2020藍橋杯B 組省賽計蒜客模擬賽(一)題解
2020藍橋杯省賽 B 組計蒜客模擬賽(一)目錄
試題 A:有趣的數位(結果填空)
題意:點此進入
蒜頭君要爬樓梯。樓梯一共有 1010 層臺階。因為腿長的限制,每次最多能上 44 層臺階。但是第 5,75,7 層樓梯壞掉了不能踩。求上樓梯的方案數。
做法:用篩法把素數篩出來再判斷數位中含不含5。
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
int a[N];
int check(int x) {
while(x) {
if(x % 10 == 5) return 1;
x /= 10;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
for(int i = 2; i*i < N; ++i) {
if(!a[i]) {
for(int j = i+i; j < N; j += i) a[j] = 1;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 5; i <= 100000; ++i) {
if(!a[i] && check(i)) cout << i << " ", ++ans;
}
cout << endl << ans;
return 0;
}
答案:3282
試題 B:爬樓梯(結果填空)
題意:點此進入
蒜頭君要爬樓梯。樓梯一共有 1010 層臺階。因為腿長的限制,每次最多能上 44 層臺階。但是第 5,75,7 層樓梯壞掉了不能踩。求上樓梯的方案數。
做法:從i-4~i-1狀態轉移過來。
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
int dp[20];
int main() {
dp[0] = 1;
_rep(1, 10, i) {
if(i == 5 || i == 7) continue;
_rep(max(i-4, 0), i-1, j) {
dp[i] += dp[j];
}
}
cout << dp[10];
return 0;
}
答案:72
試題 C:七巧板(結果填空)
題意:點此進入

做法:會發現加一根直線是多了6個區域,加兩根直線是多了7個區域,所以就是 7(+6+7+8+9+10)。
答案:47
試題 D:蘋果(結果填空)
題意:點此進入
有 30 個籃子,每個籃子裡有若干個蘋果,籃子裡的蘋果數序列已經給出。
現在要把蘋果分給小朋友們,每個小朋友要麼從一個籃子裡拿三個蘋果,要麼從相鄰的三個籃子裡各拿一個蘋果。
蘋果可以剩餘,而且不同的拿法會導致不同的答案。比如對於序列3 1 3 ,可以分給兩個小朋友變成0 1 0;也可以分給一個小朋友變成2 0 2,此時不能繼續再分了。所以答案是 2 。
求問對於以下序列,最多分給幾個小朋友?
7 2 12 5 9 9 8 10 7 10 5 4 5 8 4 4 10 11 3 8 7 8 3 2 1 6 3 9 7 1
做法:這題一開始WA了很多次,我一開始試過先優先相鄰三個取完,再來單個單個的取,發現這樣是59,WA,然後換了一種方式,先單個單個取,再相鄰三個取,這樣57,WA,正解是對於每個單個單個取完就考慮三個相鄰的,這樣結果是62,三者取最大,但我也想不到這最後一種啊 ,更正確的做法應該是dp把,可惜我不會 。
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
int a[32] = {0, 7, 2, 12, 5, 9, 9, 8, 10, 7, 10, 5, 4, 5, 8, 4, 4, 10, 11, 3, 8, 7,8,3,2,1,6,3,9,7,1};
