JavaScript---Set資料結構
2022-01-03 20:00:02
JS---Set
1. 什麼是 Set
Set 可以簡單的看作是數學上的集合。
它是一系列無序,沒有重複數值的資料集合。
2. Set 建構函式
對於 Set 的建構函式的引數,可以傳遞以下幾種形式。
2.1) 陣列
const s = new Set([1, 2, 1]);
console.log(s);
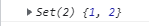
這裡傳遞了一個陣列[1, 2, 1]作為引數,由於 Set 是無重複數值的集合,所以第三個 1 自動刪除了。
2.2) 字串
const s = new Set("Hello World!");
console.log(s);

2.3) arguments
function fun() {
const s = new Set(arguments);
console.log(s);
}
fun(1, 2, 3);
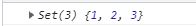
2.4) NodeList
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>set</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
<script>
const s = new Set(document.querySelectorAll('p'));
console.log(s);
</script>
</body>
</html>
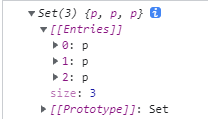
這裡將三個p標籤的參照放進了Set s中;
當我們要用的時候,就可以遍歷這個 Set,然後分別將p標籤的參照取出來,然後就可以對p標籤進行修改了。
2.5) Set
const s1 = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
const s2 = new Set(s1);
console.log(s2);
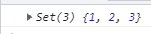
這裡相當於把s1複製過去,給了s2,不過它們不是同一個Set
console.log(s1 === s2);
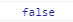
3. Set 的範例屬性和方法
Set 的屬性,有一個屬性size,用來儲存它的成員個數
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
console.log(s.size);

Set的方法
- add
給 Set 中新增成員
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
// 它的引數只能傳一個
s.add(5);
console.log(s);
// 可以連綴 add
s.add(7).add(9);
console.log(s);
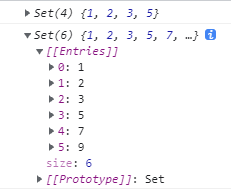
- delete
用來刪除 Set 中的成員
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
s.delete(2);
// 如果要刪除的東西在 Set 中找不到,將什麼也不會發生,也不會報錯
s.delete(5);
console.log(s);
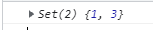
- has
用來判斷 Set 是否含有某個成員
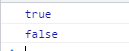
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
console.log(s.has(1));
console.log(s.has(5));
- clear
將會刪除 Set 的所有成員
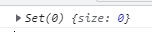
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
s.clear();
console.log(s);
4. Set 的成員存取
它的成員存取要通過 forEach 方法實現,遍歷 Set,它的遍歷是按成員的新增順序來進行遍歷的。
它有兩個引數,第一個引數為回撥函數,第二個引數設定回撥函數中this指向什麼,即
s.forEach(回撥函數, 回撥函數的指向)
- 我們先來看第一個引數:
對於第一個引數回撥函數,它有三個引數:
s.forEach(function(value, key, set){
value 就是 Set 的成員
在 Set 中,value 和 key 是相等的
set 就是前面Set的本身,即這裡 set === s
});
通過一個例子理解一下:
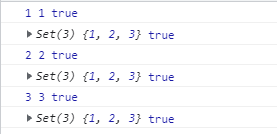
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
s.forEach(function(value, key, set) {
console.log(value, key, value === key);
console.log(set, set === s);
});
- 再來看第二個引數:
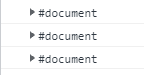
const s = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
s.forEach(function(value, key, set) {
console.log(this);
}, document);
5. Set 的注意事項
Set 對重複值的判斷基本遵循嚴格相等===的判斷
不過對於NaN,在 Set 中,NaN 等於 NaN
6. Set 的使用場景
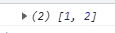
- 陣列去重
let arr = [1, 2, 1];
const s = new Set(arr);
arr = [...s];
// 也可以合成一句
// arr = [...new Set(arr)];
console.log(arr);
- 字串去重
let str = "11231131242";
const s = new Set(str);
str = [...s].join("");
// 也可以寫成一句
// str = [...new Set(str)].join("");
console.log(str);

- 存放 DOM 元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>set</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
<script>
const s = new Set(document.querySelectorAll('p'));
s.forEach((elem) => {
console.log(elem)
});
</script>
</body>
</html>