Java IO流之位元組流【一】
1.IO 概述
生活中,你肯定經歷過這樣的場景。當你編輯一個文字檔案,忘記了 ctrl+s ,可能檔案就白白編輯了。
當你電腦上插入一個U盤,可以把一個視訊,拷貝到你的電腦硬碟裡。那麼資料都是儲存在哪些裝置呢?記憶體、硬碟、外接裝置(行動硬碟,U盤)等等。
資料的傳輸可以看做是資料的流動,按照流動的方向,以記憶體為基準,分為輸入流input 和輸出流output ,即流向記憶體是輸入流,流出記憶體是輸出流。
Java的IO模型設計採用了Decorator(裝飾者模式),按功能劃分流,並且可以動態裝配。
舉例:應當組合使用 FileInputStream 和 BufferedInputStream,以實現具有緩衝功能的檔案輸入流。
2.IO流的分類
- 根據資料的流向分為:輸入流 和 輸出流。
- 輸入流 :把資料從其他裝置上讀取到記憶體中的流。
- 輸出流 :把資料從記憶體中寫出到其他裝置上的流。
- 根據資料的型別分為:位元組流 和 字元流。
- 位元組流 :以位元組為單位,讀寫資料的流。
- 字元流 :以字元為單位,讀寫資料的流。Java中的字元是Unicode編碼,一個字元佔用兩個位元組
- 根據功能分為:節點流 和 處理流
- 節點流:向一個特定的地方(節點)讀寫資料。如
FileInputStream。 - 處理流:是對一個已存在的流進行封裝。如
BufferedInputStream。處理流的構造方法需要一個流物件做引數。一個流物件可以被其他流多次封裝。
| 流的分類 | 輸入流 | 輸出流 |
|---|---|---|
| 位元組流 | InputStream(位元組輸入流) | OutputStream(位元組輸出流) |
| 字元流 | Reader(字元輸入流) | Writer(字元輸出流) |
2.2 IO流類圖結構
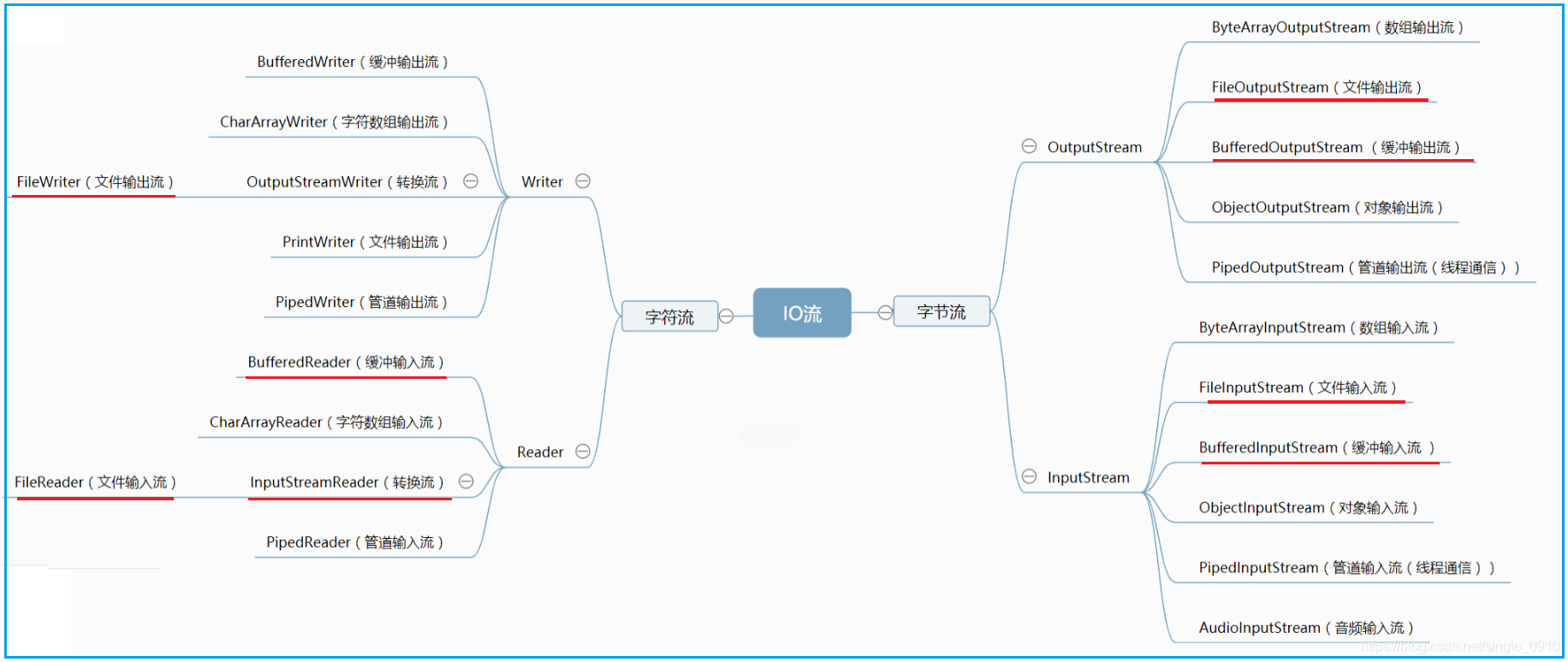
3.位元組流
在計算機中,一切檔案資料(文字、圖片、視訊等)在儲存時,都是以二進位制數位的形式儲存的,都是一個個位元組。
所以,位元組流可以傳輸任意檔案資料。
在操作流的時候,我們要時刻明確,無論使用什麼樣的流物件,底層傳輸的始終為二進位制資料。
位元組流類圖結構:
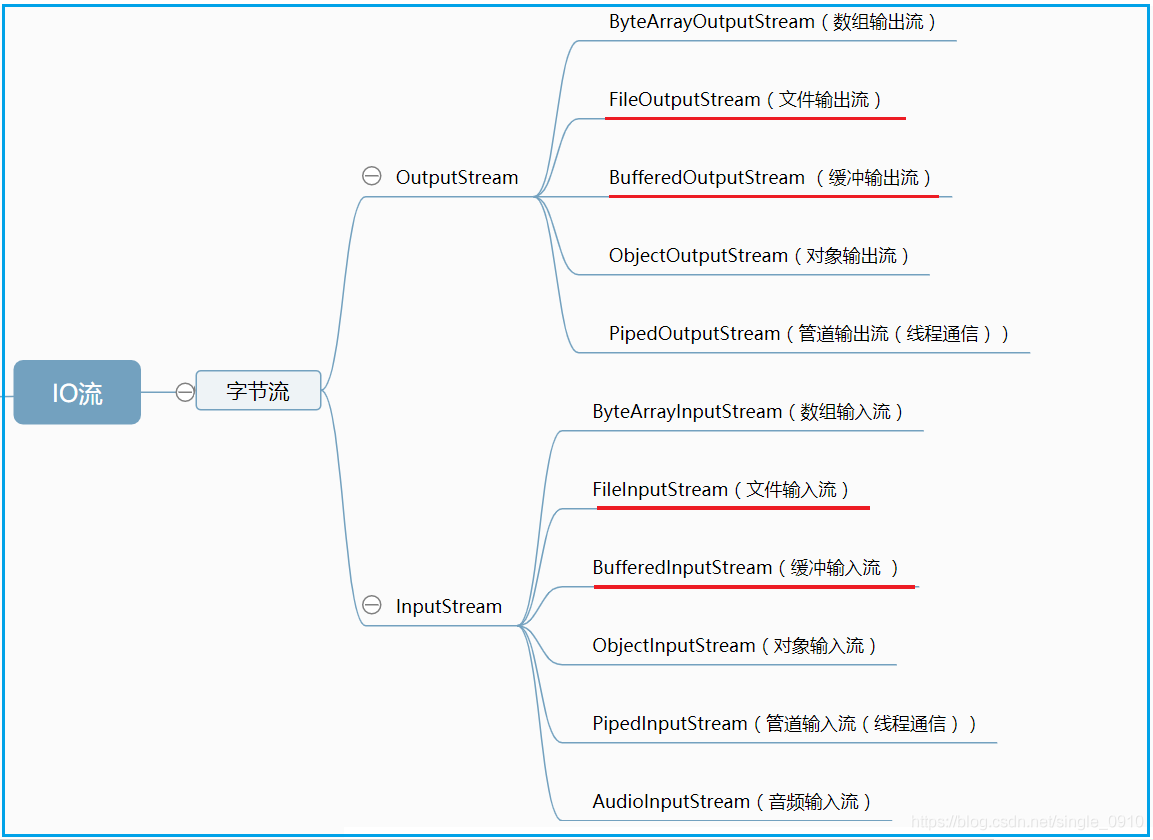
3.1 位元組
- 位元組(Byte)是計算機中表述儲存容量的計量單位,也表示程式語言中的資料型別和語言字元。
- 一個位元組儲存8位元無符號數,儲存的數值範圍為0-255。
位元組與位元
- 資料儲存是以「位元組」(Byte)為單位,資料傳輸大多是以「位」(bit,又名「位元」)為單位,一個位就代表一個0或1(即二進位制),每8個位(bit,簡寫為b)組成一個位元組(Byte,簡寫為B),是最小一級的資訊單位 [4] 。
Java基本資料型別
| 型別 | 位元組數 | 位數 | 範圍 |
|---|---|---|---|
| byte | 1 | 8位元 | 最小值是 -128(-2^7); 最大值是 127(2^7-1) |