int main() {
int ans = 0;
_rep(1, 30, i) {
ans += a[i] / 3, a[i] %= 3;
if(a[i] && a[i+1] && a[i+2]) {
int mid = min(a[i], min(a[i+1], a[i+2]));
ans += mid; a[i+2] -= mid; a[i+1] -= mid; a[i] -= mid;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
答案:62
試題 E:方陣(結果填空)
題意:點此進入

做法:這題也是做不出來系列 ,想過找規律,但是沒找出來,如果兩點能夠看見一定是基於橫座標之差與縱座標之差的gcd是1,設橫座標之差是x,縱座標之差是y:
- x為0或者y為0,是2 * n * (n-1)對,這就是k=1的時候啦。
- x,y不為0且最大公約數是1,是2 * (n - x) * ( n - y) 對
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
LL f[N];
int main() {
int n = 1000, k = 500;
LL ans = 2 * n * (n-1) % Mod;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
if(__gcd(i, j) == 1 && i*i+j*j <= k*k) {
ans = (ans + 2*(n-i)%Mod*(n-j)%Mod) % Mod;
}
}
}
cout << ans % Mod << endl;
return 0;
}
答案:916585708
試題 F:尋找重複項(程式設計)
題意:點此進入

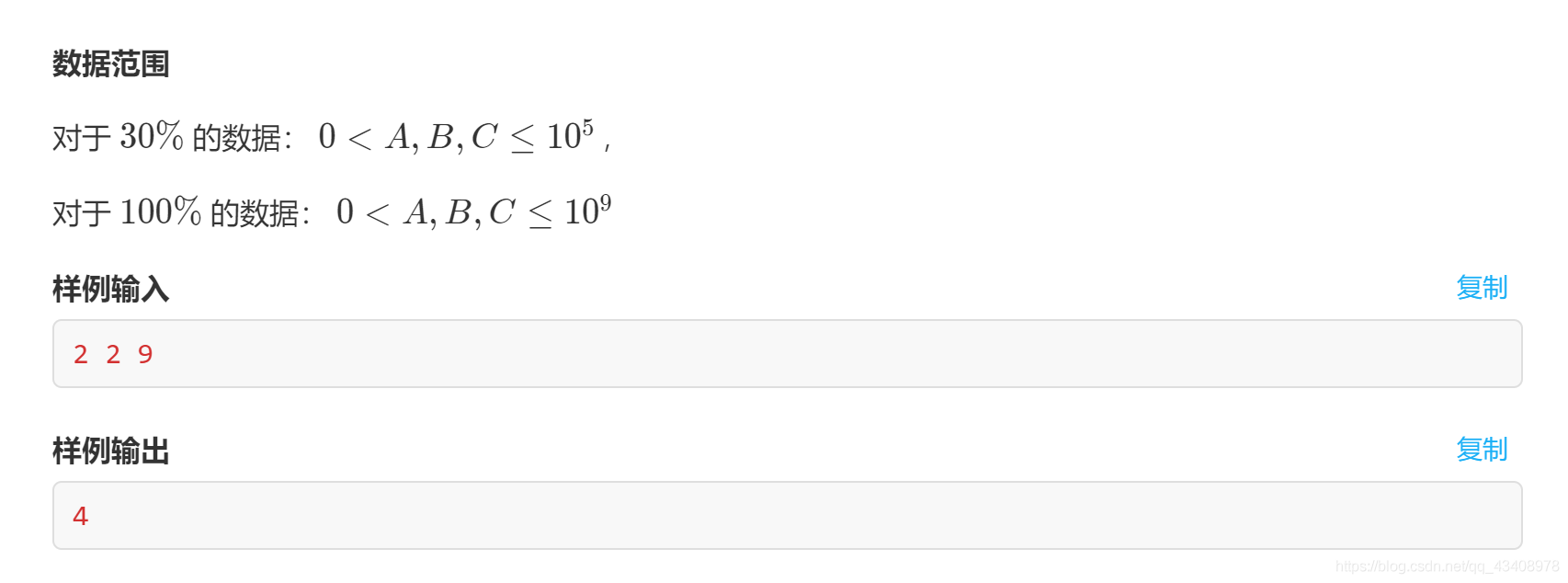
做法:用map記錄,存取到就值+1
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e6+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
LL f[N], a, b, c;
map<LL, int> mp;
int main() {
f[0] = 1;
++mp[1];
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &a, &b, &c);
int flag = 0;
_rep(1, 2000000, i) {
f[i] = (a*f[i-1]%c + f[i-1]%b)%c;
if(mp[f[i]]) { flag = i; break; }
++mp[f[i]];
}
if(!flag) puts("-1");
else printf("%d\n", flag);
return 0;
}
試題 G:被襲擊的村莊(程式設計)
題意:點此進入



做法:這就是一道卡了我一下午的模擬題,水逆的一天,這題不難,就是題目錯了…輸出的是道路、房屋、田地耐久度降為0的個數。直接模擬就好了,我是少考慮的一個邊界情況以及老眼昏花沒看見自己判斷結果的迴圈放到while迴圈裡了。
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 310;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
LL n, m;
LL a, b, c; //三種耐久度
LL k; //炮彈攻擊範圍k*k
LL w; //濺射傷害
LL q; //q枚炮彈
LL id, x, y; //炮彈編號,及中心位置
