【C++21天養成計劃】STL演演算法超全整理!(Day18)
大家好!我是【AI 菌】,一枚不熬夜的程式設計師。我
熱愛AI、熱愛分享、熱愛開源! 這部落格是我對學習的一點總結與思考。如果您也對深度學習、機器視覺、演演算法、Python、C++感興趣,可以關注我的動態,我們一起學習,一起進步~
我的部落格地址為:【AI 菌】的部落格
我的Github專案地址是:【AI 菌】的Github
一、什麼是STL演演算法
所謂STL,就是標準模板庫。標準模板庫為我們提供了易於使用的容器,比如我們前面已經學習過的 list、stack、queue、vector、string、set 和 map 類都屬於STL。
STL 還為我們提供了一部分易於使用的通用函數,這些函數位於標頭檔案 < a l g o r i t h m > <algorithm> <algorithm>中,它和容器類的成員函數一樣,能高效地幫助我們操作容器中的內容。

在程式設計過程中,經常會用法查詢、搜尋、刪除和計數等演演算法。C++中,STL通過通用的模板函數提供了這些演演算法和其他的很多演演算法,可通過迭代器對容器進行操作。這些通用的模板函數就是所說的STL演演算法。在使用STL演演算法之前,必須在程式開頭加上標頭檔案:
#include <algorithm>
二、常用的STL演演算法彙總
STL演演算法可以分為兩大類:非變序演演算法和變序演演算法。
2.1 非變序演演算法
所謂非變序演演算法就是:不改變容器中元素的順序和內容的演演算法。
下面總結一些常用的非變序演演算法:
(1) 計數演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| count | 在指定範圍內,查詢值與指定值匹配的所有元素 |
| count_if | 在指定範圍內,查詢值滿足指定條件的所有元素 |
(2) 搜尋演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| search | 在目標範圍內,根據元素相等性(或指定二元謂詞)搜尋第一個滿足條件的元素 |
| search_n | 在目標範圍內,搜尋與指定值相等或滿足指定謂詞的n個元素 |
| find | 在給定範圍內,搜尋與指定值匹配的第一個元素 |
| find_if | 在給定範圍內,搜尋滿足指定條件的第一個元素 |
| find_end | 在指定範圍內,搜尋最後一個滿足特定條件的元素 |
| find_first_of | 在目標範圍內,搜尋指定序列中的任何一個元素第一次出現的位置;在另一個過載版本中,它搜尋滿足指定條件的第一個元素 |
| adjacent_find | 在集合中搜尋兩個相等或滿足指定條件的元素 |
(3) 比較演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| equal | 比較兩個元素是否相等或使用指定的二元謂詞判斷連兩者是否相等 |
| mismatch | 使用指定的二元謂詞找出兩個元素範圍的第一個不同的地方 |
2.2 變序演演算法
變序演演算法改變其操作的序列的元素或者內容,下面我將列出一些最常用的變序演演算法:
(1) 初始化演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| fill | 將指定值分配給,指定範圍中的每個元素 |
| fill_n | 將指定值分配給,指定範圍中的前n個每個元素 |
(2) 修改演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| for_each | 對指定範圍內的每個元素,執行指定的操作 |
| transform | 對指定範圍內的每個元素,執行指定的一元函數 |
(3) 複製演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| copy | 將一個範圍複製到另一個範圍 |
| copy_backward | 將一個範圍複製到另一個範圍,但在目標範圍中將元素的排列順序反轉 |
(4) 刪除演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| remove | 將指定範圍中包含指定的值刪除 |
| remove_if | 將指定範圍中滿足指定一元謂詞的元素刪除 |
| remove_copy | 將源範圍中除包含指定值外的所有元素複製到目標範圍 |
| remove_copy_if | 將源範圍中除滿足指定一元謂詞外的所有元素複製到目標範圍 |
| unique | 比較指定範圍內的相鄰元素,並刪除重複的元素 |
| unique_copy | 將源範圍內的所有元素複製到目標範圍,但相鄰的重複元素除外 |
(5) 替換演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| replace | 用一個值來替換指定範圍中與指定值匹配的所有元素 |
| replace_if | 用一個值來替換指定範圍中滿足指定條件的所有元素 |
(6) 排序演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| sort | 使用指定的排序標準,對指定範圍內的元素進行排序,排序標準由二元謂詞提供 |
| stable_sort | 類似於sort,但在排序時保持相對順序不變 |
| partial_sort | 將源範圍內指定數量的元素排序 |
| partial_sort_copy | 將源範圍內的元素複製到目標範圍,同時對它們進行排序 |
(7) 分割區演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| partition | 在指定範圍內,將元素分為兩組:滿足指定一元謂詞的元素放在第一個組中,其他元素放在第二個組中。不一定會保持集合中元素的相對位順序 |
| stable_partition | 與partition一樣,將指定範圍分為兩組,但保持元素的相對順序不變 |
(8) 可用於排序容器的演演算法
| 演演算法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| binary_search | 用於判斷一個元素是否存在於一個排序集合中 |
| lower_bound | 根據元素的值或二元謂詞判斷元素可能插入到排序集合中的第一個位置,並返回一個指向該位置的迭代器 |
| upper_bound | 根據元素的值或二元謂詞判斷元素可能插入到排序集合中的最後一個位置,並返回一個指向該位置的迭代器 |
三、STL 常用演演算法範例
3.1 根據值或條件查詢元素find()
find()可用於在vector等容器中查詢與值匹配的元素,用法如下:
auto iElement = find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), NumToFind);
// 判斷查詢是否成功
if(iElement != vec.end())
cout<<"Result:Value Found!"<<endl;
find_if()的用法與此類似,但需要通過第三個引數提供一個一元謂詞(返回true或false的一元函數),用法如下:
// 查詢偶數
auto iElement = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int element){return (element % 2)==0;});
// 判斷是否查詢成功
if(iElement != vec.end())
cout<<"Result:Value found!"<<endl;
下面我們就來實戰演練一下,使用find()在vector中查詢一個整數,並使用find_if()以及一個用lambda表示式表示的一元謂詞查詢第一個偶數:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//display vector
void Display(vector<int> vec)
{
for(int i=0; i<vec.size(); i++)
cout<<vec[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> vecIntegers;
for(int value = 0; value<10; ++value)
vecIntegers.push_back(value);
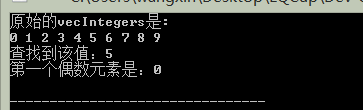
cout<<"原始的vecIntegers是:"<<endl;
Display(vecIntegers);
// 查詢vecIntegers中元素為5的值,返回迭代器的位置
auto iElement = find(vecIntegers.begin(),vecIntegers.end(),5);
if(iElement != vecIntegers.end())
cout<<"查詢到該值:"<<*iElement<<endl;
else
cout<<"沒有查詢到該值" <<endl;
// 查詢第一個偶數元素
auto iElement1 = find_if(vecIntegers.begin(), vecIntegers.end(), [](int element){return (element % 2)==0;});
if(iElement1 != vecIntegers.end())
cout<<"第一個偶數元素是:"<<*iElement1<<endl;
else
cout<<"沒有查詢到偶數元素" <<endl;
return 0;
}
執行結果:
3.2 計算包含給定值或滿足給定條件的元素數count()
count()和count_if()計算給定範圍內的元素數。find()計算包含給定值的元素值:
size_t nNumZero = count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0);
cout<<"陣列vec中值為0的個數:"<<nNumZero<<endl;
count_if()計算這樣的元素數,即滿足通過引數傳遞的一元謂詞(可以是函數物件,也可以是lambda表示式):
template <typename elementType>
// 判斷是否是偶數
bool IsEven(const elementType& number)
{
return((number % 2) == 0);
}
// 計算偶數的個數
size_t nNumEvenElements = count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), IsEven <int>);
cout<<"陣列vec中偶數的個數:"<<nNumEvenElements<<endl;
下面實戰演練一下,使用count()和count_if()分別計算有多少個元素包含指定值和滿足指定條件:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
template <typename elementType>
bool IsEven(const elementType& number)
{
return((number % 2) == 0);
}
void Display(vector<int> vec)
{
for(int i=0; i<vec.size(); i++)
cout<<vec[i]<<" ";
}
int main()
{
vector <int> vec;
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
vec.push_back(i);
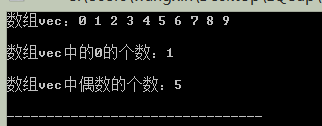
cout<<"陣列vec:";
Display(vec);
cout<<endl<<endl;
// 使用count()統計陣列中0的個數
size_t nNumZero = count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0);
cout<<"陣列vec中的0的個數:"<<nNumZero<<endl<<endl;
// 使用count_if()統計滿足偶數條件的值的個數
size_t nNumEvenElements = count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), IsEven <int>);
cout<<"陣列vec中偶數的個數:"<<nNumEvenElements<<endl;
return 0;
}
執行結果:
3.3 在集合中搜尋元素或序列search()
前面學習的find()可以在容器中查詢元素,但有時需要查詢一個序列或模式;在這種情況下,應該使用serach()和search_n()。
- search()用於在一個序列中查詢另一個序列,比如在陣列vec中查詢list序列的位置:
auto iRange = search(vec.begin(), vec.end(), list.begin(), list.end());
- search_n()用於在一個容器中查詢n個相鄰的指定值:
// 尋找999在陣列vec中出現的位置
auto iRange = search_n(vec,begin(), vec.end(), 3, 9)