| short | 2 | 16位元 | 最小值是 -32768(-2^15); 最大值是 32767(2^15 - 1) |
| int | 4 | 32位元 | 最小值是 -2,147,483,648(-2^31); 最大值是 2,147,483,647(2^31 - 1) |
| long | 8 | 64位元 | 最小值是 -2^63; 最大值是 2^63 -1 |
| float | 4 | 32位元 | 單精度、-2^128 ~ +2^128,也即-3.40E+38 ~ +3.40E+38 |
| double | 8 | 64位元 | 雙精度、-2^1024 ~ +2^1024,也即-1.79E+308 ~ +1.79E+308。 |
| char | 2 | 16 位 | 最小值是 \u0000(即為0);最大值是 \uffff(即為65,535) |
| boolean | 1 | 8 | 只有兩個取值:true(00000001) 和 false(00000000) |
3.2 【OutputStream】位元組輸出流
java.io.OutputStream 是一個抽象類,是表示位元組輸出流的所有類的超類,能夠將指定的位元組資訊寫出到目的地。它定義了位元組輸出流的基本共性功能方法。
java.io.OutputStream的方法如下:
public void close() :關閉此輸出流並釋放與此流有關的所有系統資源
public void flush() :重新整理此輸出流並強制寫出所有緩衝的輸出位元組。
public void write(byte[] b):將 b.length位元組從指定的位元組陣列寫入此輸出流。該方法等同於write(byte[], 0, b.length);
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) :從指定的位元組陣列寫入 len位元組,從索引 off開始的len 個位元組寫入此輸出流。該方法底層呼叫的是write(int b)。
public abstract void write(int b) :將指定的位元組寫入此輸出流。(要寫入的位元組是引數 b 的8個低位。b 的 24 個高位將被忽略。)
3.2.1 FileOutputStream 【檔案位元組輸出流】
作用: 將資料以位元組的形式寫入到檔案中。
構造方法:
public FileOutputStream(File file) : 相當於FileOutputStream(File file,false) 。
public FileOutputStream(File file,boolean append) : 建立一個向File物件表示的檔案中寫入資料的檔案輸出流.如果第二個引數為true,則表示追加寫入到檔案末尾,若為false,則是覆蓋寫入。
public FileOutputStream(String name) :相當於FileOutputStream(String name,false) 。
public FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append) :建立一個向具有指定名稱的檔案中寫入資料的輸出檔案流。如果第二個引數為true,則表示追加寫入到檔案末尾,若為false,則是覆蓋寫入。
public FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) : 建立一個向指定檔案描述符處寫入資料的輸出檔案流,該檔案描述符表示一個到檔案系統中的某個實際檔案的現有連線。
構造方法原始碼註釋:
public FileOutputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(file, false);
}
public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
throws FileNotFoundException
{
// 獲取構造方法中傳入的路徑名
String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null);
// 獲取系統安全管理器
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
// 驗證是否有寫許可權
security.checkWrite(name);
}
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 驗證檔案路徑是否無效
if (file.isInvalid()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Invalid file path");
}
// 建立一個檔案描述符類
this.fd = new FileDescriptor();
// 增加一個可關閉的標籤,以便跟蹤
fd.attach(this);
this.append = append;
this.path = name;
/** 開啟指定名稱的檔案以進行覆蓋寫入或追加寫入。
* append :false 覆蓋寫入
* append :true 追加寫入
*/
open(name, append);
}
// 開啟指定名稱的檔案以進行覆蓋寫入或追加寫入。
private void open(String name, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException {
open0(name, append);
}
// native方法,呼叫系統底層。
private native void open0(String name, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException;
public FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null, false);
