以太坊交易池原始碼分析
交易池概念原理
交易池工作概況:
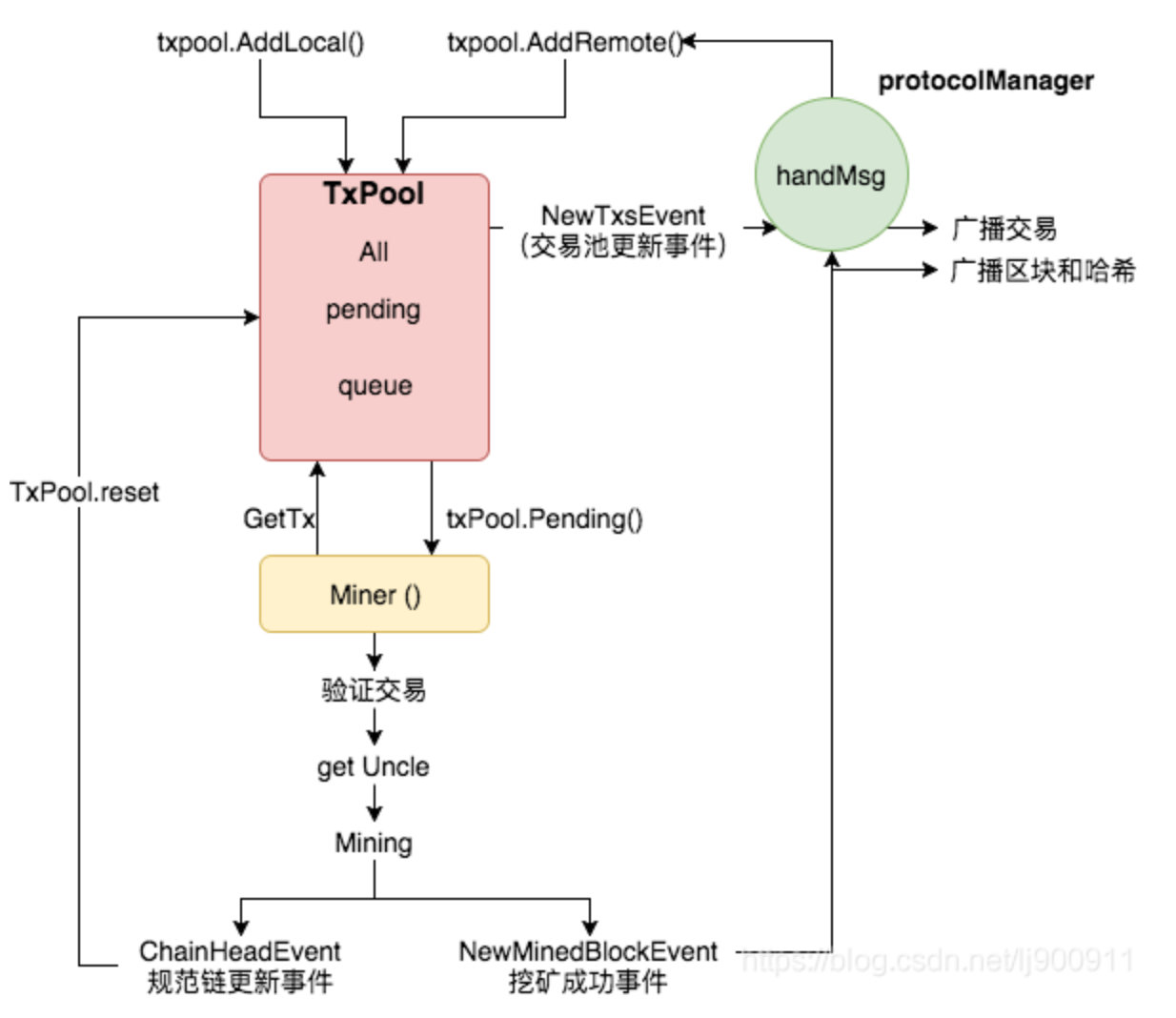
- 交易池的資料來源主要來自:
- 本地提交,也就是第三方應用通過呼叫本地以太坊節點的RPC服務所提交的交易;
- 遠端同步,是指通過廣播同步的形式,將其他以太坊節點的交易資料同步至本地節點;
- 交易池中交易去向:被Miner模組獲取並驗證,用於挖礦;挖礦成功後寫進區塊並被廣播
- Miner取走交易是複製,交易池中的交易並不減少。直到交易被寫進規範鏈後才從交易池刪除;
- 交易如果被寫進分叉,交易池中的交易也不減少,等待重新打包。
關鍵資料結構
TxPoolConfig
type TxPoolConfig struct {
Locals []common.Address // 本地賬戶地址存放
NoLocals bool // 是否開啟本地交易機制
Journal string // 本地交易存放路徑
Rejournal time.Duration // 持久化本地交易的間隔
PriceLimit uint64 // 價格超出比例,若想覆蓋一筆交易的時候,若價格上漲比例達不到要求,那麼不能覆蓋
PriceBump uint64 // 替換現有交易的最低價格漲幅百分比(一次)
AccountSlots uint64 // 每個賬戶的可執行交易限制
GlobalSlots uint64 // 全部賬戶最大可執行交易
AccountQueue uint64 // 單個賬戶不可執行的交易限制
GlobalQueue uint64 // 全部賬戶最大非執行交易限制
Lifetime time.Duration // 一個賬戶在queue中的交易可以存活的時間
}
預設設定:
Journal: "transactions.rlp", Rejournal: time.Hour, PriceLimit: 1, PriceBump: 10, AccountSlots: 16, GlobalSlots: 4096, AccountQueue: 64, GlobalQueue: 1024, Lifetime: 3 * time.Hour
TxPool
type TxPool struct {
config TxPoolConfig // 交易池設定
chainconfig *params.ChainConfig // 區塊鏈設定
chain blockChain // 定義blockchain介面
gasPrice *big.Int
txFeed event.Feed //時間流
scope event.SubscriptionScope // 訂閱範圍
signer types.Signer //簽名
mu sync.RWMutex
istanbul bool // Fork indicator whether we are in the istanbul stage.
currentState *state.StateDB // 當前頭區塊對應的狀態
pendingNonces *txNoncer // Pending state tracking virtual nonces
currentMaxGas uint64 // Current gas limit for transaction caps
locals *accountSet // Set of local transaction to exempt from eviction rules
journal *txJournal // Journal of local transaction to back up to disk
pending map[common.Address]*txList // All currently processable transactions
queue map[common.Address]*txList // Queued but non-processable transactions
beats map[common.Address]time.Time // Last heartbeat from each known account
all *txLookup // All transactions to allow lookups
priced *txPricedList // All transactions sorted by price
chainHeadCh chan ChainHeadEvent
chainHeadSub event.Subscription
reqResetCh chan *txpoolResetRequest
