Vue3元件間怎麼通訊?10+種通訊方式分享

本文講解
Vue 3.2元件多種通訊方式的基礎用法,並且使用了單檔案元件 <script setup>。
眾所周知,Vue.js 中一個很重要的知識點是元件通訊,不管是業務類的開發還是元件庫開發,都有各自的通訊方法。【相關推薦:】
本文適合:
有
Vue 3基礎的讀者。打算開發元件庫的讀者。
本文會涉及的知識點:
Props
emits
expose / ref
Non-Props
v-model
插槽 slot
provide / inject
匯流排 bus
getCurrentInstance
Vuex
Pinia
mitt.js
我會將上面羅列的知識點都寫一個簡單的 demo。本文的目的是讓大家知道有這些方法可以用,所以並不會深挖每個知識點。
建議讀者跟著本文敲一遍程式碼,然後根據本文給出的連結去深挖各個知識點。
收藏(學到)是自己的!
Props
父元件傳值給子元件(簡稱:父傳子)
Props 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-props.html
父元件
// Parent.vue <template> <!-- 使用子元件 --> <Child :msg="message" /> </template> <script setup> import Child from './components/Child.vue' // 引入子元件 let message = '雷猴' </script>
子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
msg: {
type: String,
default: ''
}
})
console.log(props.msg) // 在 js 裡需要使用 props.xxx 的方式使用。在 html 中使用不需要 props
</script>在 <script setup> 中必須使用 defineProps API 來宣告 props,它具備完整的推斷並且在 <script setup> 中是直接可用的。
更多細節請看 檔案。
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#defineprops-%E5%92%8C-defineemits
在 <script setup> 中,defineProps 不需要另外引入。
props 其實還能做很多事情,比如:設定預設值 default ,型別驗證 type ,要求必傳 required ,自定義驗證函數 validator 等等。
大家可以去官網看看,這是必須掌握的知識點!
props 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-props.html
emits
子元件通知父元件觸發一個事件,並且可以傳值給父元件。(簡稱:子傳父)
emits 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/migration/emits-option.html

父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<div>父元件:{{ message }}</div>
<!-- 自定義 changeMsg 事件 -->
<Child @changeMsg="changeMessage" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
let message = ref('雷猴')
// 更改 message 的值,data是從子元件傳過來的
function changeMessage(data) {
message.value = data
}
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
子元件:<button @click="handleClick">子元件的按鈕</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
// 註冊一個自定義事件名,向上傳遞時告訴父元件要觸發的事件。
const emit = defineEmits(['changeMsg'])
function handleClick() {
// 引數1:事件名
// 引數2:傳給父元件的值
emit('changeMsg', '鯊魚辣椒')
}
</script>和 props 一樣,在 <script setup> 中必須使用 defineEmits API 來宣告 emits,它具備完整的推斷並且在 <script setup> 中是直接可用的。
更多細節請看 檔案。
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#defineprops-%E5%92%8C-defineemits
在 <script setup> 中,defineEmits 不需要另外引入。
expose / ref
子元件可以通過 expose 暴露自身的方法和資料。
父元件通過 ref 獲取到子元件並呼叫其方法或存取資料。
expose 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/options-data.html#expose
用例子說話
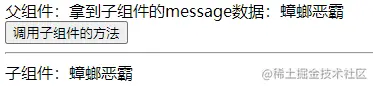
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<div>父元件:拿到子元件的message資料:{{ msg }}</div>
<button @click="callChildFn">呼叫子元件的方法</button>
<hr>
<Child ref="com" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const com = ref(null) // 通過 模板ref 繫結子元件
const msg = ref('')
onMounted(() => {
// 在載入完成後,將子元件的 message 賦值給 msg
msg.value = com.value.message
})
function callChildFn() {
// 呼叫子元件的 changeMessage 方法
com.value.changeMessage('蒜頭王八')
// 重新將 子元件的message 賦值給 msg
msg.value = com.value.message
}