}
public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
throws FileNotFoundException
{
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null, append);
}
public FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) {
// 獲取系統安全管理器
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (fdObj == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (security != null) {
// 驗證是否有寫入許可權
security.checkWrite(fdObj);
}
this.fd = fdObj;
this.append = false;
this.path = null;
fd.attach(this);
}
通過原始碼,可以看出,這幾個構造方法真正呼叫的其實都是 public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) 這個構造方法。
寫入資料的步驟:
java程式-->jvm(java虛擬機器器)-->OS(作業系統)-->OS呼叫寫資料的方法-->把資料寫入到檔案中
簡單範例:
package com.hanyxx.io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author layman
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("layman.txt");
// 寫入單個位元組
fos.write(65);
/**
* 一次性寫入多個位元組
* 如果第一個位元組是正數(0~127),那麼顯示的時候會查詢ASCII表
* 如果第一個位元組是負數,那麼第一個位元組會和第二個位元組,組成一箇中文顯示。使用系統預設碼錶(GBK)。
*/
byte[] bytes = {-65,-66,67,-68,69};
//fos.write(bytes);
/**
* write(byte b[], int off, int len):寫入位元組陣列的一部分
* off :開始寫入的陣列索引
* len :寫入的位元組個數
*/
//fos.write(bytes,1,2);
fos.close();
}
}
注意:
- 寫資料的時候,會把整數65轉為二進位制,也就是01000001。
- 任意的文字編輯器(記事本,nodepad++…,Sublime Text在開啟檔案的時候,都會去查詢編碼表,把位元組轉化為字元進行顯示。)
- 0~127 ,查詢ASCII碼錶,如果是其他值,則查詢系統預設碼錶,如果是中文,則查詢GBK。
- 所以雖然寫入了65,實際上是個A (要不起!)
