vuejs傳遞資料的幾種方法是什麼
傳遞方法:1、父元件中利用「props」向子元件傳遞資料;2、子元件利用「this.$emit(「事件」)」向父元件傳遞資料;3、兄弟元件間利用公共檔案傳遞資料;4、父子元件間利用「ref/refs」傳遞資料;5、使用Vuex傳遞資料等等。

本教學操作環境:windows7系統、vue2.9.6版,DELL G3電腦。
一.父傳子傳遞
(1)在父元件的子元件標籤上繫結一個屬性,掛載要傳輸的變數
(2)在子元件中通過props來接受資料,props可以是陣列也可以是物件,接受的資料可以直接使用 props: [「屬性 名」] props:{屬性名:資料型別}
程式碼範例:
//父元件
<template>
<p>
<i>父元件</i>
<!--頁面使用-->
<son :data='name'></son>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import son from "./son.vue";//匯入父元件
export default {
components: { son },//註冊元件
name: "父元件",
data() {
return {
name: "Frazier", //父元件定義變數
};
},
};
</script>//子元件
<template>
<p>{{data}}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: { },
name: '子元件',
props:["data"],
};
</script>二.子傳父傳遞
(1)在父元件的子元件標籤上自定義一個事件,然後呼叫需要的方法
(2)在子元件的方法中通過 this.$emit(「事件」)來觸發在父元件中定義的事件,資料是以引數的形式進行傳遞的
程式碼範例:
//父元件
<template>
<p>
<i>父元件</i>
<!--頁面使用-->
<son @lcclick="lcclick"></son>//自定義一個事件
</p>
</template>
<script>
import son from "./son.vue"; //匯入父元件
export default {
components: { son }, //註冊元件
name: "父元件",
data() {
return {};
},
methods: {
lcclick(){
alert('子傳父')
}
},
};
</script>//子元件
<template>
<p>
<button @click="lcalter">點我</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: { },
name: '子元件',
methods: {
lcalter(){
this.$emit('lcclick')//通過emit來觸發事件
}
},
};
</script>三.兄弟元件通訊(bus匯流排)
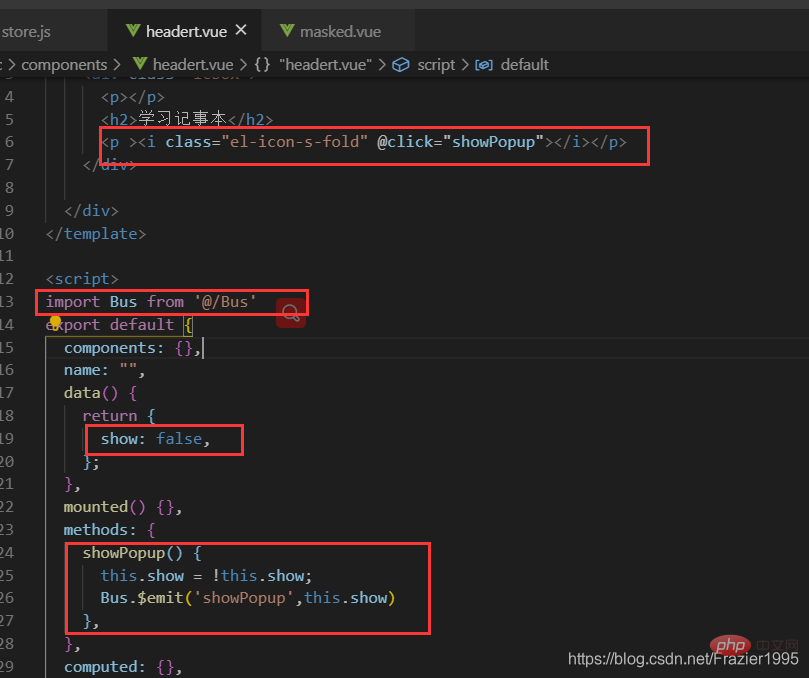
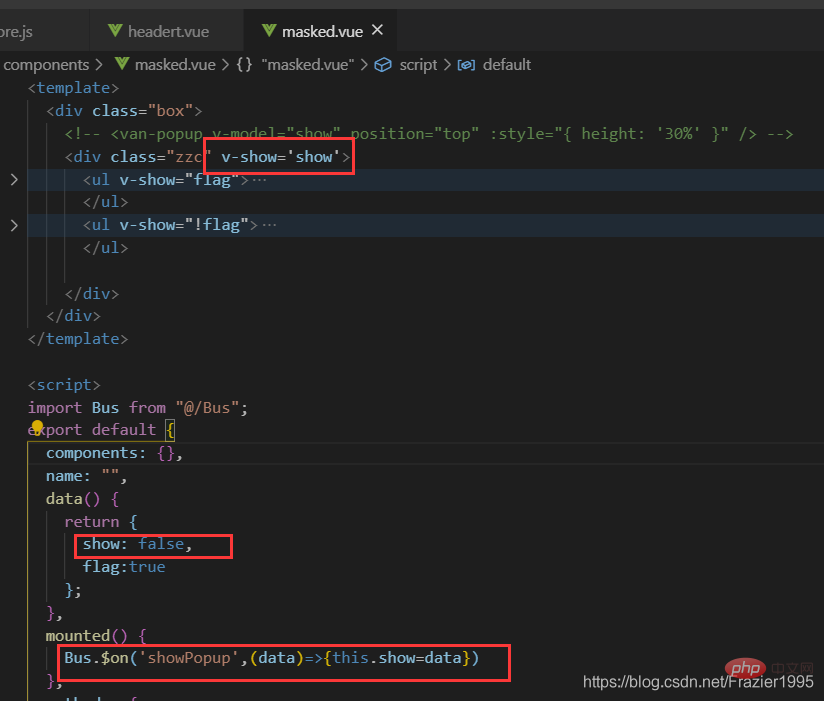
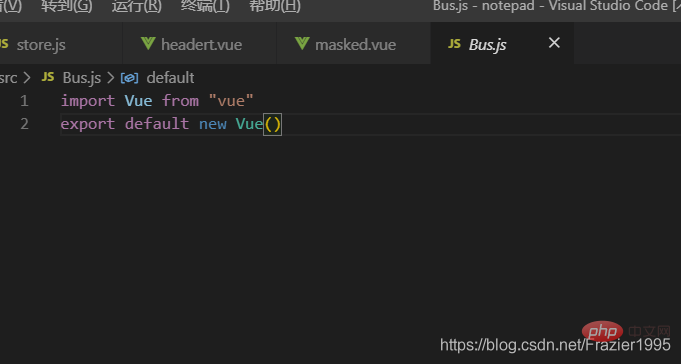
(1)在src中新建一個Bus.js的檔案,然後匯出一個空的vue範例
(2)在傳輸資料的一方引入Bus.js 然後通過Bus. e m i t ( 「 事 件 名 」 , " 參 數 " ) 來 來 派 發 事 件 , 數 據 是 以 emit(「事件名」,"引數")來來派發事件,資料是以 emit(「事件名」,"引數")來來派發事件,資料是以emit()的參 數形式來傳遞
(3)在接受的資料的一方 引入 Bus.js 然後通過 Bus.$on(「事件名」,(data)=>{data是接受的資料})
圖片範例:
四.ref/refs(父子元件通訊)
(1)ref 如果在普通的 DOM 元素上使用,參照指向的就是 DOM 元素;如果用在子元件上,參照就指向元件範例,
(2)可以通過範例直接呼叫元件的方法或存取資料。也算是子元件向父元件傳值的一種
程式碼範例:
//父元件
<template>
<p>
<button @click="sayHello">sayHello</button>
<child ref="childForRef"></child>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import child from './child.vue'
export default {
components: { child },
data () {
return {
childForRef: null,
}
},
mounted() {
this.childForRef = this.$refs.childForRef;