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>子元件:{{ message }}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const message = ref('蟑螂惡霸')
function changeMessage(data) {
message.value = data
}
使用 defineExpose 向外暴露指定的資料和方法
defineExpose({
message,
changeMessage
})
</script>在 <script setup> 中,defineExpose 不需要另外引入。
expose 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/options-data.html#expose
defineExpose 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#defineexpose
Non-Props
所謂的 Non-Props 就是 非 Prop 的 Attribute。
意思是在子元件中,沒使用 prop 或 emits 定義的 attribute,可以通過 $attrs 來存取。
常見的有 class 、style 和 id。
還是舉個例子會直觀點
單個根元素的情況
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child msg="雷猴 世界!" name="鯊魚辣椒" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
</script>子元件
// Child.vue <template> <div>子元件:開啟控制檯看看</div> </template>
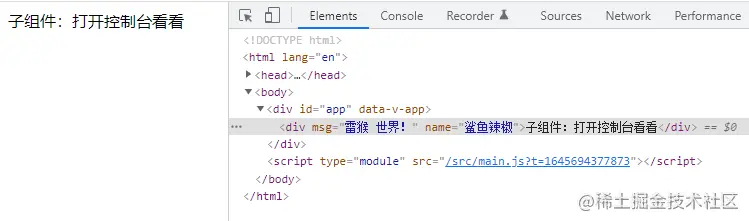
開啟控制檯可以看到,屬性被掛到 HTML 元素上了。
多個元素的情況
但在 Vue3 中,元件已經沒規定只能有一個根元素了。如果子元件是多個元素時,上面的例子就不生效了。
// Child.vue <template> <div>子元件:開啟控制檯看看</div> <div>子元件:開啟控制檯看看</div> </template>
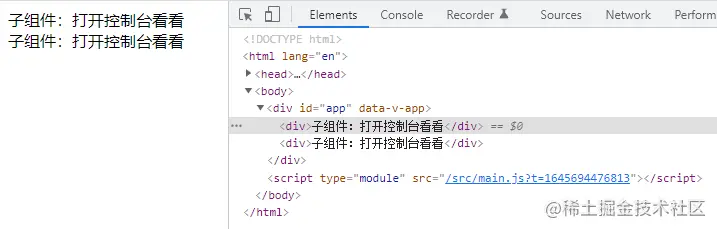
此時可以使用 $attrs 的方式進行繫結。
// Child.vue <template> <div :message="$attrs.msg">只繫結指定值</div> <div v-bind="$attrs">全繫結</div> </template>
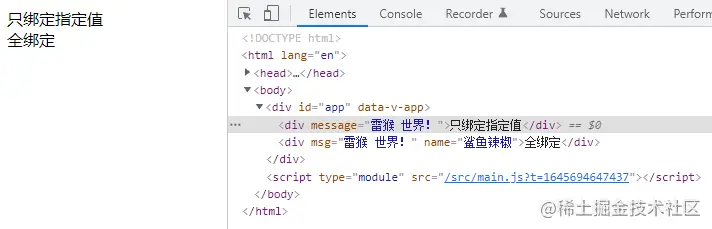
v-model
v-model 是 Vue 的一個語法糖。在 Vue3 中的玩法就更多(暈)了。
單值的情況
元件上的 v-model 使用 modelValue 作為 prop 和 update:modelValue 作為事件。
v-model 引數檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-custom-events.html#v-model-%E5%8F%82%E6%95%B0
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child v-model="message" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const message = ref('雷猴')
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 接收
const props = defineProps([
'modelValue' // 接收父元件使用 v-model 傳進來的值,必須用 modelValue 這個名字來接收
])
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']) // 必須用 update:modelValue 這個名字來通知父元件修改值
function handleClick() {
// 引數1:通知父元件修改值的方法名
// 引數2:要修改的值
emit('update:modelValue', '噴射河馬')
}
</script>
你也可以這樣寫,更加簡單
子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div @click="$emit('update:modelValue', '噴射河馬')">{{modelValue}}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 接收
const props = defineProps([
'modelValue' // 接收父元件使用 v-model 傳進來的值,必須用 modelValue 這個名字來接收
])
</script>多個 v-model 繫結
多個 v-model 繫結 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-custom-events.html#%E5%A4%9A%E4%B8%AA-v-model-%E7%BB%91%E5%AE%9A
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child v-model:msg1="message1" v-model:msg2="message2" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const message1 = ref('雷猴')
const message2 = ref('蟑螂惡霸')
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div><button @click="changeMsg1">修改msg1</button> {{msg1}}</div>
<div><button @click="changeMsg2">修改msg2</button> {{msg2}}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 接收
const props = defineProps({
msg1: String,
msg2: String
})
const emit = defineEmits(['update:msg1', 'update:msg2'])
function changeMsg1() {
emit('update:msg1', '鯊魚辣椒')
}