換行符:
windows系統: \r\n linux系統: \r mac系統: \n
3.3 InputStream【位元組輸入流】
java.io.InputStream 是一個抽象類,是表示位元組輸入流的所有類的超類,能夠將指定的位元組資訊寫入記憶體。它定義了位元組輸入流的基本共性功能方法。
java.io.InputStream的方法如下:
public int available():返回此輸入流下一個方法呼叫可以不受阻塞地從此輸入流讀取(或跳過)的估計位元組數。此方法應該由子類重寫
public void close() :關閉此輸入流並釋放與其關聯的所有系統資源。
public void mark(int readlimit):在此輸入流中標記當前位置。
public boolean markSupported():測試此輸入流是否支援 mark 和 reset 方法。
public abstract int read():從輸入流中讀取資料的下一個位元組。返回 0 到 255 範圍內的 int 位元組值。如果讀到流末尾,返回 -1。
public int read(byte[] b):從輸入流中讀取一定數量的位元組,並將其儲存在緩衝區陣列 b 中。。該方法等同於 read(b, 0, b.length)
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len):將輸入流中最多 len 個資料位元組讀入 byte 陣列。嘗試讀取 len 個位元組,但讀取的位元組也可能小於該值。
public void reset():將此流重新定位到最後一次對此輸入流呼叫 mark 方法時的位置。
public long skip(long n):跳過和丟棄此輸入流中的 n 個位元組。
3.3.1 FileInputStream【檔案位元組輸入流】
作用: 將資料以位元組的形式讀取到記憶體中。
構造方法:
public FileInputStream(File file):通過開啟與實際檔案的連線來建立一個 FileInputStream ,該檔案由File物件 指定。建立一個新 FileDescriptor 物件來表示此檔案連線。
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj):過使用檔案描述符 fdObj 建立一個 FileInputStream,該檔案描述符表示到檔案系統中某個實際檔案的現有連線。
public FileInputStream(String name):通過開啟與實際檔案的連線來建立一個 FileInputStream,該檔案通過檔案路徑名 name 指定。建立一個新 FileDescriptor 物件來表示此檔案連線。
構造方法原始碼:
public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null);
}
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null);
// 獲取系統安全管理器
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
// 驗證是否有讀許可權
security.checkRead(name);
}
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 驗證檔案路徑是否無效
if (file.isInvalid()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Invalid file path");
}
// 跟蹤
fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.attach(this);
path = name;
open(name);
}
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (fdObj == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(fdObj);
}
fd = fdObj;
path = null;
fd.attach(this);
}
通過原始碼,可以看出,構造方法底層真正呼叫的其實都是 public FileInputStream(File file) 這個構造方法。
讀取位元組的原始碼:
// 從流中讀取一個位元組
public int read() throws IOException {
return read0();
}
// 呼叫系統底層native方法
private native int read0() throws IOException;
// 讀取位元組陣列
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);
}
// 讀取一部分位元組陣列
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, off, len);
}
// 呼叫系統底層native方法
private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
簡單演示:
package com.hanyxx.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author layman
*/
public class Demo02 {
static FileInputStream fis;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
read01();
read02();
read03();
}
// 迴圈讀取單個位元組
private static void read01() throws IOException {
fis = new FileInputStream("layman.txt");
int len;
while((len = fis.read()) != -1){
// 將讀取到的位元組轉為字元,並列印輸出
System.out.print((char)len);
}
System.out.println();
fis.close();
}
/**
* int read(byte[] b):從輸入流中將最多 b.length 個位元組的資料讀入一個 byte 陣列中。
*/
private static void read02() throws IOException {
fis = new FileInputStream("layman.txt");
// fis.available():獲取流中能夠讀取到的有效位元組個數
byte[] bytes = new byte[fis.available()];
int length = fis.read(bytes);
fis.close();
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println("讀取到的位元組個數: " + length);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
/**
* int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) :從此輸入流中將最多 len 個位元組的資料讀入一個 byte 陣列中。off:偏移量,不是陣列索引
*/
private static void read03() throws IOException {
fis = new FileInputStream("layman.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[fis.available()];
int len = fis.read(bytes,2,3);
fis.close();
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println("讀取到的位元組個數: " + len);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
}
執行結果:
BIGHUGE
------------------
讀取到的位元組個數: 7
BIGHUGE
------------------
讀取到的位元組個數: 3
BIGBIGHUGE
讀取到的位元組個數: 7
BIGHUGE
讀取到的位元組個數: 3
BIG
簡單案例(圖片複製):
將D:\food.jpg複製為D:\food_copy.jpg
package com.hanyxx.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 圖片複製
* @author layman
* @date 2021/3/7
*/
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\food.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\food_copy.jpg");
int len;
//單位元組寫入
/*while((len = fis.read()) != -1){
fos.write(len);
}*/
// 使用陣列緩衝流讀取位元組(1KB)
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0 , len);
}
//流的關閉原則:先開後關,後開先關。
fos.close();
fis.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("複製耗時:" + (end-start) + "毫秒");
}
}