LL sh[N][N]; //炮彈傷害
LL ans;
LL num1, num2, num3;
LL num[N][N];
LL bx, by, ex, ey;
LL hp[N][N];
void caljs(int x, int y) { //濺射傷害
int tx, ty;
for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
tx = x + ne[i][0]; ty = y + ne[i][1];
if(tx < 1 || ty < 1 || tx > n || ty > m) continue;
hp[tx][ty] = max(0ll, hp[tx][ty] - w);
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld", &n, &m, &a, &b, &c, &k, &w);
_rep(1, k, i) _rep(1, k, j) scanf("%lld", &sh[i][j]);
_rep(1, n, i) _rep(1, m, j) {
scanf("%lld", &num[i][j]);
if(num[i][j] == 1) hp[i][j] = a;
else if(num[i][j] == 2) hp[i][j] = b;
else hp[i][j] = c;
}
scanf("%lld", &q);
while(q--) {
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &id, &x, &y);
bx = x - k/2, by = y - k/2; //炸彈範圍的起始座標
ex = x + k/2, ey = y + k/2; //炸彈範圍的終止座標
for(int i = bx, ii = 1; i <= ex, ii <= k; ++i, ++ii)
for(int j = by, jj = 1; j <= ey, jj <= k; ++j, ++jj) {
if(i < 1 || j < 1 || i > n || j > m) continue;
if(!id) caljs(i, j); hp[i][j] = max(0ll, hp[i][j]-sh[ii][jj]);
}
}
_rep(1, n, i) _rep(1, m, j) {
if(num[i][j] == 1) {
if(!hp[i][j]) ++num1;
ans += a-hp[i][j];
} else if(num[i][j] == 2) {
if(!hp[i][j]) ++num2;
ans += b-hp[i][j];
} else {
if(!hp[i][j]) ++num3;
ans += c-hp[i][j];
}
}
printf("%lld %lld %lld\n%lld", num1, num2, num3, ans);
return 0;
}
試題 H:字串(程式設計)
題意:點此進入

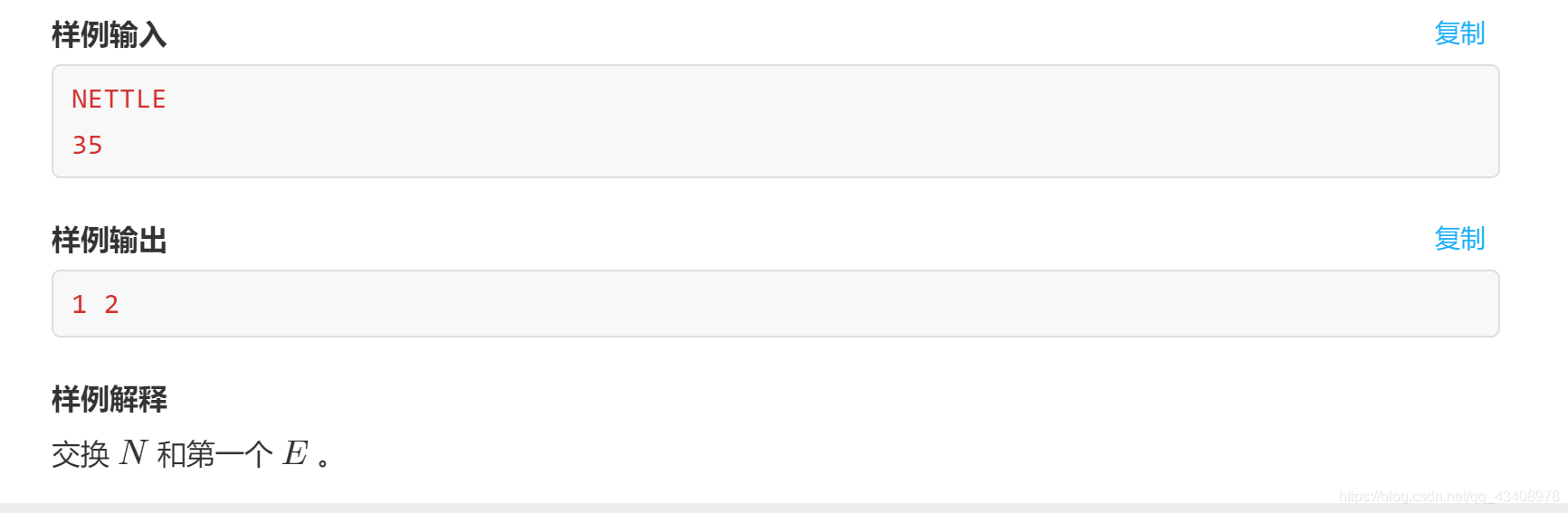
做法:這一題明顯比上一題簡單…直接暴力判斷就好了,注意下處理的技巧以防超時。
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2010;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 3e5+10;
string s, res;
LL a[N];
int main() {
int m;
cin >> s >> m;
int n = s.size();
