Spring中整合Groovy的四種方式
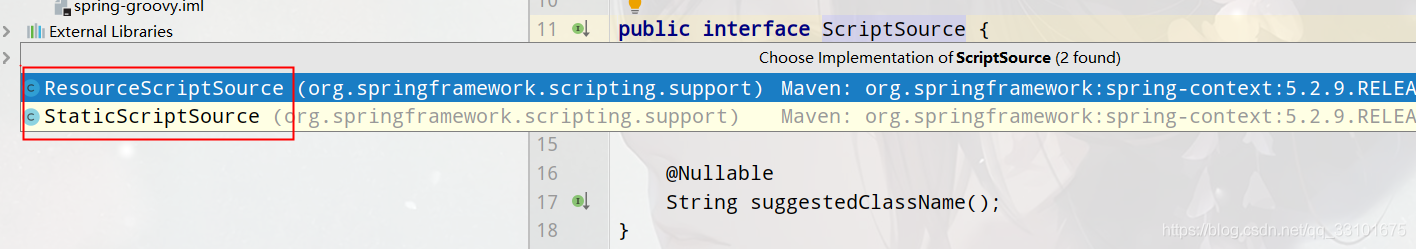
groovy是一種動態指令碼語言,適用於一些可變、和規則設定性的需求,目前Spring提供ScriptSource介面,支援兩種型別,一種是
ResourceScriptSource,另一種是 StaticScriptSource,但是有的場景我們需要把groovy程式碼放進DB中,所以我們需要擴充套件這個。
ResourceScriptSource:在 resources 下面寫groovy類
StaticScriptSource:把groovy類程式碼放進XML裡
DatabaseScriptSource:把groovy類程式碼放進資料庫中
工程模組為:
ResourceScriptSource
groovy的pom
<dependency>
<artifactId>groovy-all</artifactId>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<version>2.1.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>HelloService介面
package com.maple.resource.groovy;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: HelloService.java, v 0.1 2020年09月25日 21:26 maple Exp $
*/
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello();
}
resources下面建groovy實現類
package com.maple.resource.groovy
class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
String name;
@Override
String sayHello() {
return "Hello $name. Welcome to resource in Groovy.";
}
}
在spring-groovy.xml中設定
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang.xsd">
<lang:groovy id="helloService" script-source="classpath:groovy/HelloServiceImpl.groovy">
<lang:property name="name" value="maple"></lang:property>
</lang:groovy>
</beans>主類 GroovyResourceApplication
package com.maple.resource;
import com.maple.resource.groovy.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class GroovyResourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(GroovyResourceApplication.class, args);
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-groovy.xml");
HelloService bean = context.getBean(HelloService.class);
String sayHello = bean.sayHello();
System.out.println(sayHello);
}
}
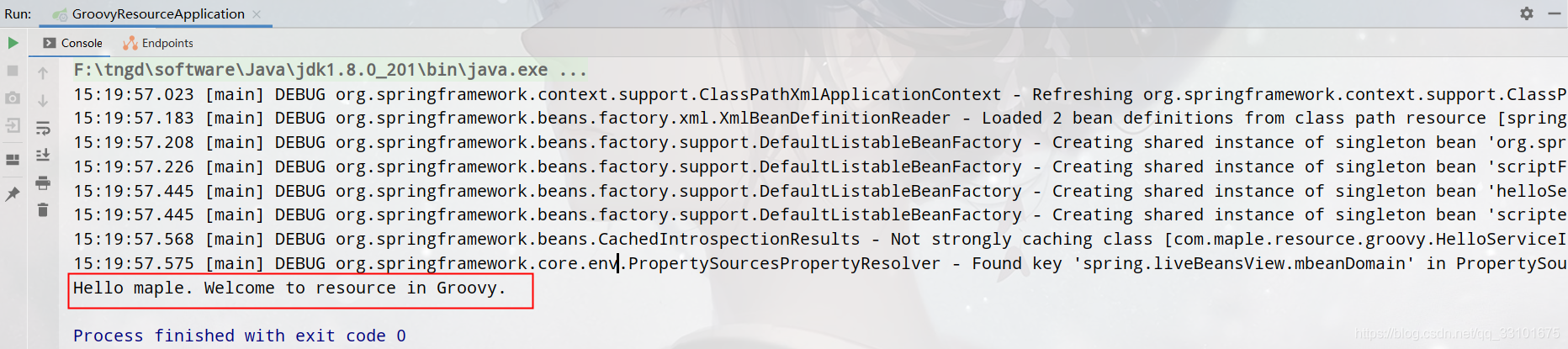
啟動並測試
StaticScriptSource
groovy的pom
<dependency>