function changeMsg2() {
emit('update:msg2', '蠍子萊萊')
}
</script>
v-model 修飾符
v-model 還能通過 . 的方式傳入修飾。
v-model 修飾符 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-custom-events.html#%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86-v-model-%E4%BF%AE%E9%A5%B0%E7%AC%A6
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child v-model.uppercase="message" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const message = ref('hello')
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>{{modelValue}}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
const props = defineProps([
'modelValue',
'modelModifiers'
])
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue'])
onMounted(() => {
// 判斷有沒有 uppercase 修飾符,有的話就執行 toUpperCase() 方法
if (props.modelModifiers.uppercase) {
emit('update:modelValue', props.modelValue.toUpperCase())
}
})
</script>
插槽 slot
插槽可以理解為傳一段 HTML 片段給子元件。子元件將 <slot> 元素作為承載分發內容的出口。
插槽 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-slots.html
本文打算講講日常用得比較多的3種插槽:預設插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽。
預設插槽
插槽的基礎用法非常簡單,只需在 子元件 中使用 <slot> 標籤,就會將父元件傳進來的 HTML 內容渲染出來。
預設插槽 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-slots.html#%E6%8F%92%E6%A7%BD%E5%86%85%E5%AE%B9
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child>
<div>雷猴啊</div>
</Child>
</template>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>具名插槽
具名插槽 就是在 預設插槽 的基礎上進行分類,可以理解為對號入座。
具名插槽 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-slots.html#%E5%85%B7%E5%90%8D%E6%8F%92%E6%A7%BD

父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child>
<template v-slot:monkey>
<div>雷猴啊</div>
</template>
<button>鯊魚辣椒</button>
</Child>
</template>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 預設插槽 -->
<slot></slot>
<!-- 具名插槽 -->
<slot name="monkey"></slot>
</div>
</template>父元件需要使用 <template> 標籤,並在標籤上使用 v-solt: + 名稱 。
子元件需要在 <slot> 標籤裡用 name= 名稱 對應接收。
這就是 對號入座。
最後需要注意的是,插槽內容的排版順序,是 以子元件裡的排版為準。
上面這個例子就是這樣,你可以仔細觀察子元件傳入順序和子元件的排版順序。
作用域插槽
如果你用過 Element-Plus 這類 UI框架 的 Table ,應該就能很好的理解什麼叫作用域插槽。
作用域插槽 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-slots.html#%E4%BD%9C%E7%94%A8%E5%9F%9F%E6%8F%92%E6%A7%BD
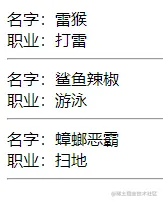
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<!-- v-slot="{scope}" 獲取子元件傳上來的資料 -->
<!-- :list="list" 把list傳給子元件 -->
<Child v-slot="{scope}" :list="list">
<div>
<div>名字:{{ scope.name }}</div>
<div>職業:{{ scope.occupation }}</div>
<hr>
</div>
</Child>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const list = ref([
{ name: '雷猴', occupation: '打雷'},
{ name: '鯊魚辣椒', occupation: '游泳'},
{ name: '蟑螂惡霸', occupation: '掃地'},
])
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 用 :scope="item" 返回每一項 -->
<slot v-for="item in list" :scope="item" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
list: {
type: Array,
default: () => []
}
})
</script>我沒寫樣式,所以用 hr 元素讓視覺上看上去比較清晰我就是懶。
provide / inject
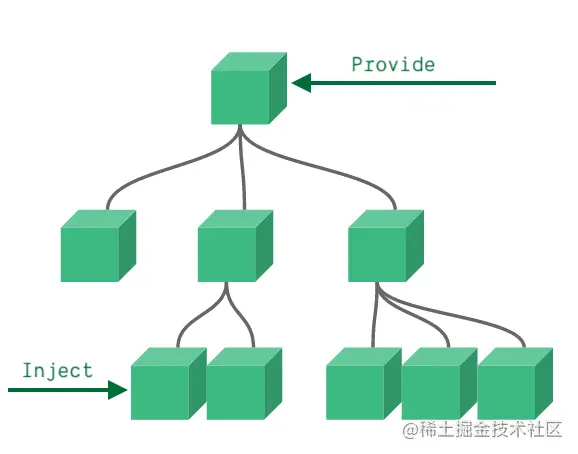
遇到多層傳值時,使用 props 和 emit 的方式會顯得比較笨拙。這時就可以用 provide 和 inject 了。
