JAVA基礎——Map集合,Map集合特點,根據鍵找值,尋找鍵和值,HashMap,TreeMap,LinkedHashMap的基本功能,hashtable與hashMap區別
2020-10-14 13:00:24
一、 Map集合概述和特點
- Map介面概述
- 將鍵對映到值的物件
- 一個對映不能包含重複的鍵
- 每個鍵最多隻能對映到一個值
- Map介面和Collection介面的不同
- Map是雙列的,Collection是單列的
- Map的鍵唯一,Collection的子體系Set是唯一的
- Map集合的資料結構(TreeMap,hashMap)值針對鍵有效,跟值無關;Collection集合的資料結構是針對元素有效
二、 Map集合的功能概述
1. 新增功能
V put(K key,V value):新增元素。- 如果鍵是第一次儲存,就直接儲存元素,返回null
- 如果鍵不是第一次存在,就用值把以前的值替換掉,返回以前的值
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
//put的返回值是根據後面的值的型別相同
Integer i1= map.put("張三", 13);
Integer i2= map.put("李四", 15);
Integer i3= map.put("王五", 14);
Integer i4= map.put("趙六", 16);
Integer i5= map.put("張三", 16);
//因為map集合種相同的鍵不儲存,值覆蓋,把被覆蓋的值返回
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println(i3);
System.out.println(i4);
System.out.println(i5);
效果如下:

2. 刪除功能
void clear():移除所有的鍵值對元素V remove(Object key):根據鍵刪除鍵值對元素,並把值返回
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("張三", 13);
map.put("李四", 15);
map.put("王五", 14);
map.put("趙六", 16);
//根據鍵刪除元素,返回鍵對應的值
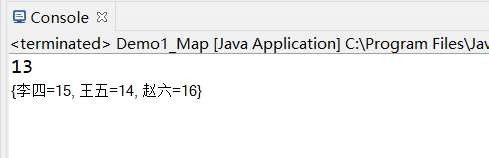
Integer value =map.remove("張三");
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(map);
效果如下:
3. 判斷功能
boolean containsKey(Object key):判斷集合是否包含指定的鍵boolean containsValue(Object value):判斷集合是否包含指定的值boolean isEmpty():判斷集合是否為空
System.out.println(map.containsKey("張三"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(100));
返回值 一個true。一個false
4. 獲取功能
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():V get(Object key):根據鍵獲取值Set<K> keySet():獲取集合中所有鍵的集合Collection<V> values():獲取集合中所有值的集合
前三個看後面的遍歷。這裡介紹最後一個
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("張三", 13);
map.put("李四", 15);
map.put("王五", 14);
map.put("趙六", 16);
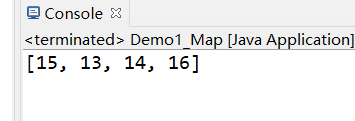
Collection<Integer>collection =map.values();
System.out.println(collection);
效果如下:
5. 長度功能
int size():返回集合中的鍵值對的個數
System.out.println(map.size());
三、 Map集合的遍歷之鍵找值
主要介紹map的獲取功能
鍵找值思路:
- 獲取所有鍵的集合
- 遍歷鍵的集合,獲取到每一個鍵
- 根據鍵找值
方式一:使用迭代器遍歷,
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("張三", 13);
map.put("李四", 15);
map.put("王五", 14);
map.put("趙六", 16);
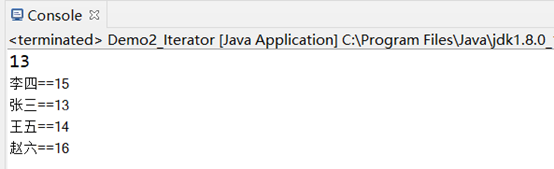
Integer i =map.get("張三"); //根據鍵獲取值
System.out.println(i);
Set<String> keySet =map.keySet(); //獲取所有鍵的集合
Iterator<String> it =keySet.iterator();//獲取迭代器
while (it.hasNext()) {
//判斷集合中是否有元素
String key = (String) it.next(); //獲取每一個鍵
Integer value =map.get(key); //根據鍵獲取值
System.out.println(key+"=="+value);
}
方式二:foreach迴圈
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("張三", 13);
map.put("李四", 15);
map.put("王五", 14);
map.put("趙六", 16);
for (String key : map.keySet()) { //map.keySet()是所有鍵的集合
System.out.println(key+"=="+map.get(key));
}
}
效果均相同:
四、 Map集合的遍歷之鍵值對物件找鍵和值
鍵值對物件找鍵和值思路:
- 獲取所有鍵值對物件的集合
- 遍歷鍵值對物件的集合,獲取到每一個鍵值對物件
- 根據鍵值對物件找鍵和值
先解釋Map.Entry<K,V>是什麼意思
interface Inter{
interface Inter2{
public void show();
}
}
//想要實現Inter2介面需要使用Inter.Inter2
class Demo implements Inter.Inter2{
@Override
public void show() {
}
}
同理:Entry是map下的一個子介面
方式一:根據迭代器查詢
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("張三", 13);
map.put("李四", 15);
map.put("王五", 14);
map.put("趙六", 16);
//Map.Entry說明Entry是Map的內部介面,將鍵和值封裝成了Entry物件,並儲存在Set集合中
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>entrySet =map.entrySet();