<artifactId>groovy-all</artifactId>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<version>2.1.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>HelloService介面
package com.maple.groovy.staticscript.groovy;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: HelloService.java, v 0.1 2020年09月25日 21:26 maple Exp $
*/
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello();
}在spring-groovy.xml中設定具體的實現類
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang.xsd">
<lang:groovy id="helloService">
<lang:inline-script>
import com.maple.groovy.staticscript.groovy.HelloService
class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
String name;
@Override
String sayHello() {
return "Hello $name. Welcome to static script in Groovy.";
}
}
</lang:inline-script>
<lang:property name="name" value="maple"/>
</lang:groovy>
</beans>主類 GroovyStaticscriptApplication
package com.maple.groovy.staticscript;
import com.maple.groovy.staticscript.groovy.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class GroovyStaticscriptApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(GroovyStaticscriptApplication.class, args);
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-groovy.xml");
HelloService bean = context.getBean(HelloService.class);
String sayHello = bean.sayHello();
System.out.println(sayHello);
}
}
啟動並測試
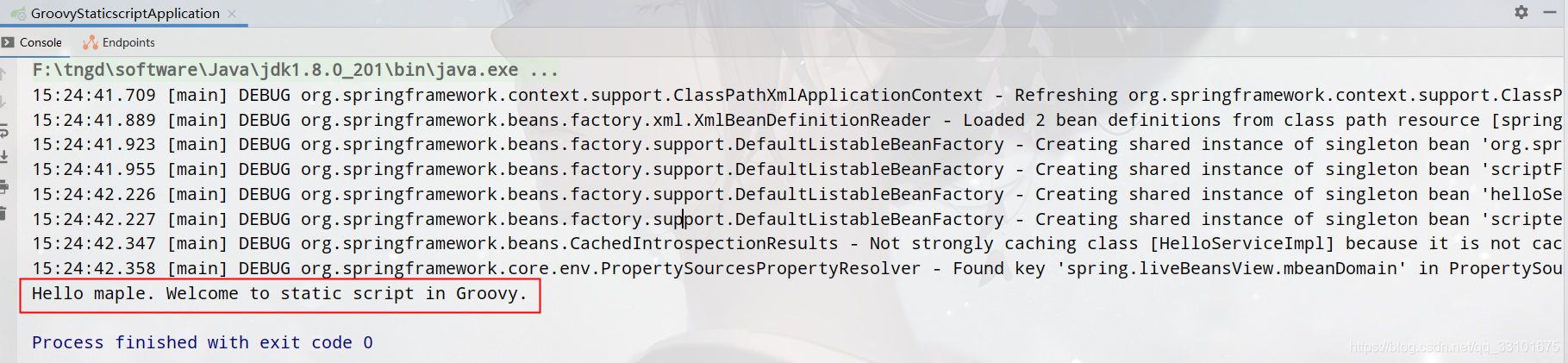
DatabaseScriptSource
下面我們先建表,把基本工作做完,這裡我使用mybatisplus,dao、service等程式碼省略
CREATE TABLE `groovy_script` (
`id` BIGINT ( 20 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`script_name` VARCHAR ( 64 ) NOT NULL COMMENT 'script name',
`script_content` text NOT NULL COMMENT 'script content',
`status` VARCHAR ( 16 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'ENABLE' COMMENT 'ENABLE/DISENABLE',