console.log(this.childForRef.name);
},
methods: {
sayHello() {
this.childForRef.sayHello()
}
}
}
</script>//子元件
<template>
<p>child 的內容</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
name: '我是 child',
}
},
methods: {
sayHello () {
console.log('hello');
alert('hello');
}
}
}
</script>五.Vuex通訊
元件通過 dispatch 到 actions,actions 是非同步操作,再 actions中通過 commit 到 mutations,mutations 再通過邏輯操作改變 state,從而同步到元件,更新其資料狀態
程式碼範例:
//父元件
template>
<p id="app">
<ChildA/>
<ChildB/>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import ChildA from './ChildA' // 匯入A元件
import ChildB from './ChildB' // 匯入B元件
export default {
components: {ChildA, ChildB} // 註冊元件
}
</script>//子元件A
<template>
<p id="childA">
<h1>我是A元件</h1>
<button @click="transform">點我讓B元件接收到資料</button>
<p>因為點了B,所以資訊發生了變化:{{BMessage}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
AMessage: 'Hello,B元件,我是A元件'
}
},
computed: {
BMessage() {
// 這裡儲存從store裡獲取的B元件的資料
return this.$store.state.BMsg
}
},
methods: {
transform() {
// 觸發receiveAMsg,將A元件的資料存放到store裡去
this.$store.commit('receiveAMsg', {
AMsg: this.AMessage
})
}
}
}
</script>//子元件B
<template>
<p id="childB">
<h1>我是B元件</h1>
<button @click="transform">點我讓A元件接收到資料</button>
<p>點了A,我的資訊發生了變化:{{AMessage}}</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
BMessage: 'Hello,A元件,我是B元件'
}
},
computed: {
AMessage() {
// 這裡儲存從store裡獲取的A元件的資料
return this.$store.state.AMsg
}
},
methods: {
transform() {
// 觸發receiveBMsg,將B元件的資料存放到store裡去
this.$store.commit('receiveBMsg', {
BMsg: this.BMessage
})
}
}
}
</script>//vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
AMsg: '',
BMsg: ''
}
const mutations = {
receiveAMsg(state, payload) {
// 將A元件的資料存放於state
state.AMsg = payload.AMsg
},
receiveBMsg(state, payload) {
// 將B元件的資料存放於state
state.BMsg = payload.BMsg
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations
})六.$parent
通過parent可以獲父元件範例 ,然 後通過這個範例就可以存取父元件的屬 性和方法 ,它還有一個兄弟parent可以獲父元件範例,然後通過這個範例就可以存取父元件的屬性和方法,它還有一個兄弟parent可以獲父元件範例,然後通過這個範例就可以存取父元件的屬性和方法,它還有一個兄弟root,可以獲取根元件範例。
程式碼範例:
// 獲父元件的資料 this.$parent.foo // 寫入父元件的資料 this.$parent.foo = 2 // 存取父元件的計算屬性 this.$parent.bar // 呼叫父元件的方法 this.$parent.baz() //在子元件傳給父元件例子中,可以使用this.$parent.getNum(100)傳值給父元件。