LL mid = 0, mid1, mid2;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) mid = (mid * 26 + s[i]-'A') % m;
a[n-1] = 1;
for(int i = n-2; i >= 0; --i) a[i] = a[i+1] * 26 % m;
if(!mid) { puts("0 0"); return 0; }
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = i+1; j < n; ++j) {
mid1 = (s[i]-s[j]) * a[j];
mid2 = (s[j]-s[i]) * a[i];
if((mid+mid1+mid2+m)%m == 0) {
printf("%d %d\n", i+1, j+1); return 0;
}
}
}
puts("-1 -1");
return 0;
}
試題 I:最短路(程式設計)
題意:點此進入


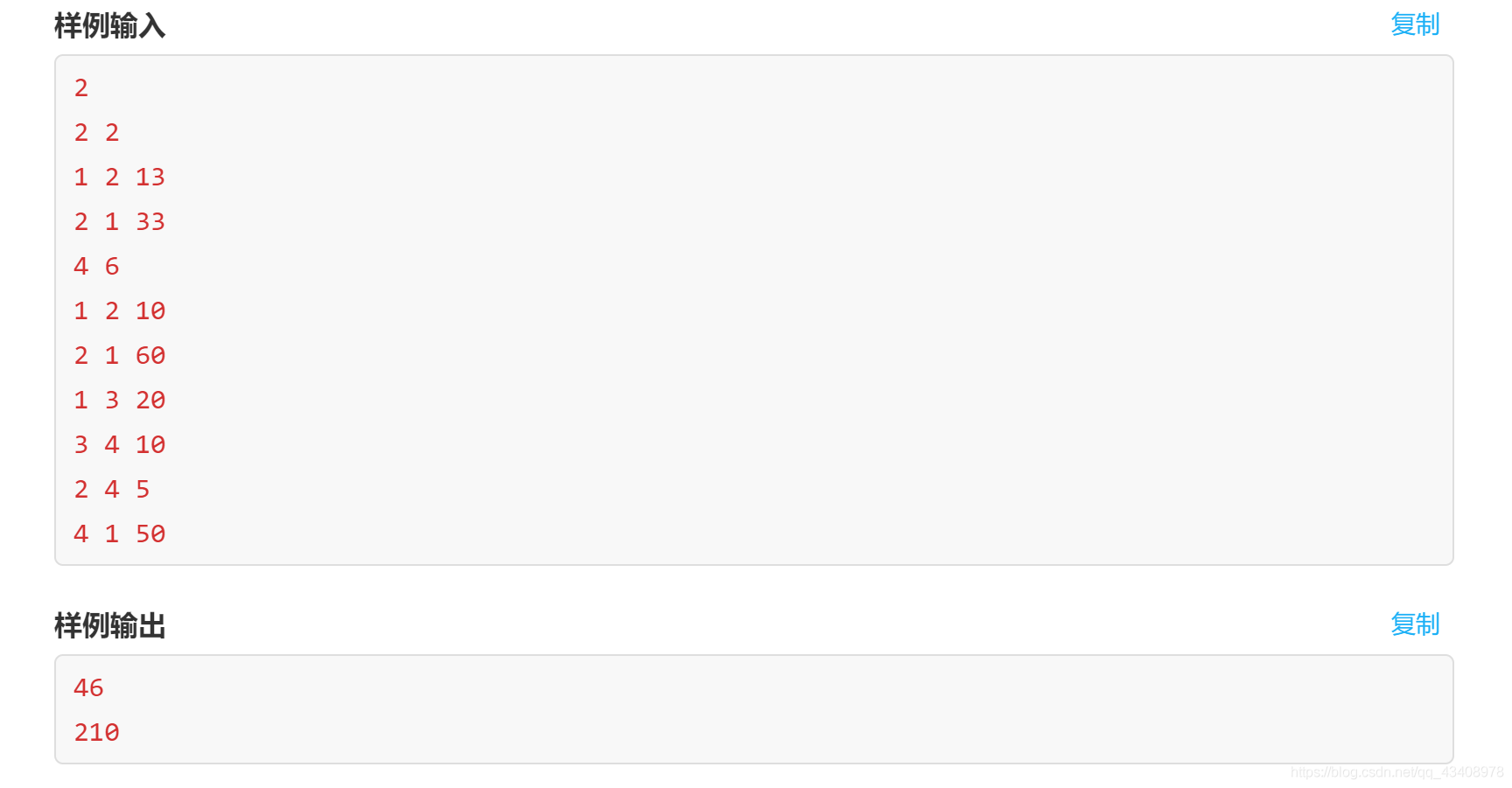
做法:正向建圖跑一遍再反向建圖跑一遍最短路就好了,最後把兩次dis的和全加起來。
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include<bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const LL INF = 1e18;
const int N = 2e4+10;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 2e5+10;
struct edge {
int u, v; LL w;
}ed[M];
struct xx {
int nxt, to; LL w;
xx() {}
xx(int a, int b, LL c) {
nxt = a; to = b; w = c;
}
}e[M];
int tot, head[N];
void Add(int u, int v, LL w) {
e[++tot] = xx(head[u], v, w);
head[u] = tot;
}
LL dis[N]; int vis[N];
priority_queue<pli, vector<pli>, greater<pli> >pq;
int n, m;
void dij() {
_rep(1, n, i) dis[i] = INF, vis[i] = 0;
dis[1] = 0;
while(!pq.empty()) pq.pop();
pq.push(make_pair(0ll, 1));
int u, v;
while(!pq.empty()) {
u = pq.top().second; pq.pop();
if(vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = 1;
for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt) {
v = e[i].to;
if(dis[v] > dis[u] + e[i].w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + e[i].w;
pq.push(make_pair(dis[v], v));
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int T; scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