`extend_info` VARCHAR ( 4096 ) DEFAULT NULL,
`created_time` TIMESTAMP ( 6 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ( 6 ),
`modified_time` TIMESTAMP ( 6 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ( 6 ) ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ( 6 ),
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` )
) ENGINE = INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = 'groovy script';INSERT INTO `gane-platform`.`groovy_script`(`id`, `script_name`, `script_content`, `status`, `extend_info`, `created_time`, `modified_time`) VALUES (1, 'helloService', 'package com.maple.resource.groovy\r\n\r\nimport com.maple.database.groovy.HelloService\r\n\r\npublic class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {\r\n\r\n @Override\r\n String sayHello(String name) {\r\n return \"Hello \"+name+\". Welcome to database in Groovy.\";\r\n }\r\n}', 'ENABLE', NULL, '2020-09-26 17:16:36.477818', '2020-09-27 08:23:10.790553');方法一:
1、實時讀取DB裡的groovy指令碼檔案
2、利用GroovyClassLoader去編譯指令碼檔案
3、把class物件注入成Spring bean
4、反射呼叫指令碼的方法
package com.maple.database.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.maple.database.entity.GroovyScript;
import com.maple.database.groovy.SpringContextUtils;
import com.maple.database.service.GroovyScriptService;
import groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: GroovyController.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 17:18 maple Exp $
*/
@RestController
public class GroovyController {
@Resource
private GroovyScriptService groovyScriptService;
@GetMapping("/groovyTest")
private String groovyTest() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
GroovyScript groovyScript = groovyScriptService.getOne(new QueryWrapper<GroovyScript>()
.eq("script_name", "helloService").eq("status", "ENABLE"));