reqPromoteCh chan *accountSet
queueTxEventCh chan *types.Transaction
reorgDoneCh chan chan struct{}
reorgShutdownCh chan struct{} // requests shutdown of scheduleReorgLoop
wg sync.WaitGroup // tracks loop, scheduleReorgLoop
}
txpool初始化
Txpool初始化主要做了以下幾件事:
-
檢查設定 設定有問題則用預設值填充
config = (&config).sanitize()對於這部分的檢查檢視TxPoolConfig的欄位。
-
初始化本地賬戶
pool.locals = newAccountSet(pool.signer)
- 將設定的本地賬戶地址加到交易池
pool.locals.add(addr)
我們在安裝以太坊使用者端往往可以指定一個資料儲存目錄,此目錄便會儲存著所有我們匯入的或者通過本地使用者端建立的帳戶keystore檔案。而這個載入過程便是從該目錄載入帳戶資料
-
更新交易池
pool.reset(nil, chain.CurrentBlock().Header()) -
建立所有交易儲存的列表,所有交易的價格用最小堆存放
pool.priced = newTxPricedList(pool.all)通過排序,優先處理gasprice越高的交易。
-
如果本地交易開啟 那麼從本地磁碟載入本地交易
if !config.NoLocals && config.Journal != "" { pool.journal = newTxJournal(config.Journal) if err := pool.journal.load(pool.AddLocals); err != nil { log.Warn("Failed to load transaction journal", "err", err) } if err := pool.journal.rotate(pool.local()); err != nil { log.Warn("Failed to rotate transaction journal", "err", err) } } -
訂閱鏈上事件訊息
pool.chainHeadSub = pool.chain.SubscribeChainHeadEvent(pool.chainHeadCh) -
開啟主迴圈
go pool.loop()
注意:local交易比remote交易具有更高的許可權,一是不輕易被替換;二是持久化,即通過一個原生的journal檔案儲存尚未打包的local交易。所以在節點啟動的時候,優先從本地載入local交易。
本地地址會被加入白名單,凡由此地址傳送的交易均被認為是local交易,不論是從本地遞交還是從遠端傳送來的。
到此為止交易池載入過程結束。
新增交易到txpool
之前我們說過交易池中交易的來源一方面是其他節點廣播過來的,一方面是本地提交的,追根到原始碼一個是AddLocal,一個是AddRemote,不管哪個都會呼叫addTxs。我們對新增交易的討論就會從這個函數開始,它主要做了以下幾件事:
-
過濾池中已經存在的交易
if pool.all.Get(tx.Hash()) != nil { errs[i] = fmt.Errorf("known transaction: %x", tx.Hash()) knownTxMeter.Mark(1) continue } -
將交易新增到佇列中
newErrs, dirtyAddrs := pool.addTxsLocked(news, local)進入到addTxsLocked函數中: replaced, err := pool.add(tx, local)進入到 pool.add函數中,這個add函數相當重要,它是將交易新增到queue中,等待後面的promote,到pending中去。如果在queue或者pending中已經存在,並且它的gas price更高時,將覆蓋之前的交易。下面來拆開的分析一下add 這個函數。
①:看交易是否收到過,如果已經收到過就丟棄
if pool.all.Get(hash) != nil { log.Trace("Discarding already known transaction", "hash", hash) knownTxMeter.Mark(1) return false, fmt.Errorf("known transaction: %x", hash) }②:如果交易沒通過驗證也要丟棄,這裡的重點是驗證函數:
validateTx: 主要做了以下幾件事 - 交易大小不能超過32kb - 交易金額不能為負 - 交易gas值不能超出當前交易池設定的gaslimit - 交易簽名必須正確 - 如果交易為遠端交易,則需驗證其gasprice是否小於交易池gasprice最小值,如果是本地,優先打包,不管gasprice - 判斷當前交易nonce值是否過低 - 交易所需花費的轉帳手續費是否大於帳戶餘額 cost == V + GP * GL - 判斷交易花費gas是否小於其預估花費gas③:如果交易池已滿,丟棄價格過低的交易
if uint64(pool.all.Count()) >= pool.config.GlobalSlots+pool.config.GlobalQueue { // If the new transaction is underpriced, don't accept it if !local && pool.priced.Underpriced(tx, pool.locals) { log.Trace("Discarding underpriced transaction", "hash", hash, "price", tx.GasPrice()) underpricedTxMeter.Mark(1) return false, ErrUnderpriced } // New transaction is better than our worse ones, make room for it drop := pool.priced.Discard(pool.all.Count()-int(pool.config.GlobalSlots+pool.config.GlobalQueue-1), pool.locals) for _, tx := range drop { log.Trace("Discarding freshly underpriced transaction", "hash", tx.Hash(), "price", tx.GasPrice()) underpricedTxMeter.Mark(1) pool.removeTx(tx.Hash(), false) } }注意這邊的GlobalSlots和GlobalQueue ,就是我們說的pending和queue的最大容量,如果交易池的交易數超過兩者之和,就要丟棄價格過低的交易。
④:判斷當前交易在pending佇列中是否存在nonce值相同的交易。存在則判斷當前交易所設定的gasprice是否超過設定的PriceBump百分比,超過則替換覆蓋已存在的交易,否則報錯返回
替換交易gasprice過低,並且把它扔到queue佇列中(enqueueTx)。if list := pool.pending[from]; list != nil && list.Overlaps(tx) { // Nonce already pending, check if required price bump is met inserted, old := list.Add(tx, pool.config.PriceBump) if !inserted { pendingDiscardMeter.Mark(1) return false, ErrReplaceUnderpriced } // New transaction is better, replace old one if old != nil { pool.all.Remove(old.Hash()) pool.priced.Removed(1) pendingReplaceMeter.Mark(1) } pool.all.Add(tx) pool.priced.Put(tx) pool.journalTx(from, tx) pool.queueTxEvent(tx) log.Trace("Pooled new executable transaction", "hash", hash, "from", from, "to", tx.To()) return old != nil, nil } // New transaction isn't replacing a pending one, push into queue replaced, err = pool.enqueueTx(hash, tx)新增交易的流程就到此為止了。接下來就是如何把queue(暫時不可執行)中新增的交易扔到pending(可執行交易)中,速成promote。
-
提升交易