//獲取每一個物件
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = entrySet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
//獲取每一個Entry物件
Map.Entry<String, Integer> en =it.next();//父類別參照指向子類物件
// Entry<String ,Integer> en=it.next; //直接獲取的是子類物件。Entry是map.Entry的子介面
//以上兩種方式均可
String key =en.getKey();
//根據鍵值對物件獲取鍵
Integer value =en.getValue();
//根據鍵值對物件獲取值
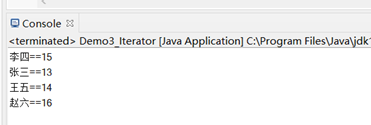
System.out.println(key+"==="+value);
}
}
方式二:foreach迴圈遍歷
Map<String, Integer> map =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("張三", 13);
map.put("李四", 15);
map.put("王五", 14);
map.put("趙六", 16);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> en : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(en.getKey()+"=="+en.getValue());
}
效果如下兩者均相同:
五、 HashMap集合鍵是Student值是String的案例
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}
注意該處我們重寫了hashCode方法和equals方法。所以當我們的姓名和年齡相同的時候視為同一物件。會對其進行覆蓋。
測試類:
//鍵表示字串物件,值代表歸屬地
HashMap<Student, String > hm =new HashMap<Student, String>();
hm.put(new Student("張三",12), "安徽");
hm.put(new Student("張三",12), "上海");
hm.put(new Student("王五",11), "廣州");
hm.put(new Student("趙六",14), "深圳");
System.out.println(hm);
效果如下:

六、 LinkedHashMap的概述和使用
LinkedHashMap的特點
* 底層是連結串列實現的可以保證怎麼存就怎麼取
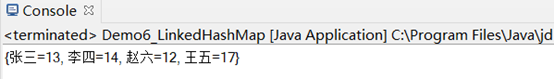
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> lhm =new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
lhm.put("張三",13);
lhm.put("李四",14);
lhm.put("趙六",12);
lhm.put("王五",17);
System.out.println(lhm);
效果如下:
七、 TreeMap集合鍵是Student值是String的案例
TreeMap<Student, String> tm =new TreeMap<Student, String>();
tm.put(new Student("張三", 13),"安徽");
tm.put(new Student("李四", 12),"安徽");
tm.put(new Student("王五", 14),"安徽");
tm.put(new Student("趙六", 15),"安徽");
System.out.println(tm);
此時我們應當重寫Comparable介面。我們按照年齡進行排序
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
int num =this.age -o.age;
return num==0? this.name.compareTo(o.name):num;
}
效果如下:

如果我們採用呼叫比較器Compartor
TreeMap<Student, String> tm =new TreeMap<Student, String>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
int num =s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
return num ==0?s1.getAge()-s2.getAge():num;
}
});
tm.put(new Student("張三", 13),"安徽");
tm.put(new Student("李四", 12),"安徽");
tm.put(new Student("王五", 14),"安徽");
tm.put(new Student("趙六", 15),"安徽");
效果如下:

八、 練習比如:aaabbbbcccc。計算a出現次數b出現次數。
分析:
- 定義一個需要被統計字元的字串
- 將字串轉換為字元陣列
- 定義雙列集合,儲存字串中字元以及字元出現的次數
- 遍歷字元陣列獲取每一個字元並將字元儲存在雙列集合中
- 儲存過程中要做判斷,如果集合中不包含這個鍵,就將該字元當作鍵,值為1儲存如果集合中包含這個鍵,就將值+1儲存
- 列印雙列集合,獲取字元出現的次數:統計字串中每個字元出現的次數
public class Demo1_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1,定義一個需要被統計字元的字串
String s="aaaabbbbccccc";
//2.將字串轉換為字元陣列
char[] arr =s.toCharArray();
//定義雙列集合儲存字串中字元以及字元出現的次數。HashMap效率最高
HashMap<Character, Integer> hm =new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
//遍歷字元陣列獲取每一個字元,並將字元儲存在雙列集合中
for (char c : arr) {
//
//if (!hm.containsKey(c)) {
// hm.put(c, 1);
//}else {
// hm.put(c,hm.get(c)+1);
//}
hm.put(c,!hm.containsKey(c)?1:hm.get(c)+1);
}
for (Character key : hm.keySet()) {
//hm.keySet代表所有鍵的集合
System.out.println(key+"="+hm.get(key));
//根據鍵獲取值
}
}
}
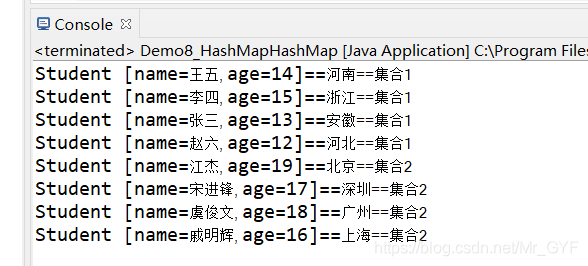
九、 集合巢狀之HashMap巢狀HashMap
//定義第一個集合