System.out.println(groovyScript.getScriptContent());
Class clazz = new GroovyClassLoader().parseClass(groovyScript.getScriptContent());
Object o = clazz.newInstance();
SpringContextUtils.autowireBean(o);
Method method = clazz.getMethod("sayHello", String.class);
return (String) method.invoke(o, "maple");
}
}
package com.maple.database.groovy;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: SpringContextUtils.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 17:29 maple Exp $
*/
@Component
public class SpringContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringContextUtils.context = applicationContext;
}
public static void autowireBean(Object bean) {
context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().autowireBean(bean);
}
public static ApplicationContext getContext() {
return context;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return context.getBean(clazz);
}
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T) context.getBean(name);
}
}啟動測試結果為:
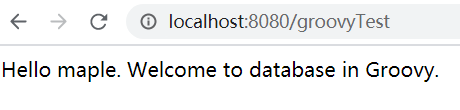
總結:
優點:實時讀取DB裡的指令碼,當指令碼更改時,可以直接修改DB,對程式碼無侵入
缺點:每次都要查詢DB,反射呼叫程式碼寫死了
方法二:
1、我們模仿groovy-resource的思路,resource的XML設定是下面這樣的
<lang:groovy id="helloService" script-source="classpath:groovy/HelloServiceImpl.groovy" />所以,我們可以把DatabaseScriptSource的XML儲存成這種格式
<lang:groovy id="helloService" script-source="database:helloService"/>2、然後模仿Spring儲存成XML格式的document的思路,我們也把groovy儲存成XML格式的document,放進記憶體裡
3、groovy的關鍵處理類是ScriptFactoryPostProcessor,當 Spring 裝載應用程式上下文時,它首先建立工廠 bean(例如 GroovyScriptFactory bean)。然後,執行ScriptFactoryPostProcessor bean,用實際的指令碼物件替換所有的工廠 bean。例如,我們本次測試的設定產生一個名為 helloService 的 bean,它的型別是groovierspring.GroovyHelloService。(如果啟用 Spring 中的 debug 級紀錄檔記錄,並觀察應用程式上下文的啟動,將會看到 Spring 首先建立一個名為 scriptFactory.helloService 的工廠 bean,然後 ScriptFactoryPostProcessor 從該工廠 bean 建立 helloService bean)。