provide 是在父元件裡使用的,可以往下傳值。
inject 是在子(後代)元件裡使用的,可以網上取值。
無論元件層次結構有多深,父元件都可以作為其所有子元件的依賴提供者。
provide / inject 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/component-provide-inject.html
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<Child></Child>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, provide, readonly } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const name = ref('猛虎下山')
const msg = ref('雷猴')
// 使用readonly可以讓子元件無法直接修改,需要呼叫provide往下傳的方法來修改
provide('name', readonly(name))
provide('msg', msg)
provide('changeName', (value) => {
name.value = value
})
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>msg: {{ msg }}</div>
<div>name: {{name}}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">修改</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { inject } from 'vue'
const name = inject('name', 'hello') // 看看有沒有值,沒值的話就適用預設值(這裡預設值是hello)
const msg = inject('msg')
const changeName = inject('changeName')
function handleClick() {
// 這樣寫不合適,因為vue裡推薦使用單向資料流,當父級使用readonly後,這行程式碼是不會生效的。沒使用之前才會生效。
// name.value = '雷猴'
// 正確的方式
changeName('虎軀一震')
// 因為 msg 沒被 readonly 過,所以可以直接修改值
msg.value = '世界'
}
</script>provide 可以配合 readonly 一起使用,詳情可以看上面例子和註釋。
provide 和 inject 其實主要是用在深層關係中傳值,上面的例子只有父子2層,只是為了舉例說明我懶。
匯流排 bus
在 Vue2 有匯流排傳值的方法,我們在 Vue3 中也可以自己模擬。
這個方式其實有點像 Vuex 或者 Pinia 那樣,弄一個獨立的工具出來專門控制資料。
但和 Vuex 或 Pinia 相比,我們自己寫的這個方法並沒有很好的資料跟蹤之類的特性。
原理
我們建立一個 Bus.js 檔案,用來控制資料和註冊事件的。
Bus.js 裡有一個 Bus 類
eventList是必須項,用來存放事件列表的。constructor裡除了eventList外,其他都是自定義資料,公共資料就是存在這裡的。$on方法用來註冊事件。$emit方法可以呼叫$on裡的事件。$off方法可以登出eventList裡的事件。
然後需要用到匯流排的元件,都匯入 Bus.js ,就可以共同操作一份資料了。
Bus.js
import { ref } from 'vue'
class Bus {
constructor() {
// 收集訂閱資訊,排程中心
this.eventList = {}, // 事件列表,這項是必須的
// 下面的都是自定義值
this.msg = ref('這是一條匯流排的資訊')
}
// 訂閱
$on(name, fn) {
this.eventList[name] = this.eventList[name] || []
this.eventList[name].push(fn)
}
// 釋出
$emit(name, data) {
if (this.eventList[name]) {
this.eventList[name].forEach((fn) => {
fn(data)
});
}
}
// 取消訂閱
$off(name) {
if (this.eventList[name]) {
delete this.eventList[name]
}
}
}
export default new Bus()父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<div>
父元件:
<span style="margin-right: 30px;">message: {{ message }}</span>
<span>msg: {{ msg }}</span>
</div>
<Child></Child>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Bus from './Bus.js'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const msg = ref(Bus.msg)
const message = ref('hello')
// 用監聽的寫法
Bus.$on('changeMsg', data => {
message.value = data
})
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
子元件:
<button @click="handleBusEmit">觸發Bus.$emit</button>
<button @click="changeBusMsg">修改匯流排裡的 msg</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import Bus from '../Bus.js'
function handleBusEmit() {
Bus.$emit('changeMsg', '雷猴啊')
}
function changeBusMsg() {
// console.log(Bus.msg)
Bus.msg.value = '在子元件裡修改了匯流排的值'
}
</script>這個方法其實還挺好用的,但光看可能有點懵,請大家務必親手敲一下程式碼實踐一下。
getCurrentInstance
getcurrentinstance 是 vue 提供的一個方法,支援存取內部元件範例。
getCurrentInstance只暴露給高階使用場景,典型的比如在庫中。強烈反對在應用的程式碼中使用getCurrentInstance。請不要把它當作在組合式 API 中獲取this的替代方案來使用。
說白了,這個方法 適合在開發元件庫的情況下使用,不適合日常業務開發中使用。
getCurrentInstance 只能在 setup 或生命週期勾點中呼叫。
getcurrentinstance 檔案
https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/composition-api.html#getcurrentinstance
在 <script setup> 中,我模擬了類似 $parent 和 $children 的方式。
父元件
// Parent.vue
<template>
<div>父元件 message 的值: {{ message }}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">獲取子元件</button>
<Child></Child>
<Child></Child>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, getCurrentInstance, onMounted } from 'vue'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
const message = ref('雷猴啊')
let instance = null
onMounted(() => {
instance = getCurrentInstance()
})
// 子元件列表
let childrenList = []
// 註冊元件
function registrationCom(com) {
childrenList.push(com)
}
function handleClick() {
if (childrenList.length > 0) {
childrenList.forEach(item => {
console.log('元件範例:', item)
console.log('元件名(name):', item.type.name)
console.log('元件輸入框的值:', item.devtoolsRawSetupState.inputValue)
console.log('---------------------------------------')
})
}
}
</script>子元件
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>----------------------------</div>
子元件:<button @click="handleClick">獲取父元件的值</button>
<br>
<input type="text" v-model="inputValue">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'ccccc'
}
</script>
<script setup>
import { getCurrentInstance, onMounted, nextTick, ref } from 'vue'
const inputValue = ref('')
let instance = null
onMounted(() => {
instance = getCurrentInstance()
nextTick(() => {
instance.parent.devtoolsRawSetupState.registrationCom(instance)
})
})
function handleClick() {
let msg = instance.parent.devtoolsRawSetupState.message
msg.value = '哈哈哈哈哈哈'
}
</script>可以將程式碼複製到你的專案中執行試試看,最好還是敲一遍咯。
Vuex
Vuex 主要解決 跨元件通訊 的問題。
在 Vue3 中,需要使用 Vuex v4.x 版本。
安裝
用 npm 或者 Yarn 安裝到專案中。
npm install vuex@next --save # 或 yarn add vuex@next --save
使用
安裝成功後,在 src 目錄下建立 store 目錄,再在 store 下建立 index.js 檔案。
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})在 store/index.js 下輸入以上內容。
state:資料倉儲,用來存資料的。getters:獲取資料的,有點像computed的用法(個人覺得)。mutations: 更改state資料的方法都要寫在mutations裡。actions:非同步非同步非同步,非同步的方法都寫在這裡,但最後還是需要通過mutations來修改state的資料。modules:分包。如果專案比較大,可以將業務拆散成獨立模組,然後分檔案管理和存放。
然後在 src/main.js 中引入
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
const app = createApp(App)
app
.use(store)
.mount('#app')State
store/index.js
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
msg: '雷猴'
}
})元件
// xxx.vue
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
console.log(store.state.msg) // 雷猴
</script>Getter
我覺得 Getter 方法和 computed 是有點像的。
比如我們需要過濾一下資料,或者返回時組裝一下資料,都可以用 Getter 方法。
store/index.js
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
msg: '雷猴'
},
getters: {
getMsg(state) {
return state.msg + ' 世界!'
}
}
})元件
// xxx.vue
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
console.log(store.getters.getMsg) // 雷猴 世界!