這兩個函數都返回一個迭代器,它指向找到的第一個位置。使用該迭代器之前,務必將其與end()進行比較,下面將演示search()和search_n()的用法:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<<*i<<" ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
int main()
{
vector <int> vec;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
vec.push_back(i);
vec.push_back(9);
vec.push_back(9);
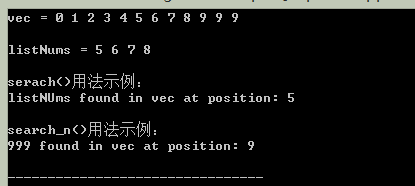
cout<<"vec = ";
Display(vec);
list <int> listNums;
for(int j=5; j<=8; ++j)
listNums.push_back(j);
cout<<"listNums = ";
Display(listNums);
cout<<"serach()用法範例:" <<endl;
auto iRange = search(vec.begin(), vec.end(), listNums.begin(), listNums.end());
if(iRange != vec.end())
cout<<"listNUms found in vec at position: "<<distance (vec.begin(), iRange)<<endl<<endl;
else
cout<<"vec中不存在這樣的listNums!"<<endl;
cout<<"search_n()用法範例:"<<endl;
auto iFound = search_n(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 3, 9);
if(iFound != vec.end())
cout<<"999 found in vec at position: "<<distance(vec.begin(), iFound)<<endl;
else
cout<<"999 isn't in vec!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
執行結果:
3.4 將容器中的元素初始化為指定值fill()
STL演演算法提供了兩個常用的函數來完成此任務:
- fill()將指定範圍內的元素設定為指定值
- fill_n()將n個元素設定為指定的值。接受的引數包括:起始位置、元素的個數以及設定的值。
下面就實戰演練一下,使用fill()和fill_n()設定容器中元素的初始值。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void Display(vector <int> vec)
{
for(int i=0; i<vec.size(); i++)
cout<<vec[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
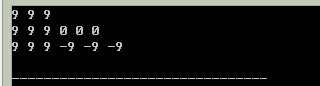
// 初始化長度為3的陣列
vector <int> vec(3);
// 用9填滿容器
fill(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 9);
Display(vec);
vec.resize(6);
Display(vec);
// 從第三個元素之後,填3個-9
fill_n(vec.begin()+3, 3, -9);
Display(vec);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
四、STL 進階演演算法範例
4.1 複製操作copy()
STL 主要提供了兩個重要的複製函數:copy() 和 copy_if()
- copy()沿向前的方向將源範圍的內容賦給目標範圍,返回的iPos是複製後,迭代器在vec中的位置:
auto iPos = copy(List.begin() // 複製源的起始位置
, List.end() // L複製源的最終位置
, vec.begin()); // 複製到vec的起始位置
- copy_if()僅在指定的一元謂詞返回true時才複製元素:
copy_if(List.begin() //複製源的起始位置
, List.end() //複製源的最終位置
, iPos; // 複製到指定容器的位置
, [](int i){return ((i % 2)==1);}); //一元謂詞,選取指定條件的元素執行復制操作
下面舉一個簡單的例子,來演示一下用法:
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<< *i << " ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
list <int> List;
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
List.push_back(i);
cout<<"List = ";
Display(List);
// 初始化陣列
vector <int> vec(20);
// 將List複製給vec,並返回複製後迭代器的位置
auto iPos = copy(List.begin(), List.end(), vec.begin());
// 將List中的奇數按順序複製到vec
copy_if(List.begin(), List.end(), iPos, [](int i){return ((i % 2)==1);});
cout<<"vec = ";
Display(vec);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
4.2 刪除操作erase()
STL 中也提供了兩個重要的刪除操作函數:remove() 和 remove_if()
- remove()將容器中與指定值匹配的元素刪除:
// 刪除vec中值為0的全部元素
auto iRemove = remove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0);
- remove_if()使用一個一元謂詞,並將容器中滿足該謂詞的元素刪除:
// 刪除vec中的所有奇數
iRemove = remove_if(vec,begin(), vec.end(), [](int i){return ((i % 2)==1);});