我們發現ScriptFactoryPostProcessor這個類中,有getScriptSource這個方法,該方法裡有convertToScriptSource方法

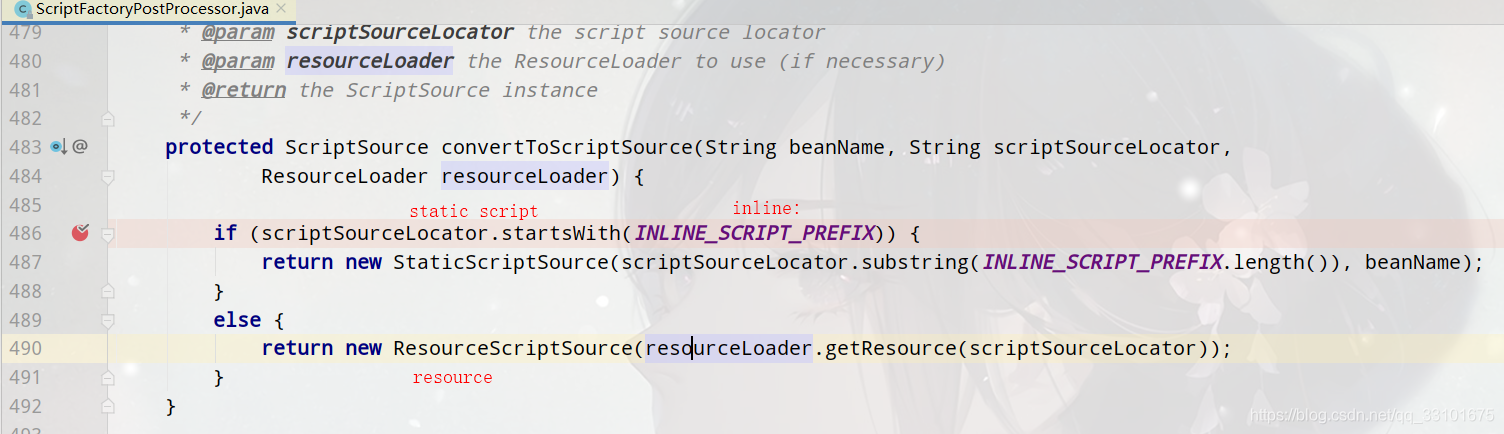
在convertToScriptSource這個方法中,他預設支援我們前面說過的static script和resource兩種型別,但是現在我們新增了一種database型別,所以我們需要重寫該方法,其他的工作都一樣,交給ScriptFactoryPostProcessor幫我們去處理。
package com.maple.database.manage;
import com.maple.database.groovy.DatabaseScriptSource;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ScriptFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.StaticScriptSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 20:36 maple Exp $
*/
@Component
public class CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor extends ScriptFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
protected ScriptSource convertToScriptSource(String beanName, String scriptSourceLocator, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
if (scriptSourceLocator.startsWith(INLINE_SCRIPT_PREFIX)) {
return new StaticScriptSource(scriptSourceLocator.substring(INLINE_SCRIPT_PREFIX.length()), beanName);
}
if (scriptSourceLocator.startsWith(GroovyConstant.SCRIPT_SOURCE_PREFIX)) {
return new DatabaseScriptSource(StringUtils.substringAfter(scriptSourceLocator, GroovyConstant.SCRIPT_SOURCE_PREFIX));
}
return new ResourceScriptSource(resourceLoader.getResource(scriptSourceLocator));
}
}
但是我們也要看看ScriptFactoryPostProcessor幫我們處理的其他工作都是什麼:
(1)predictBeanType:是 Spring 中從 BeanDefinition 中提取 Bean 型別的底層 API
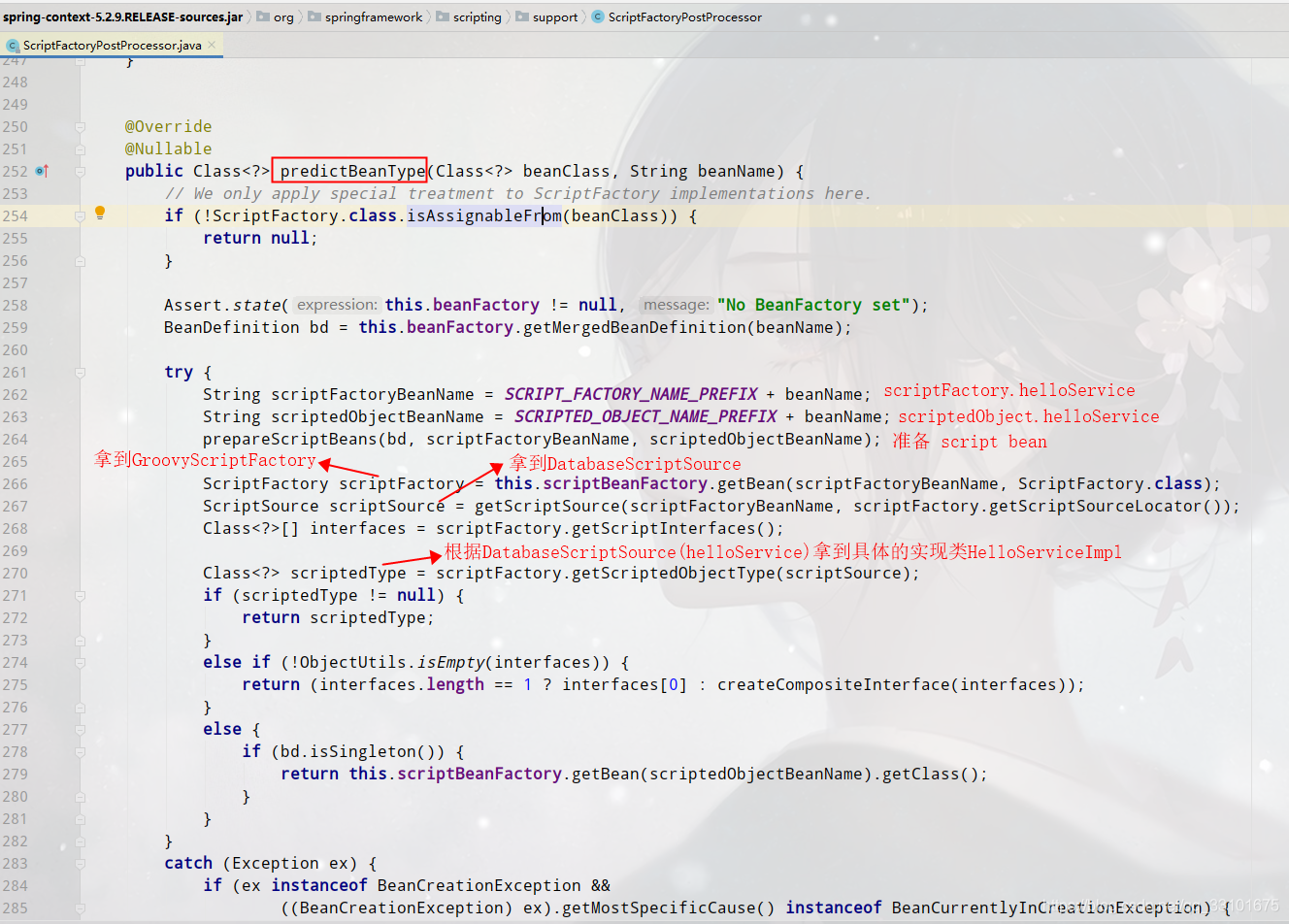
(2)我們再來看prepareScriptBeans準備了什麼
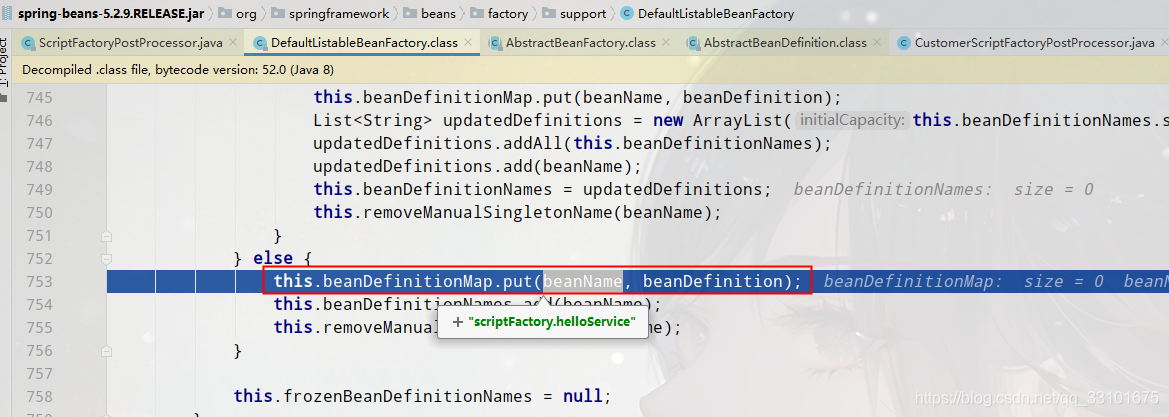
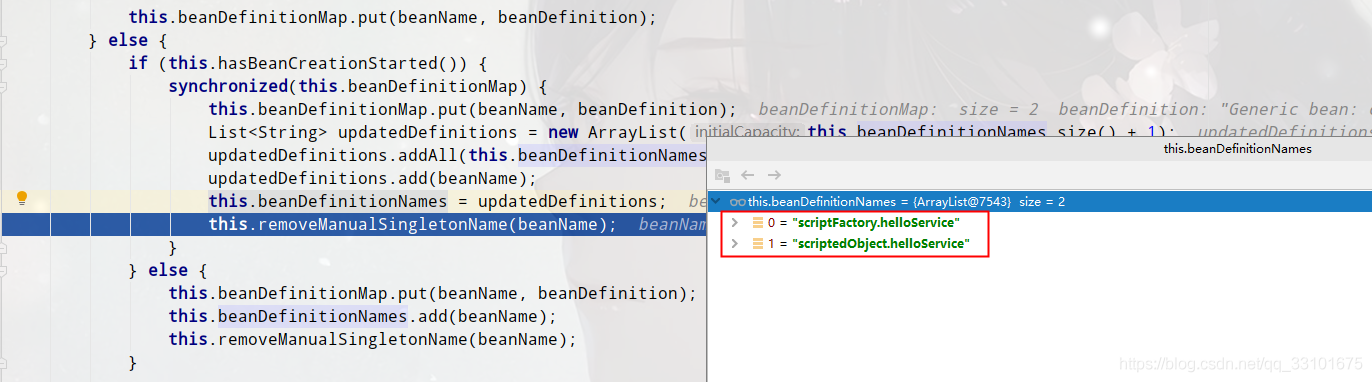
(3)scriptBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition,向beanDefinitionMap裡put鍵值對

(4)createScriptedObjectBeanDefinition
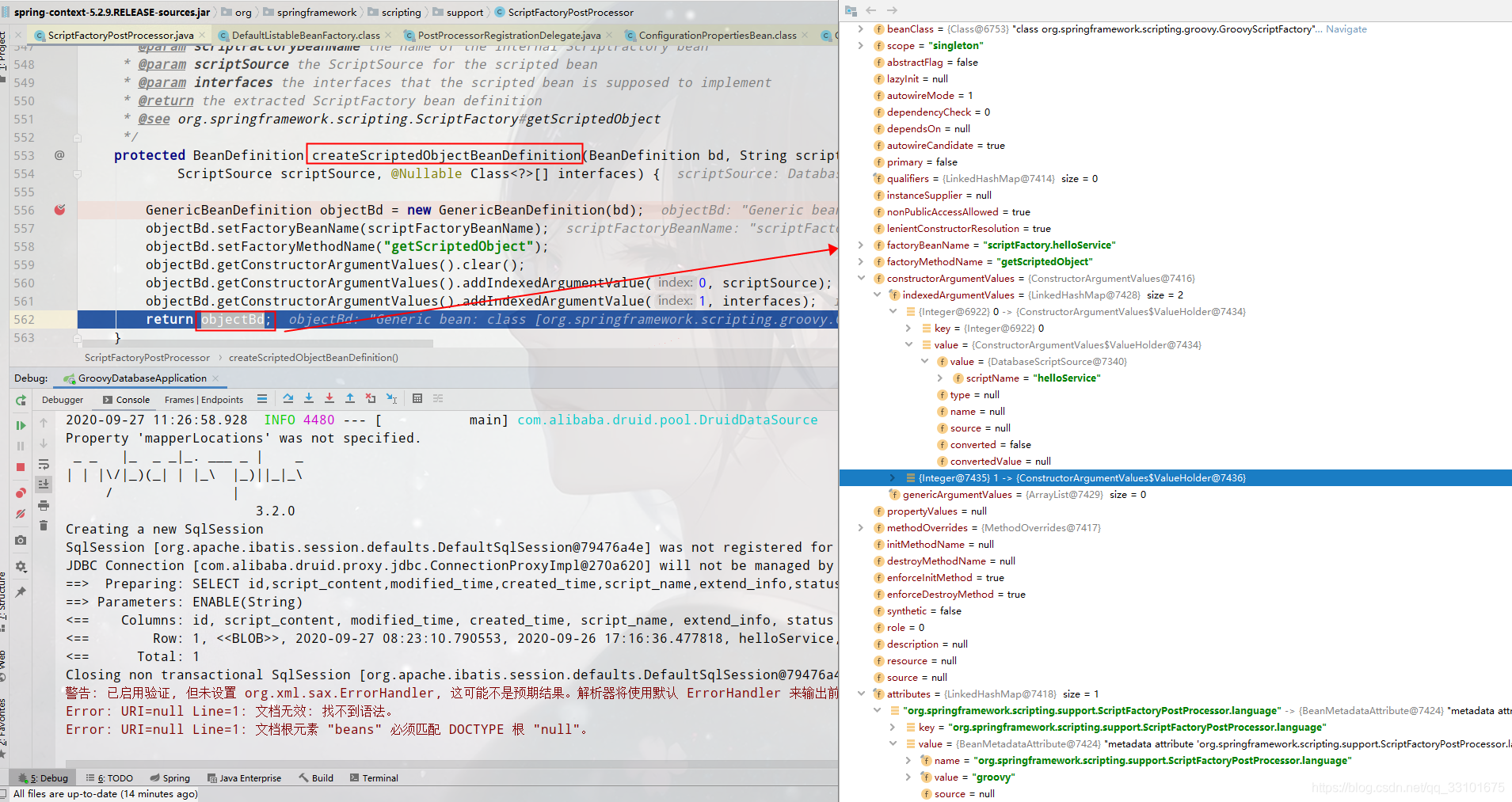