提升交易主要把交易從queue扔到pending中,我們在接下來的裡面重點講
done := pool.requestPromoteExecutables(dirtyAddrs)
交易升級
promoteExecutables將future queue中的交易移動到pending中,同時也會刪除很多無效交易比如nonce低或者餘額低等等,主要分以下步驟:
①:將所有queue中nonce低於賬戶當前nonce的交易從all裡面刪除
forwards := list.Forward(pool.currentState.GetNonce(addr))
for _, tx := range forwards {
hash := tx.Hash()
pool.all.Remove(hash)
log.Trace("Removed old queued transaction", "hash", hash)
}
②:將所有queue中花費大於賬戶餘額 或者gas大於限制的交易從all裡面刪除
drops, _ := list.Filter(pool.currentState.GetBalance(addr), pool.currentMaxGas)
for _, tx := range drops {
hash := tx.Hash()
pool.all.Remove(hash)
log.Trace("Removed unpayable queued transaction", "hash", hash)
}
③:將所有可執行的交易從queue裡面移到pending裡面(proteTx)
注:可執行交易:將pending裡面nonce值大於等於賬戶當前狀態nonce的且nonce連續的幾筆交易作為準備好的交易
readies := list.Ready(pool.pendingNonces.get(addr))
for _, tx := range readies {
hash := tx.Hash()
if pool.promoteTx(addr, hash, tx) {
log.Trace("Promoting queued transaction", "hash", hash)
promoted = append(promoted, tx)
}
}
重點就是 promoteTx的處理,這個方法與add的不同之處在於,add是獲得到的新交易插入pending,而promoteTx是將queue列表中的Txs放入pending接下來我們先看看裡面是如何來處理的:
inserted, old := list.Add(tx, pool.config.PriceBump)
if !inserted {
// An older transaction was better, discard this
// 老的交易更好,刪除這個交易
pool.all.Remove(hash)
pool.priced.Removed(1)
pendingDiscardMeter.Mark(1)
return false
}
// Otherwise discard any previous transaction and mark this
// 現在這個交易更好,刪除舊的交易
if old != nil {
pool.all.Remove(old.Hash())
pool.priced.Removed(1)
pendingReplaceMeter.Mark(1)
} else {
// Nothing was replaced, bump the pending counter
pendingGauge.Inc(1)
}
主要就做了這幾件事:
- 將交易插入pending中,如果待插入的交易nonce在pending列表中存在,那麼待插入的交易gas price大於或等於原交易價值的110%(跟pricebump設定有關)時,替換原交易
- 如果新交易替換了某個交易,從all列表中刪除老交易
- 最後更新一下all列表
經過proteTx之後,要扔到pending的交易都放在了promoted []*types.Transaction中,再回到promoteExecutables中,繼續下面步驟:
④:如果非本地賬戶queue大於限制(AccountQueue),從最後取出nonce較大的交易進行remove
if !pool.locals.contains(addr) {
caps = list.Cap(int(pool.config.AccountQueue))
for _, tx := range caps {
hash := tx.Hash()
pool.all.Remove(hash)
...