</script>Mutation
Mutation 是修改 State 資料的唯一方法,這樣 Vuex 才可以跟蹤資料流向。
在元件中通過 commit 呼叫即可。
store/index.js
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
msg: '雷猴'
},
mutations: {
changeMsg(state, data) {
state.msg = data
}
}
})元件
// xxx.vue
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
store.commit('changeMsg', '蒜頭王八')
console.log(store.state.msg) // 蒜頭王八
</script>Action
我習慣將非同步的東西放在 Action 方法裡寫,然後在元件使用 dispatch 方法呼叫。
store/index.js
// store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
msg: '雷猴'
},
mutations: {
changeMsg(state, data) {
state.msg = data
}
},
actions: {
fetchMsg(context) {
// 模擬ajax請求
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeMsg', '鯊魚辣椒')
}, 1000)
}
}
})元件
// xxx.vue
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
store.dispatch('fetchMsg')
</script>Module
Module 就是傳說中的分包了。這需要你將不同模組的資料拆分成一個個 js 檔案。
我舉個例子,目錄如下
store |- index.js |- modules/ |- user.js |- goods.js
index.js對外的出口(主檔案)modules/user.js使用者相關模組modules/goods.js商品模組
index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import user from './modules/user'
import goods from './modules/goods'
export default createStore({
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {
user,
goods
}
})user.js
const user = {
state: {
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
}
}
export default usergoods.js
const goods = {
state: {
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
}
}
export default goods然後在各個模組裡放入相應的資料和方法就行。
在組建中呼叫方法和存取資料,都和之前的用法差不多的。
以上就是 Vuex 的基礎用法。除此之外,Vuex 還有各種語法糖,大家可以自行查閱 官方檔案(https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/)
Pinia
Pinia 是最近比較火熱的一個工具,也是用來處理 跨元件通訊 的,極大可能成為 Vuex 5 。
Pinia 檔案
https://pinia.vuejs.org/
從我使用 Pinia 一陣後的角度來看,Pinia 跟 Vuex 相比有以下優點:
- 呼叫時程式碼跟簡潔了。
- 對
TS更友好。 - 合併了
Vuex的Mutation和Action。天然的支援非同步了。 - 天然分包。
除此之外,Pinia 官網還說它適用於 Vue2 和 Vue3。但我沒試過在 Vue2 中使用我懶得試。
Pinia 簡化了狀態管理模組,只用這3個東西就能應對日常大多工。
state:儲存資料的倉庫getters:獲取和過濾資料(跟computed有點像)actions:存放 「修改state」的方法
我舉個簡單的例子
安裝
npm install pinia # 或 yarn add pinia
註冊
在 src 目錄下建立 store 目錄,再在 store 裡建立 index.js 和 user.js
目錄結構如下
store |- index.js |- user.js
index.js
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
const store = createPinia()
export default storeuser.js
常見的寫法有2種,選其中一種就行。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
// 寫法1
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user', // id必填,且需要唯一
state: () => {
return {
name: '雷猴'
}
},
getters: {
fullName: (state) => {
return '我叫 ' + state.name
}
},
actions: {
updateName(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
})
// 寫法2
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user',{
state: () => {
return {
name: '雷猴'
}
},
getters: {
fullName: (state) => {
return '我叫 ' + state.name
}
},
actions: {
updateName(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
})然後在 src/main.js 中引入 store/index.js
src/main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
const app = createApp(App)
app
.use(store)
.mount('#app')在元件中使用
元件
// xxx.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>name: {{ name }}</div>
<div>全名:{{ fullName }}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">修改</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'
const userStore = useUserStore()
// const name = computed(() => userStore.name)
// 建議
const { name, fullName } = storeToRefs(userStore)
function handleClick() {
// 不建議這樣改
// name.value = '蠍子萊萊'
// 推薦的寫法!!!
userStore.updateName('李四')
}
</script>囉嗦兩句
其實 Pinia 的用法和 Vuex 是挺像的,預設就是分包的邏輯,在這方面我支援 菠蘿(Pinia)。
Pinia 還提供了多種語法糖,強烈建議閱讀一下 官方檔案(https://pinia.vuejs.org/)。
mitt.js
我們前面用到的 匯流排 Bus 方法,其實和 mitt.js 有點像,但 mitt.js 提供了更多的方法。
比如:
on:新增事件emit:執行事件off:移除事件clear:清除所有事件
mitt.js 不是專門給 Vue 服務的,但 Vue 可以利用 mitt.js 做跨元件通訊。
github 地址:https://github.com/developit/mitt
npm 地址:https://www.npmjs.com/package/mitt
安裝
npm i mitt
使用
我模擬一下 匯流排Bus 的方式。
我在同級目錄建立3個檔案用作模擬。
Parent.vue Child.vue Bus.js
Bus.js
// Bus.js import mitt from 'mitt' export default mitt()
Parent.vue
// Parent.vue
<template>
<div>
Mitt
<Child />
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import Child from './Child.vue'
import Bus from './Bus.js'
Bus.on('sayHello', () => console.log('雷猴啊'))
</script>Child.vue
// Child.vue
<template>
<div>
Child:<button @click="handleClick">打聲招呼</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import Bus from './Bus.js'
function handleClick() {
Bus.emit('sayHello')
}
</script>此時,點選 Child.vue 上的按鈕,在控制檯就會執行在 Parent.vue 裡定義的方法。
mitt.js 的用法其實很簡單,建議跟著 官方範例 敲一下程式碼,幾分鐘就上手了。
(學習視訊分享:)
以上就是Vue3元件間怎麼通訊?10+種通訊方式分享的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!