(5)Class<?> scriptedType = scriptFactory.getScriptedObjectType(scriptSource);
這句是為了拿到我們具體的實現類,也是我們的基礎,它裡面就是用GroovyClassLoader去編譯我們的groovy指令碼內容,並返回了Class<?> scriptClass我們的HelloServiceImpl
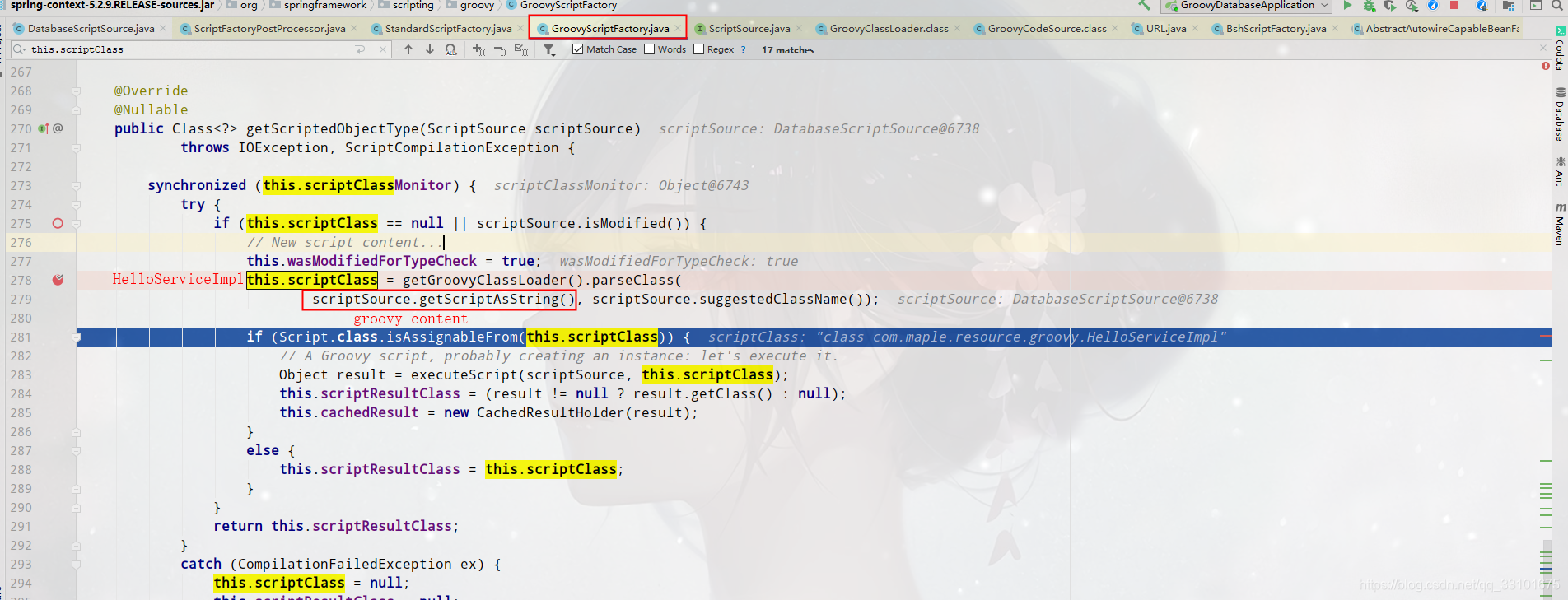
(6)ScriptSource scriptSource = getScriptSource(scriptFactoryBeanName, scriptFactory.getScriptSourceLocator());

這裡首先去我們下面新增的DatabaseScriptSource裡拿到groovy指令碼內容,並放進map裡,返回DatabaseScriptSource
4、新增DatabaseScriptSource類
package com.maple.database.groovy;
import com.maple.database.groovy.cache.GroovyCache;
import org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: DatabaseScriptSource.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 15:37 maple Exp $
*/
public final class DatabaseScriptSource implements ScriptSource {
/**
* 指令碼名稱
*/
private String scriptName;
/**
* 建構函式
*
* @param scriptName
*/
public DatabaseScriptSource(String scriptName) {
this.scriptName = scriptName;
}
@Override
public String getScriptAsString() throws IOException {
return GroovyCache.getByName(scriptName).getGroovyContent();
}
@Override
public boolean isModified() {
return false;
}
@Override
public String suggestedClassName() {
return StringUtils.stripFilenameExtension(this.scriptName);
}
}
5、把我們的CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor放進Spring的List<BeanPostProcessor>中
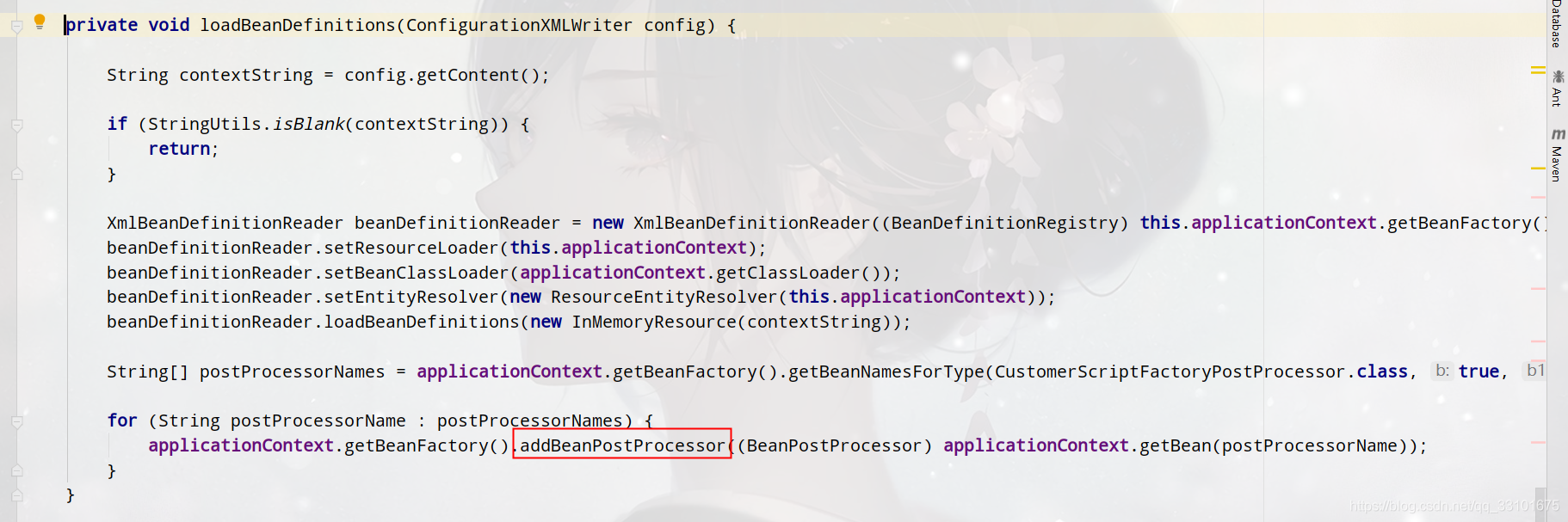
這樣的話,我們就能從Spring容器中獲取helloService的bean範例了,測試:
package com.maple.database.controller;
import com.maple.database.groovy.HelloService;
import com.maple.database.groovy.SpringContextUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: GroovyController.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 17:18 maple Exp $
*/
@RestController
public class NewGroovyController {
@GetMapping("/newGroovyTest")
private String newGroovyTest() {
