前URL進行拼接,然後再借助HackRequests庫對拼接後的URL進行request請求驗證。當返回狀態碼為200時,則認為當前請求的目錄或者檔案存在。
def dirfilebp(filename,domain):
try:
f = open(filename,encoding='utf8')
lines = f.readlines()
i = -1
for key in lines:
i=i+1
key=str(lines[i].strip('\n'))
url = domain+key
threads = [20]
t=threading.Thread(target=bp(url),args=url)
for ti in threads:
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
for ti in threads:
t.join()
except Exception as e:
print("輸入有誤,或檔案路徑找不到,請檢查並按格式輸入!")
time.sleep(2)
def bp(url):
user_agent=UserAgent().random
header={"User-Agent":user_agent}
try:
h = HackRequests.hackRequests()
res = h.http(url,headers=header)
if (res.status_code==200):
print("成功爆破出目錄或檔案:"+url)
except:
pass
埠掃描服務探測功能的實現
埠掃描功能一方面是藉助Python中的Socket模組建立TCP三次握手連線,並通過返回值是否為0來判斷埠是否存活。另外一方面則是藉助Python中的Nmap模組,來呼叫埠掃描神器Nmap進行埠掃描功能。
服務探測主要是通過Socket模組中的sendall方法來傳送請求,然後接收響應包並對響應包中的內容與本地儲存的服務特徵資訊進行關鍵字匹配,以此來判斷開放埠對應的服務型別,同時輸出返回資訊,可以在本地無法匹配到相關特徵時進行人工判斷服務型別。
def sorun(queue_s,ip):
while not queue_s.empty():
try:
port=queue_s.get()
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.settimeout(1)
c=s.connect_ex((ip,port))
if (c==0):
print ("%s:%s is open" % (ip,port))
else:
# print "%s:%s is not open" % (ip,port)
pass
except:
pass
def somain(ip,spo,epo):
threads = []
threads_count = 100 # 執行緒數,預設 100
queue_s = queue.Queue()
#ip=ip
try:
for i in range(spo,epo+1): # 預設掃描1-1000的埠,可以手動修改這裡的埠範圍
queue_s.put(i) # 使用 queue.Queue().put() 方法將埠新增到佇列中
for i in range(threads_count):
threads.append(sorun(queue_s,ip)) # 掃描的埠依次新增到執行緒組
for i in threads:
i.start()
for i in threads:
i.join()
except:
pass
def nmscan(hosts,port):
nm = nmap.PortScanner()
nm.scan(hosts=hosts, arguments=' -v -sS -p '+port)
try:
for host in nm.all_hosts():
print('----------------------------------------------------') #輸出主機及主機名
print('Host : %s (%s)' % (host, nm[host].hostname())) #輸出主機狀態,如up、down
print('State : %s' % nm[host].state())
for proto in nm[host].all_protocols(): #遍歷掃描協定,如tcp、udp
print('----------') #輸入協定名
print('Protocol : %s' % proto) #獲取協定的所有掃描埠
lport = nm[host][proto].keys() #埠列表排序
list(lport).sort() #遍歷埠及輸出埠與狀態
for port in lport:
print('port : %s\tstate : %s' % (port, nm[host][proto][port]['state']))
except:
pass
def regex(response, port):
text = ""
if re.search(b'<title>502 Bad Gateway', response):
proto = {"Service failed to access!!"}
for pattern in SIGNS:
pattern = pattern.split(b'|')
if re.search(pattern[-1], response, re.IGNORECASE):
proto = "["+port+"]" + " open " + pattern[1].decode()
break
else:
proto = "["+port+"]" + " open " + "Unrecognized"
print(proto)
def request(ip,port):
response = ''
PROBE = 'GET / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n'
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.settimeout(10)
result = sock.connect_ex((ip, int(port)))
if result == 0:
try:
sock.sendall(PROBE.encode())
response = sock.recv(256)
print(response)
if response:
regex(response, port)
except ConnectionResetError:
pass
else:
pass
sock.close()
def fwmain(ip,port):
print("Scan report for "+ip+"\n")
for line in port.split(','):
request(ip,line)
time.sleep(0.2)
print("\nScan finished!....\n")
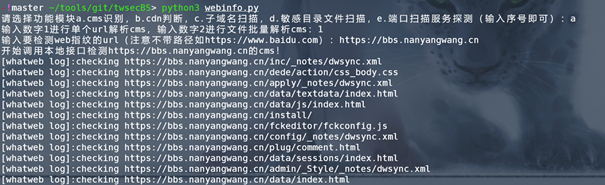
執行演示和程式碼地址
執行演示如下圖
本文來自部落格園,作者:twsec,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/TWX521/p/16308471.html