下面舉一個簡單的例子,來演示一下用法:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<< *i << " ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
vector <int> vec;
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
vec.push_back(i);
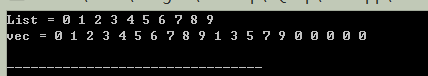
cout<<"vec = ";
Display(vec);
cout<<"刪除所有值為0的元素:"<<endl;
auto iRemove = remove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0);
vec.erase(iRemove, vec.end());
Display(vec);
cout<<"刪除所有的奇數:"<<endl;
iRemove = remove_if(vec.begin(),vec.end(),[](int i){return ((i % 2)==1);});
vec.erase(iRemove, vec.end());
Display(vec);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
4.3 替換操作replace()
STL 中也提供了兩個重要的替換操作函數:replace() 和 replace_if()
- replace()用於替換集合中等於指定值的元素:
// 將vec中的值為1的元素全部替代為2
replace(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 1, 2);
- replace_if()用於替換集合中滿足指定條件的元素:
// 將vec中的值為偶數的元素全部替代為0
replace_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int i){return ((i % 2)==0);}, 0);
下面舉一個簡單的例子,來演示一下用法:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void Display(vector<int> vec)
{
for(int i=0; i<vec.size(); ++i)
{
cout<<vec[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
vector <int> vec(10, 1);
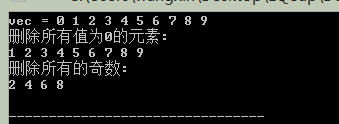
cout<<"vec =";
Display(vec);
cout<<"將vec中的值為1的元素全部替代為2:" <<endl;
replace(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 1, 2);
Display(vec);
cout<<"將vec中的值為偶數的元素全部替代為0:" <<endl;
replace_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int i){return ((i % 2)==0);}, 0);
Display(vec);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
4.4 排序操作sort()
為了方便對一組資訊進行排序,C++ STL演演算法專門提供了sort()函數。下面舉例幾種sort()的常用情況:
- 預設情況下,sort()進行升序排序,方法如下:
// 對vec中的元素進行升序排序
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
- 如果要改變預設的排序標註,需要專門指定謂詞;比如下面進行降序排序:
// 對vec中的元素進行降序排序
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a, int b){return(a>b);});
同樣,也可以用如下方式實現:
// 自定義降序排序謂詞
bool compare(int a, int b){
return a>b;
}
// 對vec中的元素進行降序排序
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), compare);
- 除了對整型陣列進行排序,也可以對字串進行排序。
bool compare(string s1, string s2){
return s1 > s2;
}
sort(arr_str.begin(), arr_str.end(), compare)
下面舉一個簡單的例子,來演示一下用法:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<< *i << " ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> vecNums;
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
vecNums.push_back(i);
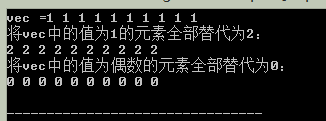
cout<<"vecNums = ";
Display(vecNums);
cout<<"降序排序:"<<endl;
sort(vecNums.begin(), vecNums.end(), [](int a, int b){return(a>b);});
Display(vecNums);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
下面演示一下,對字串陣列使用sort()的例子:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<< *i << endl;
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
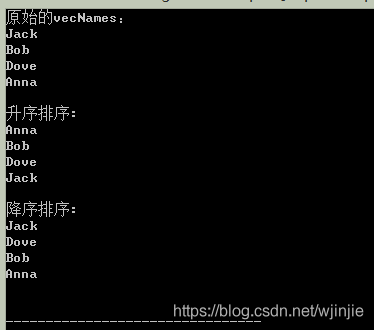
vector<string> vecNames;
vecNames.push_back("Jack");
vecNames.push_back("Bob");
vecNames.push_back("Dove");
vecNames.push_back("Anna");
cout<<"原始的vecNames:"<<endl;