memset(head, 0, sizeof head); tot = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
_for(0, m, i) {
scanf("%d%d%lld", &ed[i].u, &ed[i].v, &ed[i].w);
Add(ed[i].u, ed[i].v, ed[i].w);
}
LL ans = 0;
dij(); _rep(2, n, i) ans += dis[i];
memset(head, 0, sizeof head); tot = 0;
_for(0, m, i) Add(ed[i].v, ed[i].u, ed[i].w);
dij(); _rep(2, n, i) ans += dis[i];
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
試題 J:迷宮(程式設計)
題意:點此進入


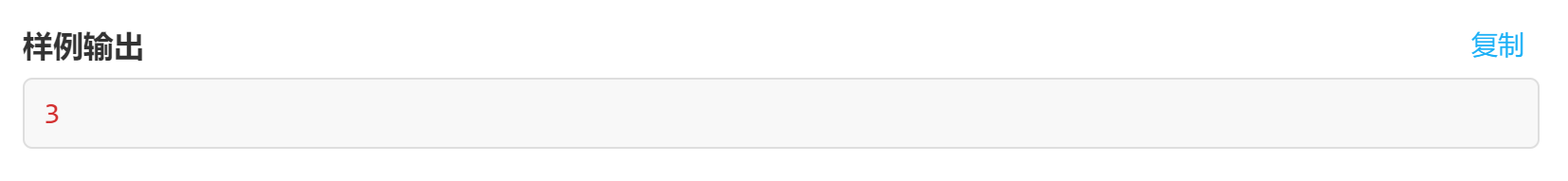
做法:bfs搜尋題,乍看一眼很簡單,實際上有點坑。
- 迴圈跳傳送門
- 迴圈跳過程中有障礙
- 迴圈跳過程中經過了終點
- 迴圈跳過程中經過了起點
- 起點就是終點
- 起點或終點就是障礙物
程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <bitset>
#define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define _for(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i < (m); ++i)
#define _rep(n,m,i) for (register int i = (n); i <= (m); ++i)
#define lson rt<<1, l, mid
#define rson rt<<1|1, mid+1, r
#define PI acos(-1)
#define eps 1e-9
#define rint register int
#define F(x) ((x)/3+((x)%3==1?0:tb))
#define G(x) ((x)<tb?(x)*3+1:((x)-tb)*3+2)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, int> pdi;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pll;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef map<int, int> mii;
typedef map<LL, int> mli;
typedef map<char, int> mci;
typedef map<string, int> msi;
template<class T>
void read(T &res) {
int f = 1; res = 0;
char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') { if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { res = res * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
res *= f;
}
const int ne[8][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1};