七.sessionStorage傳值
sessionStorage 是瀏覽器的全域性物件,存在它裡面的資料會在頁面關閉時清除 。運用這個特性,我們可以在所有頁面共用一份資料。
程式碼範例:
// 儲存資料到 sessionStorage
sessionStorage.setItem('key', 'value');
// 從 sessionStorage 獲取資料
let data = sessionStorage.getItem('key');
// 從 sessionStorage 刪除儲存的資料
sessionStorage.removeItem('key');
// 從 sessionStorage 刪除所有儲存的資料
sessionStorage.clear();注意:裡面存的是鍵值對,只能是字串型別,如果要存物件的話,需要使用 let objStr = JSON.stringify(obj) 轉成字串然後再儲存(使用的時候 let obj = JSON.parse(objStr) 解析為物件)。
推薦一個庫 good-storage ,它封裝了sessionStorage ,可以直接用它的API存物件
//localStorage storage.set(key,val) storage.get(key, def) //sessionStorage storage.session.set(key, val) storage.session.get(key, val)
八.路由傳值
使用問號傳值
A頁面跳轉B頁面時使用 this. r o u t e r . p u s h ( ' / B ? n a m e = d a n s e e k ' ) B 頁 面 可 以 使 用 t h i s . router.push('/B?name=danseek') B頁面可以使用 this. router.push('/B?name=danseek')B頁面可以使用this.route.query.name 來獲取A頁面傳過來的值
上面要注意router和route的區別
使用冒號傳值
設定如下路由:
{
path: '/b/:name',
name: 'b',
component: () => import( '../views/B.vue')
},在B頁面可以通過 this.$route.params.name 來獲取路由傳入的name的值
使用父子元件傳值
由於router-view本身也是一個元件,所以我們也可以使用父子元件傳值方式傳值,然後在對應的子頁面里加上props,因為type更新後沒有重新整理路由,所以不能直接在子頁面的mounted勾點裡直接獲取最新type的值,而要使用watch
<router-view :type="type"></router-view>
// 子頁面
props: ['type']
watch: {
type(){
// console.log("在這個方法可以時刻獲取最新的資料:type=",this.type)
},
},九.祖傳孫 $attrs
正常情況下需要藉助父親的props作為中間過渡,但是這樣在父親元件就會多了一些跟父元件業務無關的屬性,耦合度高,藉助$attrs可以簡化些,而且祖跟孫都無需做修改
祖元件:
<template>
<section>
<parent name="grandParent" sex="男" age="88" hobby="code" @sayKnow="sayKnow"></parent>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import Parent from './Parent'
export default {
name: "GrandParent",
components: {
Parent
},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
sayKnow(val){
console.log(val)
}
},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>父元件
<template>
<section>
<p>父元件收到</p>
<p>祖父的名字:{{name}}</p>
<children v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"></children>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children'
export default {
name: "Parent",
components: {
Children
},
// 父元件接收了name,所以name值是不會傳到子元件的
props:['name'],