HelloService helloService = SpringContextUtils.getBean("helloService");
String hello = helloService.sayHello("maple");
System.out.println(hello);
return hello;
}
}
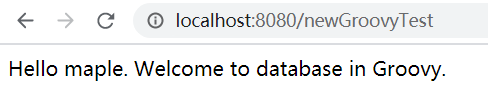
總結:
優點:專案初始化的時候,就把DB裡的groovy指令碼讀取到,放進本次快取裡,並交給Spring管理,減少與DB的互動次數;沒有寫死,擴充套件性更好。
缺點:當DB裡的groovy指令碼檔案需要修改時,我們改完之後不能立即生效,需要重新啟動工程或者重新整理本次快取,再次放進Spring容器裡才行
附上核心處理類:GroovyDynamicLoader,部分程式碼不全的話,可以私信我
package com.maple.database.manage;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.maple.database.entity.GroovyScript;
import com.maple.database.groovy.cache.GroovyCache;
import com.maple.database.groovy.cache.GroovyInfo;
import com.maple.database.service.GroovyScriptService;
import groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ResourceEntityResolver;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: GroovyDynamicLoader.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 20:00 maple Exp $
*/
@Configuration
public class GroovyDynamicLoader implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
}
@Resource
private GroovyScriptService groovyScriptService;
private static final GroovyClassLoader groovyClassLoader = new GroovyClassLoader(GroovyDynamicLoader.class.getClassLoader());
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
init();
}
private void init() {
List<GroovyScript> groovyScripts = groovyScriptService.list(new QueryWrapper<GroovyScript>().eq("status", "ENABLE"));
List<GroovyInfo> groovyInfos = groovyScripts.stream().map(groovyScript -> {
GroovyInfo groovyInfo = new GroovyInfo();
groovyInfo.setClassName(groovyScript.getScriptName());
groovyInfo.setGroovyContent(groovyScript.getScriptContent());
return groovyInfo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(groovyInfos)) {
return;
}
ConfigurationXMLWriter config = new ConfigurationXMLWriter();