}
⑤:最後如果佇列中此賬戶的交易為空則刪除此賬戶
if list.Empty() {
delete(pool.queue, addr)
}
到此我們的升級交易要做的事情就完畢了。
交易降級
交易降級的幾個場景:
- 出現了新的區塊,將會從pending中移除出現在區塊中的交易到queue中
- 或者是另外一筆交易(gas price 更高),則會從pending中移除到queue中
關鍵函數:demoteUnexecutables,主要做的事情如下:
①:遍歷pending中所有地址對應的交易列表
for addr, list := range pool.pending {
...}
②:刪除所有認為過舊的交易(low nonce)
olds := list.Forward(nonce)
for _, tx := range olds {
hash := tx.Hash()
pool.all.Remove(hash)
log.Trace("Removed old pending transaction", "hash", hash)
}
③:刪除所有費用過高的交易(餘額低或用盡),並將所有無效者送到queue中以備後用
drops, invalids := list.Filter(pool.currentState.GetBalance(addr), pool.currentMaxGas)
for _, tx := range drops {
hash := tx.Hash()
log.Trace("Removed unpayable pending transaction", "hash", hash)
pool.all.Remove(hash)
}
pool.priced.Removed(len(olds) + len(drops))
pendingNofundsMeter.Mark(int64(len(drops)))
for _, tx := range invalids {
hash := tx.Hash()
log.Trace("Demoting pending transaction", "hash", hash)