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>子元件
<template>
<section>
<p>子元件收到</p>
<p>祖父的名字:{{name}}</p>
<p>祖父的性別:{{sex}}</p>
<p>祖父的年齡:{{age}}</p>
<p>祖父的愛好:{{hobby}}</p>
<button @click="sayKnow">我知道啦</button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Children",
components: {},
// 由於父元件已經接收了name屬性,所以name不會傳到子元件了
props:['sex','age','hobby','name'],
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
sayKnow(){
this.$emit('sayKnow','我知道啦')
}
},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>十.孫傳祖使用$listeners
文字內容同第九個
祖元件
<template>
<p id="app">
<children-one @eventOne="eventOne"></children-one>
{{ msg }}
</p>
</template>
<script>
import ChildrenOne from '../src/components/children.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
ChildrenOne,
},
data() {
return {
msg: ''
}
},
methods: {
eventOne(value) {
this.msg = value
}
}
}
</script>父元件
<template>
<p>
<children-two v-on="$listeners"></children-two>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import ChildrenTwo from './childrenTwo.vue'
export default {
name: 'childrenOne',
components: {
ChildrenTwo
}
}
</script>子元件
<template>
<p>
<button @click="setMsg">點選傳給祖父</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'children',
methods: {
setMsg() {
this.$emit('eventOne', '123')
}
}
}
</script>十一.promise傳參
promise 中 resolve 如何傳遞多個引數
//類似與這樣使用,但實際上後面兩個引數無法獲取
promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
let a = 1
let b = 2
let c = 3
resolve(a,b,c)
})
promise.then((a,b,c)=>{
console.log(a,b,c)
})resolve() 只能接受並處理一個引數,多餘的引數會被忽略掉。
如果想多個用陣列,或者物件方式。。
陣列
promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
resolve([1,2,3])
})
promise.then((arr)=>{
console.log(arr[0],arr[1],arr[2])
})物件
promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
resolve({a:1,b:2,c:3})
})
promise.then(obj=>{
console.log(obj.a,obj.b,obj.c)
})十二.全域性變數
定義一個全域性變數,在有值的元件直接賦值,在需要的元件內直接使用就可以了,具體的話看我這篇部落格就可以,
部落格連結點選就好 全域性變數 篇
到此這篇關於vue傳值方式的十二種方法總結的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關vue傳值方式內容請搜尋指令碼之家以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以後多多支援指令碼之家!
相關推薦:《》
以上就是vuejs傳遞資料的幾種方法是什麼的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!