addConfiguration(config, groovyInfos);
GroovyCache.put2map(groovyInfos);
loadBeanDefinitions(config);
}
private void addConfiguration(ConfigurationXMLWriter config, List<GroovyInfo> groovyInfos) {
for (GroovyInfo groovyInfo : groovyInfos) {
writeBean(config, groovyInfo);
}
}
private void writeBean(ConfigurationXMLWriter config, GroovyInfo groovyInfo) {
if (checkSyntax(groovyInfo)) {
DynamicBean bean = composeDynamicBean(groovyInfo);
config.write(GroovyConstant.SPRING_TAG, bean);
}
}
private boolean checkSyntax(GroovyInfo groovyInfo) {
try {
groovyClassLoader.parseClass(groovyInfo.getGroovyContent());
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private DynamicBean composeDynamicBean(GroovyInfo groovyInfo) {
DynamicBean bean = new DynamicBean();
String scriptName = groovyInfo.getClassName();
Assert.notNull(scriptName, "parser className cannot be empty!");
//設定bean的屬性,這裡只有id和script-source。
bean.put("id", scriptName);
bean.put("script-source", GroovyConstant.SCRIPT_SOURCE_PREFIX + scriptName);
return bean;
}
private void loadBeanDefinitions(ConfigurationXMLWriter config) {
String contextString = config.getContent();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(contextString)) {
return;
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
beanDefinitionReader.setBeanClassLoader(applicationContext.getClassLoader());
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this.applicationContext));
beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new InMemoryResource(contextString));
String[] postProcessorNames = applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String postProcessorName : postProcessorNames) {
applicationContext.getBeanFactory().addBeanPostProcessor((BeanPostProcessor) applicationContext.getBean(postProcessorName));
}
}
}