const LL INF = 1e18;
const int N = 1010;
const LL Mod = 1e9+7;
const int M = 110;
int n, m, Q, mid;
char tu[N][N];
int door[N][N], vis[N][N];
pii d[M];
int ex, ey;
struct xx {
int x, y, step;
}u;
queue<xx> q;
int check(int tx, int ty) {
if(tx < 1 || ty < 1 || tx > n || ty > m ) return 0;
if(vis[tx][ty] || tu[tx][ty] != '.') return 0;
return 1;
}
int bfs() {
int tx = 1, ty = 1;
while(door[tx][ty] && !vis[tx][ty] && tu[tx][ty] == '.') {
if(tx == ex && ty == ey) return 0;
mid = door[tx][ty];
vis[tx][ty] = 1; tx = d[mid].first, ty = d[mid].second;
if(tx == ex && ty == ey) return 0;
}
if(!check(tx, ty)) return -1;
q.push(xx{tx, ty, 0}); vis[tx][ty] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
u = q.front(); q.pop();
if(u.x == ex && u.y == ey) return u.step;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
tx = u.x + ne[i][0], ty = u.y + ne[i][1];
if(!check(tx, ty)) continue;
while(door[tx][ty] && !vis[tx][ty] && tu[tx][ty] == '.') {
if(tx == ex && ty == ey) return u.step+1;
mid = door[tx][ty];
vis[tx][ty] = 1; tx = d[mid].first, ty = d[mid].second;
if(tx == ex && ty == ey) return u.step+1;
}
if(!check(tx, ty)) continue;
vis[tx][ty] = 1; q.push(xx{tx, ty, u.step+1});
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
_rep(1, n, i) scanf("%s", tu[i]+1);
scanf("%d", &Q);
int x, y;
_rep(1, Q, i) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x, &y, &d[i].first, &d[i].second);
door[x][y] = i;
}
scanf("%d%d", &ex, &ey);
int res = bfs();
if(res == -1) puts("No solution");
else printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
/*
3 4
..*.
..*.
..*.
3
2 2 2 4
2 4 3 1
3 1 1 4
1 4
*/