pool.enqueueTx(hash, tx)
}
④:如果交易前面有間隙,將後面的交易移到queue中
if list.Len() > 0 && list.txs.Get(nonce) == nil {
gapped := list.Cap(0)
for _, tx := range gapped {
hash := tx.Hash()
log.Error("Demoting invalidated transaction", "hash", hash)
pool.enqueueTx(hash, tx)
}
pendingGauge.Dec(int64(len(gapped)))
}
注:間隙的出現通常是因為交易餘額問題導致的。假如原規範鏈A 上交易m花費10,分叉後該賬戶又在分叉鏈B發出一個交易m花費20,這就導致該賬戶餘額本來可以支付A鏈上的某筆交易,但在B鏈上可能就不夠了。這個餘額不足的交易在B如果是n+3,那麼在A鏈上n+2,n+4號交易之間就出現了空隙,這就導致從n+3開始往後所有的交易都要降級;
到底交易降級結束。
重置交易池
重置交易池將檢索區塊鏈的當前狀態(主要由於更新導致鏈狀態變化),並確保交易池的內容對於鏈狀態而言是有效的。
流程圖如下:
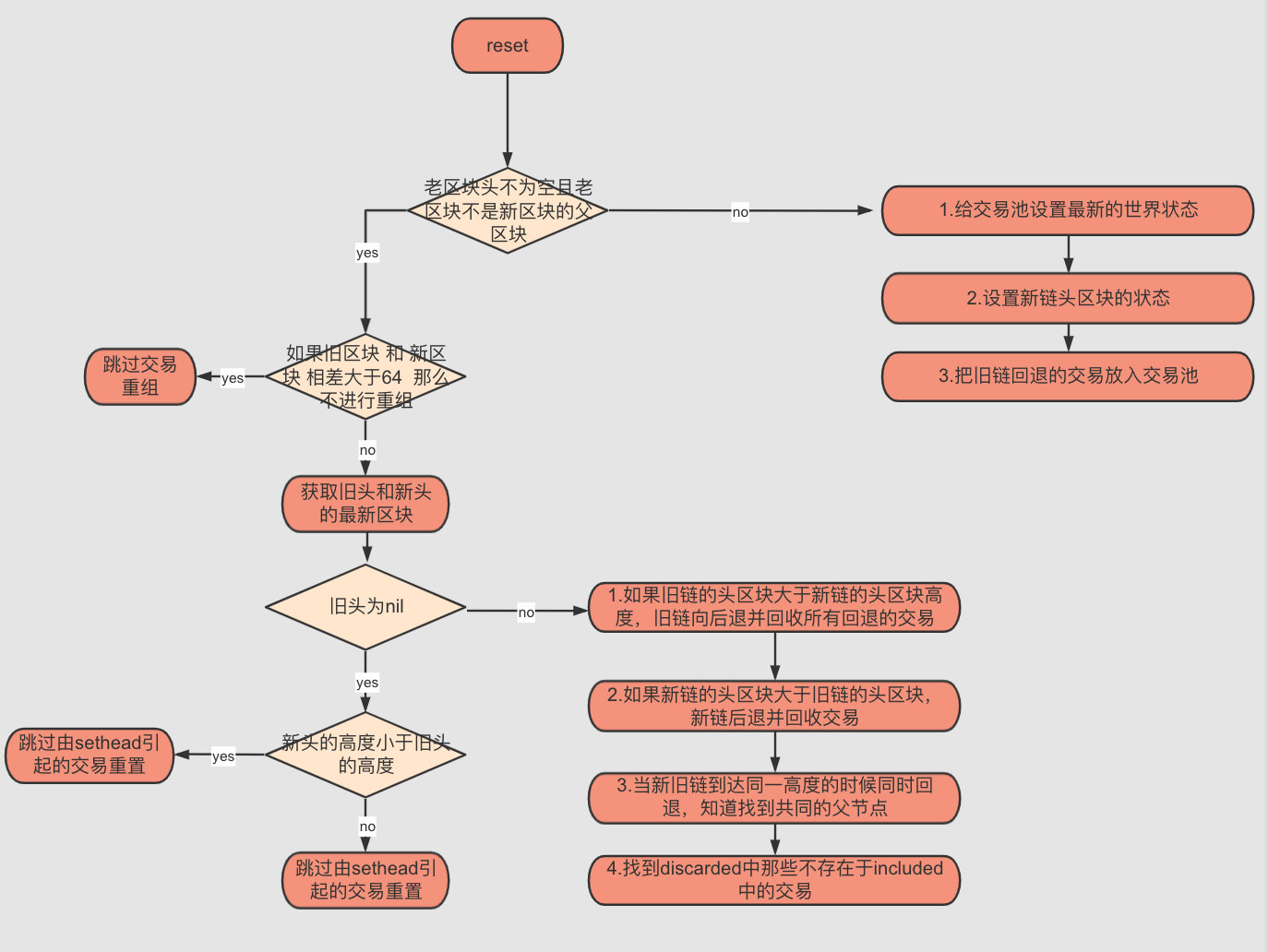
根據上面流程圖,主要功能是由於規範鏈的更新,重新整理交易池:
- 找到由於規範鏈更新而作廢的交易
- 給交易池設定最新的世界狀態
- 把舊鏈退回的交易重新放入交易池
參考:
https://github.com/mindcarver/blockchain_guide (很優秀的區塊鏈開源學習營地)
https://learnblockchain.cn/2019/06/03/eth-txpool/#%E6%B8%85%E7%90%86%E4%BA%A4%E6%98%93%E6%B1%A0
https://blog.csdn.net/lj900911/article/details/84825739