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"升序排序:"<<endl;
sort(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end());
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"降序排序:"<<endl;
sort(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end(), [](string a, string b){return(a>b);});
Display(vecNames);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
4.5 刪除重複元素操作unique()
在容器中,如果有重複的元素;可以使用STL演演算法中的unique()刪除相鄰的重複值:
auto iDel = unique(vec.begin(), vec.end())
vec.erase(iDel, vec.end());
下面舉一個簡單的例子,來演示一下用法:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<< *i << endl;
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
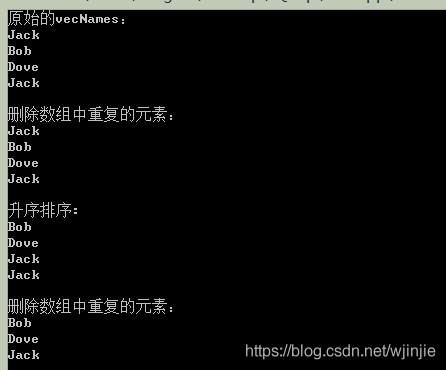
vector<string> vecNames;
vecNames.push_back("Jack");
vecNames.push_back("Bob");
vecNames.push_back("Dove");
vecNames.push_back("Jack");
cout<<"原始的vecNames:"<<endl;
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"刪除陣列中重複的元素:"<<endl;
auto iDel = unique(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end());
vecNames.erase(iDel, vecNames.end());
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"升序排序:"<<endl;
sort(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end());
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"刪除陣列中重複的元素:"<<endl;
auto iDel0 = unique(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end());
vecNames.erase(iDel0, vecNames.end());
Display(vecNames);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
分析:
第一次使用unique()並沒有刪除重複的元素"Jack";但是,經過升序排序後,第二次再使用uniqueI()成功刪除了重複的元素。這是因為,經過排序後,兩個Jack成了相鄰的元素。而unique()恰恰刪除的是相鄰的元素,對於不相鄰的元素並無作用。
4.6 插入元素操作insert()
使用insert()在容器指定位置執行插入操作時,需要先知道待插入的位置。大多數情況下,我們可以使用find()找到待插入元素的位置。這裡介紹另外一種方法,使用STL提供的 lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 確定待插入元素位置。
- 使用lower_bound()在指定元素前插入新的元素
auto iMinPos = lower_bound(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end(), "Dove");
vecNames.insert(iMinPos, "Lucy");
- 使用upper_bound()在指定元素後插入新的元素
auto iMaxPos = upper_bound(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end(), "Dove");
vecNames.insert(iMaxPos, "Lucy");
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Display(const T& Input)
{
for(auto i=Input.begin(); i!=Input.end(); ++i)
cout<< *i << endl;
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
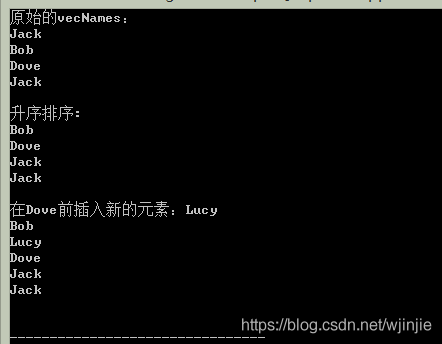
vector<string> vecNames;
vecNames.push_back("Jack");
vecNames.push_back("Bob");
vecNames.push_back("Dove");
vecNames.push_back("Jack");
cout<<"原始的vecNames:"<<endl;
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"升序排序:"<<endl;
sort(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end());
Display(vecNames);
cout<<"在Dove前插入新的元素:Lucy"<<endl;
auto iMinPos = lower_bound(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end(), "Dove");
vecNames.insert(iMinPos, "Lucy");
//在Dove後插入新的元素
//auto iMaxPos = upper_bound(vecNames.begin(), vecNames.end(), "Dove");
//vecNames.insert(iMaxPos, "Lucy");
Display(vecNames);
return 0;
}
執行結果:
今天的分享就到這裡啦,希望對你的學習有所幫助!

養成習慣,先贊後看!你的支援是我創作的最大動力!
更多文章可戳戳 :