HashMap<Student, String> hm1 =new HashMap<Student, String>();
hm1.put(new Student("張三", 13),"安徽");
hm1.put(new Student("李四", 15),"浙江");
hm1.put(new Student("王五", 14),"河南");
hm1.put(new Student("趙六", 12),"河北");
//定義第二個集合
HashMap<Student, String> hm2 =new HashMap<Student, String>();
hm2.put(new Student("戚明輝", 16),"上海");
hm2.put(new Student("江傑", 19),"北京");
hm2.put(new Student("虞俊文", 18),"廣州");
hm2.put(new Student("宋進鋒", 17),"深圳");
//定義一個總的集合
HashMap<HashMap<Student, String>, String> hm3 =new HashMap<HashMap<Student,String>, String>();
hm3.put(hm1, "集合1");
hm3.put(hm2, "集合2");
//遍歷雙列集合
for (HashMap<Student, String> h : hm3.keySet()) { //hm3.keySet()代表的是雙列集合中鍵的集合
String value =hm3.get(h); //get(h)根據鍵物件獲取值物件
//遍歷鍵的雙列集合物件
for (Student key : h.keySet()) {//h.keySet獲取集合中所有的學生鍵物件
String value2=h.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"=="+value2+"=="+value);
}
}
效果如下:
十、 HashMap和Hashtable的區別
- Hashtable是JDK1.0版本出現的,是執行緒安全的,效率低,HashMap是JDK1.2版本出現的,是執行緒不安全的,效率高
- Hashtable不可以儲存null鍵和null值,HashMap可以儲存null鍵和null值
共同點:底層都是雜湊演演算法,都是雙列集合
HashMap<String, Integer> hm =new HashMap<String, Integer>();
hm.put(null, 23);
hm.put("李四", 24);
System.out.println(hm);
Hashtable<String, Integer> ht =new Hashtable<String, Integer>();
ht.put(null, 23);
ht.put("張三",null);
System.out.println(ht);
輸出效果:map不報錯,可以儲存null。但是table會報錯。
十一、 Collections工具類的概述和常見方法講解
當一個類中所有的方法都是靜態的,那麼它會私有自己的構造方法
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list)
自動排序
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?> list,T key)
二分法查詢
public static <T> T max(Collection<?> coll)
獲取最大值
public static void reverse(List<?> list)
將集合反轉
public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
將集合隨機置換。類似於洗牌
案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
demo1();
demo2();
demo3();
demo4();
demo5();
}
public static void demo5() {
List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("f");
list.add("g");
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println("demo5測試結果:");
Collections.shuffle(list); //隨機置換
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void demo4() {
List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("f");
list.add("g");
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println("demo4測試結果:");
Collections.reverse(list); //反轉集合
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void demo3() {
List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("f");
list.add("g");
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println("demo3測試結果:");
System.out.println(Collections.max(list)); //根據預設排序結果獲取集合中的最大值
}
public static void demo2() {
List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("f");
list.add("g");
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println("demo2測試結果:");
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list, "c"));
//如果搜尋鍵包含在列表中,則返回搜尋鍵的索引;否則返回(-(插入點)-1)
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list, "b"));
}
public static void demo1() {
List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("c");
list.add("a");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("d");
Collections.sort(list); //將集合排序
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println("demo1測試結果:");
System.out.println(list);
}
效果如下:
